Understanding the Risk Reversal Payoff Strategy: A Comprehensive Guide - SiteName
Understanding the Risk Reversal Payoff Strategy In the world of options trading, risk management is paramount. Traders are constantly looking for …
Read Article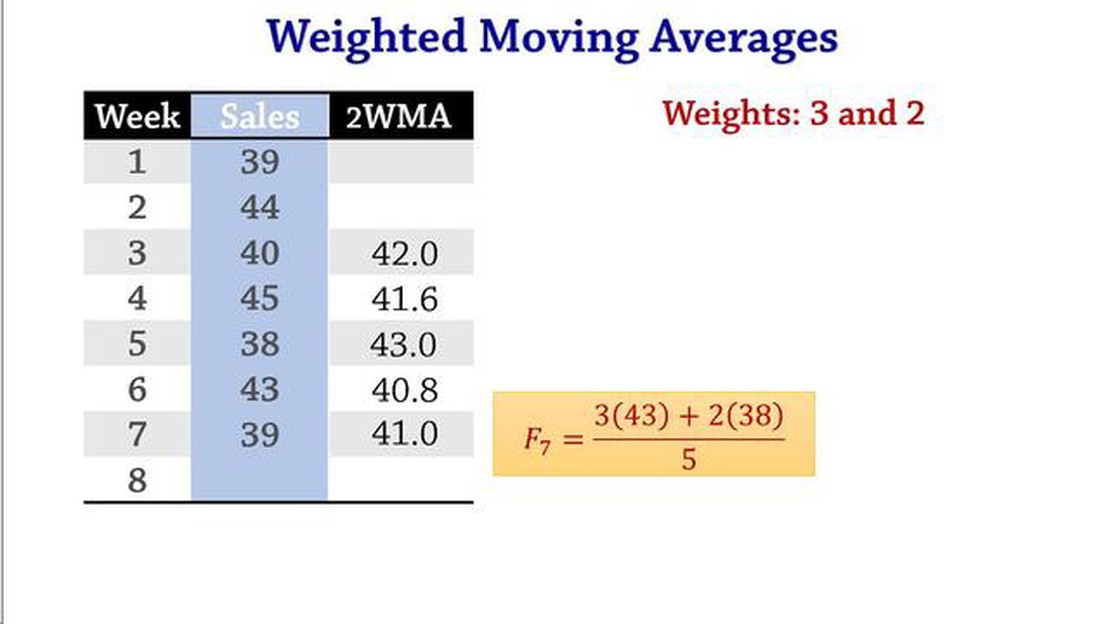
Technical analysis is an essential tool for traders and investors in the financial markets. It helps them make informed decisions based on past market data. One popular technical indicator is the weighted moving average (WMA), which provides a smoother representation of price trends over a specified period. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the L weighted moving average, a variation of the WMA that gives more weight to recent price data.
The L weighted moving average is an advanced indicator that takes into account recent market movements more heavily than traditional moving averages. It is calculated by assigning a weight coefficient to each price data point, with higher weights given to recent data and lower weights given to older data. By doing so, the L weighted moving average can more accurately capture short-term price fluctuations and identify potential trend reversals.
Traders and investors use the L weighted moving average in various ways. It can be used as a standalone indicator to identify buy or sell signals when the price crosses above or below the moving average line. Additionally, it is often used in combination with other technical indicators to confirm trend direction or generate trading signals. By understanding the L weighted moving average, traders can gain valuable insights into market trends and make more informed trading decisions.
In this guide, we will cover the basic calculation of the L weighted moving average, discuss its strengths and limitations, and provide examples of how it can be used in real trading scenarios. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced trader, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to effectively incorporate the L weighted moving average into your trading strategy.
The L Weighted Moving Average is a technical analysis indicator that is used to identify trends and potential buying or selling opportunities in financial markets. It is a variation of the simple moving average (SMA), which calculates the average price of an asset over a specific period of time.
The L Weighted Moving Average differs from the SMA in that it gives greater weight to more recent data points. This means that the L Weighted Moving Average is more sensitive to recent price changes and can react faster to market trends.
The formula for calculating the L Weighted Moving Average takes into consideration the closing prices of the asset over a specific number of periods, giving each period a weight based on its position relative to the most recent period. The weights are typically assigned in a linear manner, decreasing linearly as the periods move further away from the most recent period.
| Period | Weight |
|---|---|
| Most recent period | Weight 1 |
| Second most recent period | Weight 2 |
| Third most recent period | Weight 3 |
| And so on… | And so on… |
By assigning weights to each period, the L Weighted Moving Average places a greater emphasis on recent data, allowing traders and analysts to get a better understanding of the current market dynamics.
The L Weighted Moving Average can be plotted on a price chart to visually represent the average price movement over time. Traders often use it in conjunction with other technical indicators or trendlines to confirm signals and make informed trading decisions.
Overall, the L Weighted Moving Average is a valuable tool for technical analysis, providing insights into market trends and potential price reversal points. It is widely used by traders and analysts to identify optimal entry and exit points in financial markets.
Read Also: Can Muslims Trade Forex?: Understanding Islamic Forex Trading Principles
The L Weighted Moving Average (LWMA) is a widely used financial indicator in technical analysis. It is a type of moving average that assigns more weight to the most recent data points, making it especially useful for short-term analysis. Financial analysts utilize the LWMA to identify trends and predict future price movements.
One of the main advantages of using the LWMA is its responsiveness to recent price changes. By assigning more weight to the most recent data points, the LWMA reflects the current market conditions and captures short-term price fluctuations more effectively than other moving averages. This makes it a valuable tool for traders and investors who want to spot short-term trading opportunities.
Another significant aspect of the LWMA is that it helps smoothen out the impact of sudden price spikes or drops. By giving more weight to recent data, the LWMA emphasizes the impact of recent prices while filtering out the noise caused by extreme price movements. This can provide a clearer picture of the underlying trends in a financial instrument’s price movement.
In financial analysis, the LWMA is often used in conjunction with other technical indicators, such as the Simple Moving Average (SMA) or the Exponential Moving Average (EMA). Analysts rely on these indicators to confirm signals and validate their trading decisions. The LWMA’s unique weighting scheme adds an additional layer of information to these analyses, helping traders make more informed decisions.
Furthermore, the LWMA can be adjusted according to different timeframes, allowing analysts to customize their analysis based on their trading strategies or investment objectives. Shorter LWMA periods are commonly used for intraday trading, while longer periods are preferred for long-term investment analysis.
In conclusion, the L Weighted Moving Average is a powerful tool in financial analysis due to its ability to capture short-term price fluctuations and smoothen out extreme market movements. When used in conjunction with other technical indicators, the LWMA provides valuable insights into market trends and helps traders make informed trading decisions.
Read Also: Withdrawal Methods: How to Get Your Money from Forex
The L Weighted Moving Average (LWMA) is a technical analysis tool used to smooth out price data over a specific time period. It assigns a higher weight to the most recent data points, making it more responsive to current price movements. The LWMA can help traders identify trends and potential reversals in the market.
To calculate the LWMA, follow these steps:
Here is the formula for calculating the LWMA:
LWMA = (n * P1 + (n-1) * P2 + (n-2) * P3 + … + 2 * Pn-1 + 1 * Pn) / (n + (n-1) + (n-2) + … + 2 + 1)
Where:
By using the LWMA, traders can gain a clearer understanding of price trends and potential reversals in the market. It is important to note that the LWMA is just one tool among many in technical analysis and should be used in conjunction with other indicators for more accurate trading decisions.
An L Weighted Moving Average is a type of moving average that assigns greater emphasis to more recent data points and less emphasis to older data points. It is calculated using a weighted sum of the data points, with the weights decreasing exponentially as the data points get older.
An L Weighted Moving Average is calculated by taking the sum of the products of the data points and the corresponding weights. The weights are calculated using an exponential decay formula, where the weight for each data point is given by the formula e^(-lambda * (n-1)), where n is the position of the data point and lambda is a smoothing factor.
The purpose of using an L Weighted Moving Average is to smoothen out the fluctuations in a time series data and identify the underlying trends. It helps in making predictions and forecasting future values based on the historical data.
The smoothing factor lambda for an L Weighted Moving Average is chosen based on the desired level of smoothing. A smaller value of lambda will lead to a smoother curve, while a larger value of lambda will be more responsive to recent changes in the data. The choice of lambda depends on the specific application and the trade-off between smoothing and responsiveness.
Understanding the Risk Reversal Payoff Strategy In the world of options trading, risk management is paramount. Traders are constantly looking for …
Read ArticleHow to Withdraw Money from a Forex Broker Withdrawing money from a forex broker is an essential part of trading. Whether you have made a profit or …
Read ArticleHow Much Does it Cost to Withdraw Money on FOREX? When trading on the Foreign Exchange Market (FOREX), it is crucial to consider all the costs …
Read ArticleEnron’s Tactics: Unveiling the Strategies of a Corporate Giant Enron, once considered a shining example of corporate success, is now infamous for its …
Read ArticleRisks of High-Frequency Trading In recent years, high-frequency trading (HFT) has become a major force in the world of financial markets. HFT is a …
Read ArticleTradingview Currency Strength Meter: Does it Exist? When it comes to trading in the Forex market, having a deep understanding of currency strength can …
Read Article