Understanding Stock Options: A Comprehensive Guide for Employees
Understanding Stock Options for Employees: A Complete Guide Stock options are a valuable form of compensation that many employees receive as a part of …
Read Article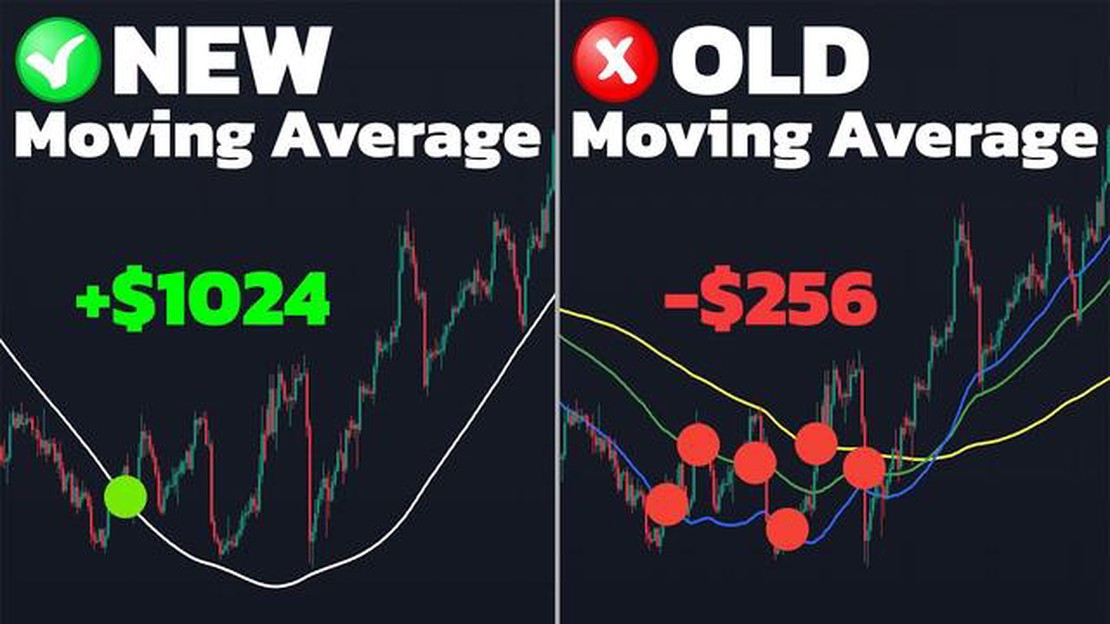
In the world of finance and investing, it is essential to understand various technical indicators that can help in making informed decisions. One such indicator is the moving average, which is widely used by traders and analysts to identify trends and potential entry or exit points. However, it is important to recognize that moving averages suffer from a lag, meaning they provide information about past price movements rather than current or future ones. This article aims to explore the concept of lag in moving averages and its implications for traders.
A moving average is a mathematical calculation that smooths out price data over a specific period of time, providing a line on a chart that represents an average price during that time frame. It is commonly used to identify trends and filter out noise in price movements. However, due to its nature, moving averages inherently lag behind the actual price action, as they are based on historical data. This lag can be particularly problematic in fast-moving markets where prices change rapidly.
The lag in moving averages can result in delayed signals, which means traders may miss out on potential profit opportunities or enter trades at less favorable prices. For example, if a moving average indicates a buy signal after a significant price rally has already occurred, traders who rely solely on this indicator may enter the market at higher prices, potentially reducing their profits or increasing their losses. Similarly, a sell signal might be generated after a price decline has already taken place, causing traders to exit positions at lower prices.
It is crucial for traders to be aware of the lag in moving averages and use them in conjunction with other indicators and analysis techniques to minimize the impact of lag. Combining moving averages with momentum indicators, such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), can provide a more comprehensive view of the current market conditions. Additionally, adjusting the parameters of the moving averages, such as the time period or type of average used, can help reduce lag and generate more timely signals.
In conclusion, while moving averages are valuable tools in technical analysis, understanding their lag is essential for successful trading. By acknowledging and accounting for this lag, traders can make more informed decisions and avoid potential pitfalls caused by delayed signals. Utilizing a combination of indicators and analysis techniques can help mitigate the impact of lag and provide a more accurate representation of the current market conditions.
In the context of moving averages, lag refers to the delay or slowness in the response of the moving average indicator to changes in the underlying data. Moving averages are used to smooth out the price or other time series data by averaging out the fluctuations over a specific period of time.
However, this smoothing process results in a lag between the moving average line and the actual data points. The lag is caused by the mathematical calculation involved in computing the moving average. The longer the time period used to calculate the moving average, the greater the lag.
The lag in moving averages can have both advantages and disadvantages. On one hand, the lag helps filter out noise and short-term fluctuations in the data, allowing traders and investors to focus on the overall trend. By removing the smaller fluctuations, the moving average provides a clearer picture of the underlying direction of the data.
On the other hand, the lag can be a disadvantage when it comes to timely decision-making. Since the moving average is slower to respond to changes in the data, it may not provide timely signals for entering or exiting a position. This lag can cause traders to miss out on certain trading opportunities or result in delayed decision-making.
To mitigate the lag in moving averages, traders often use shorter time periods or other forms of moving averages, such as exponential moving averages (EMAs) or weighted moving averages (WMAs). These alternative moving averages respond faster to changes in the data and have less lag compared to simple moving averages.
Overall, understanding the lag in moving averages is essential for effectively using this technical indicator in trading and investing. Traders should consider the trade-off between lag and responsiveness when choosing the appropriate moving average for their analysis.
Read Also: Understanding the Basics of Binary Option Trading: A Comprehensive Guide
When using moving averages in technical analysis, it is important to understand the concept of lag. Lag refers to the delay between the occurrence of a data point and its impact on the moving average.
The lag in moving averages can have a significant impact on the interpretation of the data and the effectiveness of the analysis. A moving average is calculated by taking the average of a certain number of data points over a given period of time. The lag refers to the time it takes for a data point to be included in the calculation and affect the moving average value.
The lag in moving averages can result in delayed signals and inaccuracies in trend identification. For example, if the moving average is based on a 10-day period, it may take several days for a significant price change to be incorporated into the average. This can lead to delayed buy or sell signals, as the moving average may not react quickly enough to changes in the market.
It is also important to consider the length of the moving average when assessing the impact of lag. Longer moving averages, such as 50-day or 200-day averages, tend to have more lag compared to shorter moving averages. This means that longer-term trends may be more accurately captured, but short-term fluctuations may be less apparent.
Read Also: Exploring the Various Types of Bank Audits: A Comprehensive Guide
To mitigate the impact of lag, traders and analysts often use multiple moving averages of different lengths. By combining shorter and longer-term moving averages, they can gain a more comprehensive view of the market and reduce the likelihood of false signals.
In conclusion, the lag in moving averages is an important factor to consider when using this technical analysis tool. Understanding the impact of lag can help traders and analysts make more informed decisions and improve the accuracy of their analysis.
Moving averages are a popular technical analysis tool that is used to identify trends and potential buy or sell signals. It is calculated by averaging the closing prices of a security over a specific period of time, and then plotting the result on a chart. The moving average line smooths out the price data, making it easier to identify the overall trend of the security.
The lag in moving averages refers to the delay in the moving average line catching up to the actual price action of a security. Because moving averages are calculated based on historical price data, they are inherently lagging indicators. This means that the moving average line will always be slightly behind the current price, which can make it difficult to use for real-time trading decisions.
Traders can compensate for the lag in moving averages by using shorter time periods for their moving averages. By using shorter time periods, the moving average line will respond more quickly to changes in price and reduce the lag. However, it’s important to note that shorter time periods can also increase the number of false signals, so it’s important to find the right balance.
Despite the lag, moving averages offer several advantages for traders. Firstly, they help to smooth out the noise in price data and provide a clearer picture of the overall trend. Secondly, they can help traders identify potential support and resistance levels, as prices often tend to bounce off moving averages. Finally, moving averages are easy to understand and widely used, making them a popular tool among traders.
Yes, there are alternative indicators that can be used to reduce lag. Some examples include exponential moving averages (EMAs) and weighted moving averages (WMAs). These types of moving averages give more weight to recent price data, which allows them to respond more quickly to changes in price compared to simple moving averages. However, it’s important to note that these alternative indicators may introduce their own unique set of challenges and considerations.
Moving averages are indicators used in technical analysis to identify trends and patterns in the price of an asset. They are calculated by taking the average of a set number of previous price points. Traders use moving averages to determine potential support and resistance levels, signals for buying or selling, and to identify trend reversals.
The lag with moving averages occurs because they are based on historical data and are backward-looking in nature. Since moving averages are calculated based on past prices, they cannot accurately predict future price movements. The lag is the delay between the occurrence of a trend or a change in price and the signal generated by the moving average.
Understanding Stock Options for Employees: A Complete Guide Stock options are a valuable form of compensation that many employees receive as a part of …
Read ArticleUnderstanding Nifty and Sensex When it comes to investing in the stock market, understanding key indices like the Nifty and Sensex is crucial. These …
Read ArticleWhat is the Moving Average Crossover Strategy for Forex? Forex trading is a complex and ever-evolving market, where traders are constantly seeking new …
Read ArticleHow often do you move houses? Relocating to a new home is a major life decision that many people face at some point in their lives. Whether it’s for …
Read ArticleTD Ameritrade Fees: Are They High? When it comes to investing, fees can play a significant role in determining your overall returns. TD Ameritrade is …
Read ArticleIs Botswana’s Exchange Rate Fixed or Flexible? Botswana, a landlocked country in Southern Africa, has often been heralded as one of the success …
Read Article