How Accurate is an SKS at 100 Yards? Discover the Rifle's Precision.
Accuracy of an SKS at 100 yards The SKS is a popular semi-automatic rifle known for its reliability and affordability. Originally designed in the …
Read Article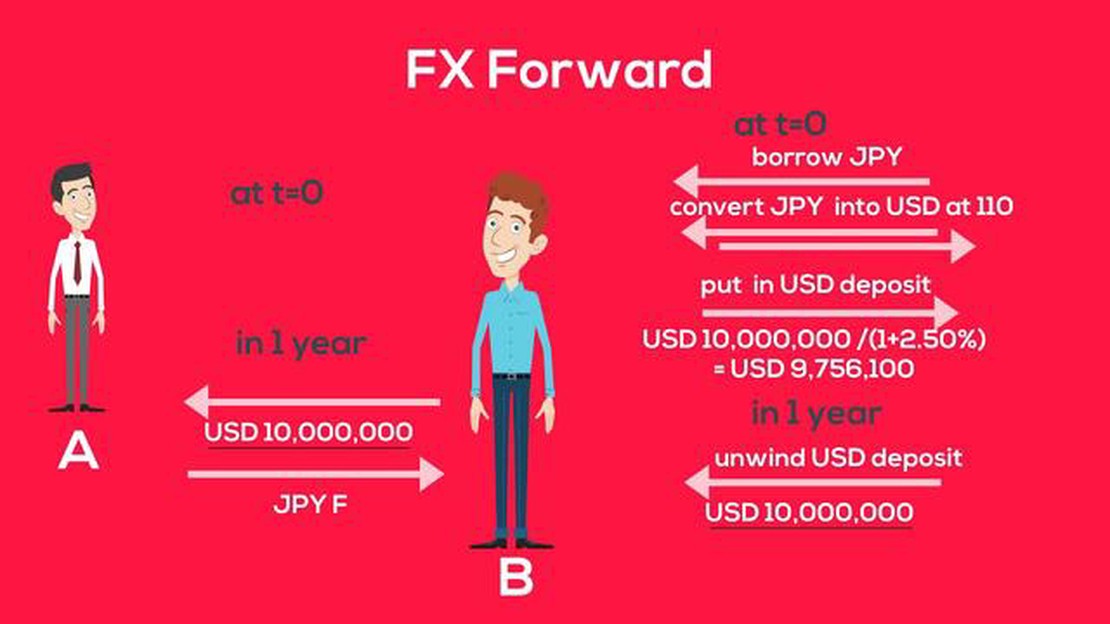
A foreign exchange forward contract, also known as FX FWD, is a financial instrument used in the global currency market. This type of contract allows individuals and businesses to lock in an exchange rate for a future date. It is a popular tool for managing foreign currency risk, as it provides a way to hedge against potential fluctuations in exchange rates.
FX FWD contracts are typically used by companies that engage in international trade, such as importers and exporters. By entering into a forward contract, these businesses can protect themselves from fluctuations in currency prices, which can impact the profitability of their transactions. The contract allows them to buy or sell a specific amount of currency at a predetermined rate, which remains fixed until the contract expires.
One of the key features of FX FWD contracts is the settlement date. This is the date on which the exchange of currencies takes place. It is important to note that FX FWD contracts are not intended for immediate currency transactions, but rather for transactions that will occur in the future. The settlement date can range from a few days to several months or even years, depending on the terms of the contract.
When entering into an FX FWD contract, both parties agree on the exchange rate and the amount of currency to be exchanged. The exchange rate is typically set at a premium or discount to the spot rate, which is the current market rate for immediate currency transactions. The premium or discount reflects the interest rate differential between the two currencies involved in the transaction.
Overall, understanding FX FWD contracts is essential for anyone involved in international trade or currency speculation. By utilizing these contracts, individuals and businesses can mitigate their exposure to exchange rate risk and ensure the stability of their financial transactions.
FX FWD, or foreign exchange forward contracts, are agreements between two parties to exchange currencies at a future date and at a predetermined exchange rate. This type of contract is commonly used by businesses and individuals to hedge against potential currency fluctuations.
Forward contracts are different from spot contracts, which involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the prevailing market rate. In a forward contract, the exchange rate is agreed upon at the time of contract initiation, but the actual exchange of currencies takes place at a later date, known as the maturity or delivery date.
The main purpose of a forward contract is to minimize the risk associated with fluctuating exchange rates. By entering into a forward contract, participants can protect themselves against potential losses that may occur due to unfavorable exchange rate movements.
FX FWD contracts are typically used by businesses engaged in international trade, where they need to convert one currency into another at a future date. For example, if a company based in the United States is expecting payment in euros three months from now, it can enter into a forward contract to lock in the exchange rate and protect itself from potential losses if the euro weakens against the US dollar.
It’s important to note that forward contracts are legally binding agreements and should be entered into with caution. The terms of the contract, including the exchange rate, the amount of currency to be exchanged, and the maturity date, are all specified upfront and cannot be changed without mutual consent.
In conclusion, FX FWD contracts provide businesses and individuals with a way to manage currency risk by locking in future exchange rates. These contracts can help to reduce uncertainty and protect against potential losses resulting from adverse movements in foreign exchange rates.
Read Also: Is Scottrade Still in Business? Find Out Here!
In the world of international business and finance, foreign exchange (FX) forward contracts play a significant role. These contracts are financial instruments that allow individuals and businesses to hedge against fluctuations in currency exchange rates. By entering into a foreign exchange forward contract, parties can set an agreed-upon exchange rate for a future date. This provides them with certainty and helps them manage their foreign exchange risk.
Foreign exchange forward contracts function as agreements between two parties to exchange a specified amount of one currency for another at an agreed-upon exchange rate on a specific date in the future. This is different from spot contracts, where the exchange occurs immediately.
Read Also: Understanding the Mechanics of Option Clearing for Beginners
One of the primary purposes of entering into a foreign exchange forward contract is to mitigate the risk of currency fluctuations. Businesses that engage in international trade often face exposure to foreign exchange risk. Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact the profitability of their operations and affect the overall financial health of the company.
Foreign exchange forward contracts provide businesses with the ability to lock in exchange rates for future transactions. This allows them to plan their budgets, forecast cash flows, and minimize uncertainty. By securing an exchange rate in advance, companies can protect themselves from adverse currency movements and ensure the predictability of their financial outcomes.
Foreign exchange forward contracts are commonly used by importers and exporters to manage their currency risk. For example, an importer may enter into a forward contract to buy a certain amount of foreign currency at a fixed exchange rate in the future. This protects them from potential depreciation of the foreign currency and helps them maintain their profit margins.
On the other hand, an exporter may enter into a forward contract to sell a certain amount of foreign currency at a fixed exchange rate in the future. This protects them from potential appreciation of the foreign currency and ensures that they receive a predetermined amount of their local currency.
In summary, foreign exchange forward contracts provide individuals and businesses with a useful tool for managing currency risk. By allowing parties to lock in exchange rates for future transactions, these contracts help mitigate the uncertainty associated with fluctuating exchange rates. Whether it’s importers, exporters, or multinational corporations, foreign exchange forward contracts are widely used in the global marketplace to protect against currency fluctuations and ensure the stability of international transactions.
A foreign exchange forward contract is a financial instrument that allows individuals and businesses to hedge against future currency exchange rate fluctuations. It is a binding agreement between two parties to exchange a specified amount of one currency for another at a predetermined exchange rate on a future date.
Foreign exchange forward contracts can be used by individuals, businesses, and financial institutions that have exposure to foreign exchange risk. Importers and exporters, multinational corporations, and investors who hold assets in different currencies are some of the common users of these contracts.
Using foreign exchange forward contracts provides several benefits, such as minimizing currency risk, allowing for budgeting and planning, protecting profits, and facilitating international trade. These contracts help in reducing uncertainty and ensuring stability in transactions involving different currencies.
The pricing of foreign exchange forward contracts is based on the spot exchange rate, interest rate differentials between the two currencies, and the time to maturity of the contract. The forward rate is calculated using these factors, and it reflects the market expectations of future currency exchange rates.
Accuracy of an SKS at 100 yards The SKS is a popular semi-automatic rifle known for its reliability and affordability. Originally designed in the …
Read ArticleUnderstanding IB Rebate: A Comprehensive Guide IB rebate, also known as Introducing Broker rebate, is a form of compensation that Introducing Brokers …
Read ArticleUSD ZAR Selling Rate: What You Need to Know Looking to exchange your US dollars for South African Rand (ZAR)? Stay up to date with the latest exchange …
Read ArticleWhy do traders go to Dubai? The choice of a trade hub plays a crucial role in the success of any business. Dubai, the cosmopolitan city of the United …
Read ArticleChoosing the Right Trendline: A Definitive Guide When analyzing data, it is essential to understand the trends and patterns that emerge. One way to …
Read ArticleIs Forex Trading Haram? Exploring the Islamic Perspective Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is a popular investment opportunity …
Read Article