Forex Trading in Kenya: Which Time Zone to Follow?
Forex Trading Time Zone in Kenya When it comes to Forex trading, one of the most important factors to consider is the time zone in which you are …
Read Article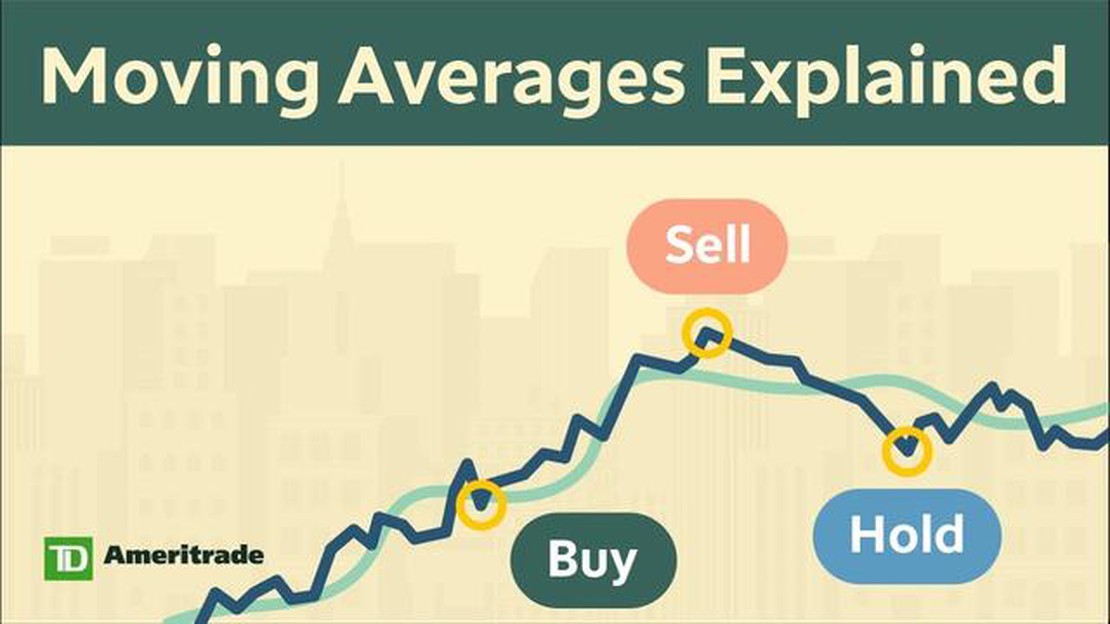
The Law of Moving Average is a statistical concept that is widely used in various fields, including finance, economics, and data analysis. It is a technique that helps in smoothing out fluctuations and identifying underlying trends in a set of data over a specific period of time. By using the Law of Moving Average, analysts and researchers are able to make predictions, identify patterns, and make informed decisions.
The calculation of Moving Average involves taking the average of a set of data points over a specific period of time, and then moving this average forward or backward in time. This moving average can be calculated for various intervals, such as days, weeks, months, or years, depending on the scope and purpose of the analysis. The result is a smooth line or curve that represents the average value of the data points within the chosen timeframe.
The Law of Moving Average has numerous applications. In finance, it is commonly used to analyze stock prices, exchange rates, and other financial indicators. By analyzing the moving averages of these variables, traders and investors can identify trends and make predictions about future market movements. In economics, moving averages are used to analyze economic indicators, such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and unemployment rates, to identify long-term trends and assess the health of the economy. Additionally, the Law of Moving Average is also used in data analysis to analyze trends in customer behavior, sales figures, and other business metrics.
In conclusion, the Law of Moving Average is a powerful tool for analyzing data and identifying underlying trends. By calculating and analyzing moving averages, analysts and researchers are able to make predictions, spot patterns, and make informed decisions in various fields. Whether in finance, economics, or data analysis, understanding and applying the Law of Moving Average is essential for making accurate and reliable assessments of data.
The moving average is a commonly used statistical calculation that helps identify trends and patterns in data. It is widely used in various fields, including finance, economics, and forecasting. By smoothing out fluctuations and noise in the data, the moving average provides a clearer picture of the underlying trends.
The law of moving average states that the more data points included in the calculation, the smoother the average will be. This means that a longer period moving average will be slower to respond to changes in the data, while a shorter period moving average will be more sensitive to recent changes. The choice of the length of the moving average depends on the specific application and the desired level of responsiveness.
The calculation of a moving average involves summing up a specific number of data points and dividing the sum by the number of data points. For example, a 5-day moving average would involve summing up the closing prices of the last 5 days and dividing the sum by 5. The resulting value represents the average price over the specified period.
Moving averages are often used to identify trend reversals and support or resistance levels. When the price crosses above the moving average, it may indicate a bullish trend, while a crossover below the moving average may suggest a bearish trend. Traders and investors can use moving averages as a tool to make informed decisions about buying or selling assets.
In conclusion, understanding the law of moving average is essential for analyzing data and making predictions. By utilizing moving averages, individuals and businesses can gain valuable insights into market trends and make strategic decisions. Whether in finance, economics, or other fields, the moving average is an invaluable tool for understanding and forecasting data.
The moving average is a statistical calculation that is used to analyze trends over a specific period of time. It is commonly used in finance, economics, and other fields to smooth out data and identify patterns or trends.
The moving average is calculated by taking the average of a set of data points over a given time period. The time period can vary, depending on the specific analysis being conducted and the frequency of the data being used.
For example, a simple moving average (SMA) of a stock price over a 10-day period would involve adding up the closing prices of the stock for the last 10 days and then dividing that sum by 10. This calculation is repeated every day to create a new average.
Read Also: The Secret Behind Binary Trading: Unveiling the Truth
The moving average is often used to identify support and resistance levels in technical analysis. When the price of an asset moves above its moving average, it is seen as a bullish signal, indicating a potential upward trend. Conversely, when the price moves below its moving average, it is seen as a bearish signal, indicating a potential downward trend.
| Period | Data Point 1 | Data Point 2 | Data Point 3 | … | Data Point n | Moving Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | 100 | 110 | 120 | … | 90 | 104.5 |
| Day 2 | 110 | 120 | 90 | … | 95 | 105.5 |
| Day 3 | 120 | 90 | 85 | … | 105 | 100 |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| Day n | 90 | 100 | 105 | … | 120 | 108 |
In order to calculate the moving average, you need to follow a few simple steps. First, determine the time period over which you want to calculate the moving average. This could be a specific number of days, weeks, months, or any other time interval.
Next, add up the closing prices of the asset for the specified time period. The closing price is the price of the asset at the end of each trading day.
Read Also: Option Trading in Australia: Everything You Need to Know
Once you have the sum of the closing prices, divide it by the number of periods you are using to calculate the moving average. This will give you the average price over the specified time period.
Repeat this process for each subsequent time period, taking into account the most recent closing price and dropping the oldest closing price from the calculation.
For example, let’s say you are calculating the 5-day moving average of a stock. You would add up the closing prices of the stock for the last 5 days and divide the sum by 5 to get the average price. Then, you would move forward one day and repeat the process using the new closing price and dropping the oldest closing price from the calculation.
The moving average is a useful tool for smoothing out price data and identifying trends. It can be used in various ways, such as determining support and resistance levels, identifying entry and exit points for trades, and generating trading signals.
The Law of Moving Average is a statistical calculation used to analyze trends in a set of data over a specific time period. It is often used to determine the average value of a variable and to smooth out fluctuations in the data.
The Moving Average is calculated by adding up all the values in a set of data over a specific time period, and then dividing the sum by the number of data points in that period. The result is the average value for that time period.
The purpose of using Moving Averages is to identify trends and patterns in data. It is often used in technical analysis to determine the direction of a trend, to identify support and resistance levels, and to generate buy and sell signals.
Yes, Moving Averages can be used for both short-term and long-term analysis. Short-term moving averages are typically used to analyze trends over a shorter time period, while long-term moving averages are used to assess trends over a longer time frame.
Yes, there are different types of Moving Averages, including the Simple Moving Average (SMA) and the Exponential Moving Average (EMA). The SMA is calculated by taking the sum of the data points over a specific time period and dividing it by the number of data points. The EMA gives more weight to recent data points and is often used to spot trends more quickly.
The Law of Moving Average is a statistical calculation used to analyze data over a certain period of time by taking the average of a set of values.
The Moving Average is calculated by adding up a set of values over a specific period of time and dividing it by the number of values in that set.
Forex Trading Time Zone in Kenya When it comes to Forex trading, one of the most important factors to consider is the time zone in which you are …
Read ArticleExchange Rate for Lloyds Bank GBP to Australian Dollar If you are planning a trip to Australia or have business transactions with Australian …
Read ArticleCurrent Dollar Exchange Rate Today Knowing the current exchange rate of the dollar is essential for both individuals and businesses involved in …
Read ArticleWhat is the maximum leverage in CMS Prime? Are you looking to maximize your trades? Look no further than CMS Prime. With our cutting-edge trading …
Read ArticleReporting Non-Qualified Stock Options: A Step-by-Step Guide When it comes to reporting non-qualified stock options (NQSOs), it’s important to …
Read ArticleCan I still buy Celgene stock? Investing in the stock market can be a complex and challenging task, especially when it comes to choosing the right …
Read Article