Understanding the Basics of Chat Marketing: What is it and How it Works
Understanding the Chat Market: Everything You Need to Know In the modern digital landscape, businesses are constantly seeking innovative ways to …
Read Article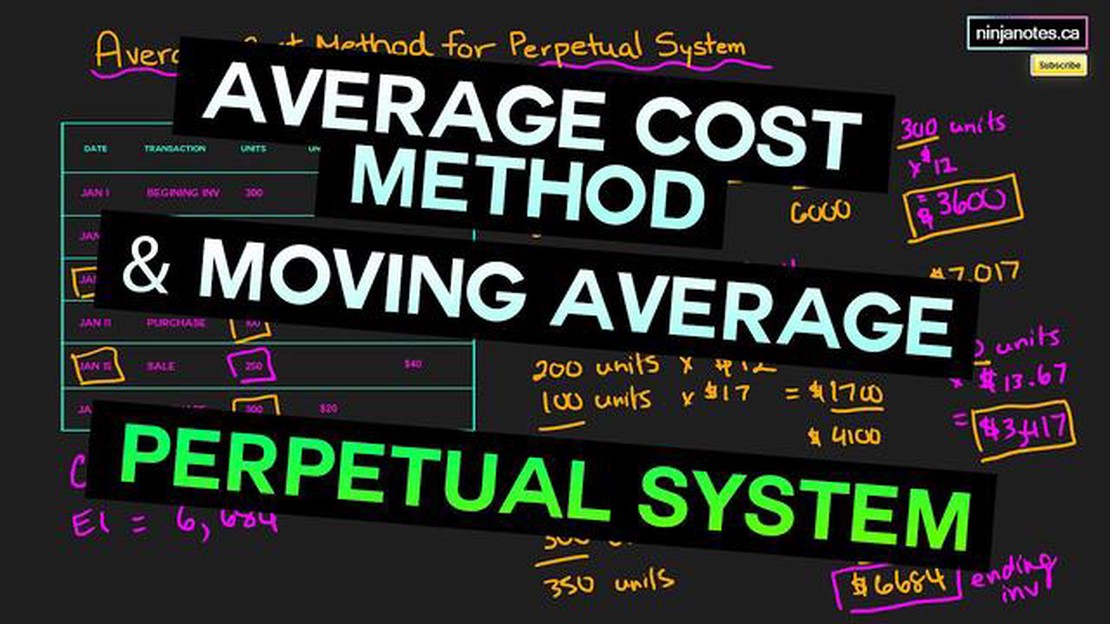
In the world of inventory management, understanding the perpetual moving average cost (PMAC) is essential for optimizing financial analysis and decision-making processes. The PMAC method is a widely used approach for calculating the value of inventory at any given time, providing businesses with insights into their cost of goods sold (COGS).
The PMAC takes into account the cost of acquiring inventory, as well as any subsequent changes in the value of that inventory due to factors such as price fluctuations or currency exchange rates. By continuously updating the average cost based on recent transactions, the PMAC method provides a more accurate representation of a company’s inventory value compared to other costing methods.
One of the key benefits of using the perpetual moving average cost method is its ability to smooth out the impact of price fluctuations. Instead of relying on outdated or historical costs, the PMAC method accounts for changes in inventory value in real-time. This allows businesses to make more informed decisions regarding pricing strategies, order quantities, and overall inventory management.
Moreover, the PMAC method also helps businesses mitigate potential losses by accounting for changes in currency exchange rates. This is particularly useful for companies that operate in multiple countries or engage in international trade. By factoring in fluctuations in exchange rates, the PMAC method provides a more accurate representation of the true cost of inventory, enabling businesses to identify and mitigate potential risks associated with foreign exchange.
Overall, understanding and implementing the perpetual moving average cost method in inventory management can greatly enhance a company’s financial analysis and decision-making capabilities. By providing a real-time view of inventory value and accounting for price fluctuations and currency exchange rates, the PMAC method allows businesses to make more informed and strategic decisions regarding their inventory management. This ultimately helps optimize financial performance, reduce risks, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Perpetual Moving Average Cost is a method used in inventory management to calculate the average cost of inventory items. Unlike other inventory costing methods, such as First In, First Out (FIFO) or Last In, First Out (LIFO), the perpetual moving average cost method calculates the average cost of inventory items by taking into account all past purchases and sales.
Under the perpetual moving average cost method, the cost of inventory items is updated each time a purchase or sale occurs. When a purchase is made, the cost of the new inventory is added to the total cost of the existing inventory items. Similarly, when a sale is made, the cost of the sold inventory is subtracted from the total cost of the remaining inventory items.
Read Also: How Much Does It Cost to Move a 3-Bedroom House in the UK? | [Your Company Name]
The formula for calculating the perpetual moving average cost is as follows:
The perpetual moving average cost method is particularly useful in industries with volatile costs, where the cost of inventory items can fluctuate frequently. It provides a more accurate and up-to-date measure of the average cost of inventory items, which can help businesses make informed pricing and inventory management decisions.
In addition, the perpetual moving average cost method can also be beneficial for businesses that want to track the historical cost of inventory items. It allows them to analyze trends and patterns in the cost of inventory over time, which can be valuable for financial reporting and performance evaluation purposes.
However, it’s important to note that the perpetual moving average cost method may not be suitable for all businesses. It requires regular and accurate tracking of inventory costs, which can be time-consuming and may require sophisticated inventory management systems. Additionally, it may not be appropriate for industries with stable or predictable costs, where other costing methods may provide more accurate results.
In conclusion, the perpetual moving average cost method is a valuable tool in inventory management, allowing businesses to calculate the average cost of inventory items based on all past purchases and sales. It provides a more accurate and up-to-date measure of inventory costs, which can help businesses make informed pricing and inventory management decisions.
In conclusion, the perpetual moving average cost offers several benefits in inventory management. It provides accurate cost calculation, real-time inventory valuation, smoother cost fluctuations, fair and consistent pricing, and easy cost allocation. By utilizing this method, businesses can improve their inventory management processes and make more informed decisions.
Read Also: Activate Your CIMB ATM Card Overseas: Easy Steps and Quick Guide
Perpetual moving average cost is a method used in inventory management to calculate the average cost of inventory by considering the cost of each unit as it is purchased or produced.
Unlike other methods such as specific identification or FIFO (First in, First out), perpetual moving average cost takes into account the cost of each unit of inventory instead of relying on specific identification or the order in which they were purchased or produced.
Perpetual moving average cost is important because it provides a more accurate and up-to-date representation of the cost of inventory. This allows businesses to have a clearer understanding of their inventory valuation, profit margins, and pricing decisions.
Perpetual moving average cost is calculated by dividing the total cost of inventory available for sale by the total number of units in inventory. This gives the average cost per unit, which is then used to value the inventory on hand as well as any units sold.
Perpetual moving average cost can be used for most types of inventory, especially those with similar or consistent costs. However, it may not be suitable for inventory with significant cost fluctuations or unique items that require specific identification.
Understanding the Chat Market: Everything You Need to Know In the modern digital landscape, businesses are constantly seeking innovative ways to …
Read ArticleTrading Partners of Iran Iran, a country in the Middle East, has a rich history and culture. It is also known for its thriving trade partnerships with …
Read ArticleWhat are CTA stocks? Commodity Trading Advisors, or CTAs, play an important role in the world of finance. These professionals are responsible for …
Read ArticleIs QQQ a good choice for options trading? Options trading is a popular investment strategy that allows traders to profit from the movement of …
Read ArticleHigh-Frequency Trading: A Comprehensive Guide High-Frequency Trading (HFT) is a trading strategy that relies on the use of powerful computers and …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Forex Fundamentals: The Key to Successful Trading In the world of finance, the foreign exchange market, or Forex, is one of the most …
Read Article