Are You a Skilled Forex Trader? Here's How to Find Out
Signs You’re a Skillful Forex Trader Forex trading is a highly complex and volatile financial market, requiring a unique set of skills. Whether you …
Read Article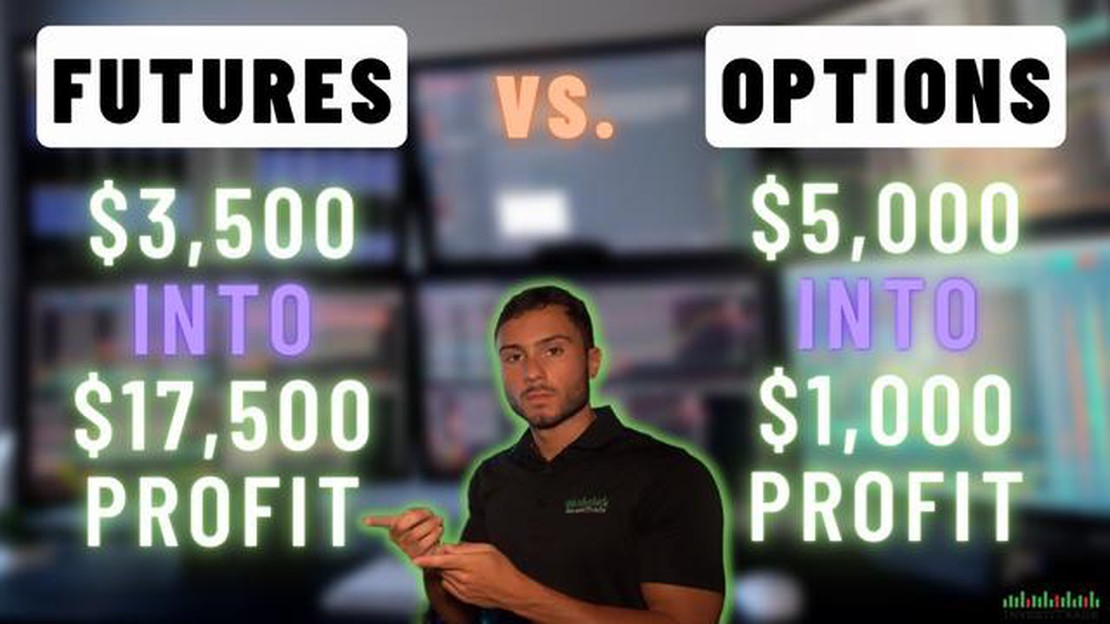
Investing in the financial markets can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to choosing between different investment options. Two popular choices among traders are futures and options. Both instruments offer the potential for high returns, but they also come with their own set of risks and complexities.
Futures are contracts that oblige the buyer to purchase an asset or the seller to sell an asset at a predetermined price on a specified date in the future. One of the key advantages of futures is their liquidity. They are traded on organized exchanges, allowing investors to enter and exit positions with ease. Futures also offer the potential for leverage, meaning investors can control a larger position with a smaller upfront investment.
Options, on the other hand, provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a specified price within a certain period. Unlike futures, options offer more flexibility for investors. They can choose whether or not to exercise the option, depending on market conditions. Options also allow investors to limit their potential losses with the premium paid for the option.
When deciding between futures and options, it is important to consider your investment goals, risk tolerance, and market outlook. Futures may be more suitable for investors seeking higher leverage and more liquidity. Options, on the other hand, may be better suited for those looking for more flexibility and risk management.
Ultimately, the choice between futures and options depends on your individual preferences and investment strategy. It is important to thoroughly understand the characteristics of each instrument and evaluate how they align with your goals before making a decision. Seeking advice from a financial professional can also help guide you in choosing the best investment option for your specific needs.
When it comes to investing in derivatives, it’s important to understand the differences between futures and options. While both are financial contracts that allow investors to profit from movements in the price of an underlying asset, there are several key distinctions to be aware of:
By understanding these key differences, investors can make more informed decisions when choosing between futures and options. Each derivative has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice ultimately depends on the investor’s risk tolerance, investment goals, and market outlook.
Benefits:
Read Also: What is the Best CAD to USD Exchange Rate?5. Diversification: Futures markets offer a wide range of assets to trade, including commodities, currencies, and financial instruments. This allows investors to diversify their portfolios and reduce risk by spreading investments across different asset classes.
Risks:
Read Also: Discover the Key Differences Between Trek FX Sport and FX 3 Bikes3. Counterparty risk: Futures contracts involve an agreement between two parties, and there is always a risk that the counterparty may default on their obligations. This risk can be mitigated by using reputable exchanges and clearinghouses. 4. Complexity: Futures markets can be complex and require a deep understanding of the underlying assets and market dynamics. Novice traders may find it difficult to navigate these markets and make informed trading decisions. 5. Margin calls: When trading futures on margin, investors must maintain a certain level of funds in their trading account to cover potential losses. If the account falls below this level, they may receive a margin call and be required to deposit additional funds or close their positions.
In conclusion, futures contracts offer several benefits, such as leverage, hedging, price discovery, liquidity, and diversification. However, they also come with risks, including leverage-induced losses, price volatility, counterparty risk, complexity, and margin calls. It is important for investors to carefully consider these factors and conduct thorough research before engaging in futures trading.
There are several key differences between futures and options. One main difference is that futures are contracts that require the parties involved to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a specific date in the future, while options give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price within a specified period of time. Another difference is that futures have unlimited profit potential and unlimited loss potential, whereas options have limited profit potential (the premium paid for the option) but limited loss potential (the premium paid for the option).
Both futures and options can be complex and risky investments, so it is important for beginners to thoroughly understand the mechanics and risks of each before investing. However, for beginners, options may be a more suitable investment choice as they allow for more flexibility and limited loss potential. Options also generally require less capital investment compared to futures.
When choosing between futures and options, there are several factors to consider. These include your risk tolerance, investment goals, market conditions, and your understanding of the products. Futures may be more suitable for investors with higher risk tolerance and who have a clear understanding of the underlying asset and market dynamics. Options may be more suitable for investors looking for flexibility and limited risk.
Yes, both futures and options can be used for hedging purposes. Hedging involves taking a position in futures or options to offset potential losses in the underlying asset. For example, if you own a portfolio of stocks and are concerned about a potential market downturn, you can buy put options to protect against a decline in the value of your stocks. Similarly, if you are a farmer who wants to lock in a certain price for your crop, you can sell futures contracts to hedge against a potential decline in crop prices.
Both futures and options offer the potential for profit, but the potential for profit is generally higher with futures. Futures have unlimited profit potential, meaning that if the price of the underlying asset moves in your favor, your profit can be substantial. Options, on the other hand, have limited profit potential as they are typically priced based on the premium paid for the option. However, options can still offer significant profit potential if the price of the underlying asset moves significantly in your favor.
Futures and options are both types of financial derivatives that allow investors to speculate on the future price movements of underlying assets. Futures contracts obligate the buyer to purchase an asset at a predetermined price and time in the future, while options give the buyer the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price within a specific time period.
Investing in futures has several advantages. Firstly, futures provide a high level of leverage, allowing investors to control a large position with a relatively small amount of capital. Secondly, futures offer the ability to both profit from bullish or bearish market movements, as investors can take a long (buy) or short (sell) position. Lastly, futures can provide a more efficient way to hedge against price fluctuations in commodities or other assets.
Signs You’re a Skillful Forex Trader Forex trading is a highly complex and volatile financial market, requiring a unique set of skills. Whether you …
Read ArticleCapacity of Remington 870 Shotgun: How Many Shells Can It Hold? If you own a Remington 870 shotgun, one of the most common questions you may have is …
Read ArticleTips and strategies to avoid losses on the forex market Forex trading can be a highly profitable venture, but it is not without its risks. Many new …
Read ArticleMaster the Art of Forex Trading: Learn How to Trade without Incurring Losses Trading in the foreign exchange market, also known as forex, can be an …
Read ArticleThe Advantages of a Stock Swap Stock swaps have become an increasingly popular method for business mergers and acquisitions. This exchange of stocks …
Read ArticleDiscover the Benefits of Unity Plus Subscription Unity Plus is a powerful software package that offers a range of benefits and features for both …
Read Article