Discover Exciting Career Opportunities in the Forex Market
Everything You Need to Know About Forex Careers The forex market, also known as the foreign exchange market, offers a wide range of exciting career …
Read Article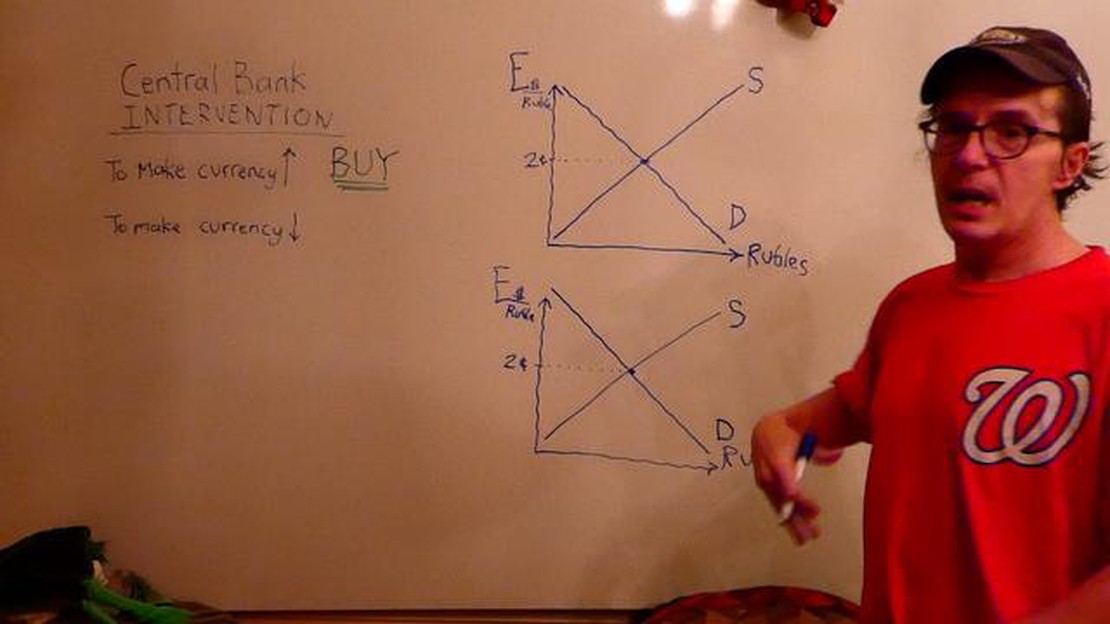
Central bank interventions in foreign exchange markets have long been a topic of debate and scrutiny among economists and policymakers. This practice, which involves a central bank buying or selling its currency in the foreign exchange market, aims to influence the exchange rate and stabilize the domestic economy.
Such interventions can be motivated by various factors, including the desire to maintain price stability, ensure financial stability, or promote economic growth. Central banks may choose to intervene in the foreign exchange market to prevent excessive volatility, counter speculative attacks, or address imbalances in the currency market.
Central bank interventions can take different forms, ranging from verbal interventions and signaling to actual market interventions through direct purchases or sales of foreign currency reserves. These actions can have significant implications for the exchange rate, interest rates, and overall market sentiment.
However, the effectiveness of central bank interventions remains a subject of ongoing debate. Some argue that interventions can have a temporary impact on the exchange rate and provide short-term stability. Others question their effectiveness and argue that interventions can distort market signals, create moral hazards, or lead to unintended consequences.
In this in-depth analysis, we will examine the various dimensions of central bank interventions in foreign exchange markets. We will explore their objectives, tools, and outcomes, as well as the challenges and limitations associated with these interventions. Through a comprehensive review of academic research and case studies, we aim to shed light on the complex dynamics and implications of central bank interventions in foreign exchange markets.
Central bank interventions in foreign exchange markets are a crucial tool used by central banks to stabilize and regulate currency markets. These interventions can take various forms and are aimed at managing exchange rates, ensuring price stability, and maintaining the overall stability of the financial system.
A central bank intervention occurs when a central bank buys or sells its own currency in the foreign exchange market. The central bank intervenes to influence the value of its currency relative to other currencies, either to prevent excessive appreciation or depreciation. Such interventions are often carried out in response to excessive volatility or speculative attacks on a currency.
Read Also: What does an FX analyst do? | The role and responsibilities of an FX analyst
Central bank interventions can be classified into two main types: sterilized and unsterilized interventions. Sterilized interventions involve offsetting the impact of the intervention on the money supply through the use of other monetary tools, such as open market operations or changes in reserve requirements. Unsterilized interventions, on the other hand, do not involve any offsetting measures and directly affect the money supply.
Central bank interventions can have significant short-term effects on exchange rates and can provide stability to markets in times of crisis. However, the long-term effectiveness of interventions is a subject of debate among economists. Critics argue that interventions may distort market mechanisms, create moral hazard, and ultimately lead to inefficient resource allocation. Proponents, on the other hand, believe that interventions can help prevent excessive exchange rate fluctuations and promote economic stability.
Overall, central bank interventions play a vital role in maintaining stability in foreign exchange markets. The decision to intervene and the form of intervention chosen depend on various factors, including the current economic conditions, exchange rate regime, and policy objectives of the central bank. In recent years, central bank interventions have become increasingly important in the context of global financial crises and currency wars.
In conclusion, central bank interventions are an essential tool used by central banks to manage and regulate foreign exchange markets. These interventions can have short-term impacts on exchange rates and are aimed at maintaining stability in the financial system. While the long-term effectiveness of interventions is debatable, their importance in times of crisis cannot be overstated.
Central bank interventions in foreign exchange markets refer to the actions taken by a country’s central bank to influence the value of its currency in relation to other currencies. These interventions can involve buying or selling large amounts of foreign currency, in order to alter the supply and demand dynamics of the foreign exchange market.
The purpose of central bank interventions in foreign exchange markets can vary depending on the specific goals of the country’s monetary policy. Some common objectives include:
Types of central bank interventions can vary in terms of their magnitude and transparency. Some interventions are conducted openly, with the central bank announcing its intentions and actions in advance. These are known as “sterilized interventions.” Other interventions are conducted covertly, also known as “unsterilized interventions,” where the central bank does not disclose its actions.
Additionally, central bank interventions can be categorized as spot market interventions or forward market interventions. Spot market interventions involve immediate buying or selling of foreign currency, while forward market interventions entail entering into agreements to buy or sell foreign currency at a future date.
Read Also: Is binary trading legal in Singapore? Find out the regulations and laws on binary options trading in Singapore
In summary, central bank interventions in foreign exchange markets are actions taken by central banks to influence the value of their currency. These interventions serve various purposes, including stabilizing the exchange rate, managing inflation, supporting economic growth, and addressing imbalances. They can take different forms, such as sterilized or unsterilized interventions, as well as spot or forward market interventions.
The purpose of central bank interventions in foreign exchange markets is to influence the value of a country’s currency. Central banks may intervene in the foreign exchange market to stabilize exchange rates or to correct perceived imbalances in the value of the currency. They can buy or sell their own currency in the market to affect its supply and demand.
Central bank interventions typically involve the buying or selling of a country’s currency in the foreign exchange market. If a central bank wants to weaken its currency, it will sell its own currency in exchange for a foreign currency, increasing the supply of its currency in the market. This increased supply can lower the value of the currency. Conversely, if a central bank wants to strengthen its currency, it will buy its own currency in the market, reducing the supply and potentially raising the value.
The effects of central bank interventions on exchange rates can vary. In some cases, interventions may have a short-term impact on exchange rates, causing them to move in the desired direction. However, the long-term effects of interventions are less certain. Market forces and other factors can influence exchange rates, making it difficult for central banks to maintain a specific target. Additionally, interventions can have unintended consequences and may affect investor confidence.
The effectiveness of central bank interventions in controlling currency exchange rates is a subject of debate. While interventions can have short-term impacts on exchange rates, their ability to maintain a specific target over the long term is limited. Market forces and other factors can outweigh the effects of interventions. Additionally, interventions can have unintended consequences and may not always have the desired impact on exchange rates. Other monetary policy tools and economic factors also play a role in determining exchange rates.
Everything You Need to Know About Forex Careers The forex market, also known as the foreign exchange market, offers a wide range of exciting career …
Read ArticleDiscovering the Role of 360T in the Financial Industry 360T is a leading provider of trading and workflow solutions for financial institutions, …
Read ArticleEffective Risk Management Strategies for Forex Trading Forex trading is a high-risk investment activity where traders speculate on the changes in …
Read ArticleWhat is the most important high impact Forex news? Forex trading is significantly influenced by economic news events. Traders and investors closely …
Read ArticleWhen to Buy Weekly Options Trading options can be a profitable venture, but timing is everything when it comes to buying weekly options. These …
Read ArticleWhat is the significance of the meta 200-day moving average? The Meta 200-Day Moving Average is a key technical analysis tool that is widely used by …
Read Article