Are Forex Traders in Singapore Required to Pay Taxes?
Guide to Tax Implications for Forex Traders in Singapore Forex trading has gained popularity in Singapore over the years, with many individuals trying …
Read Article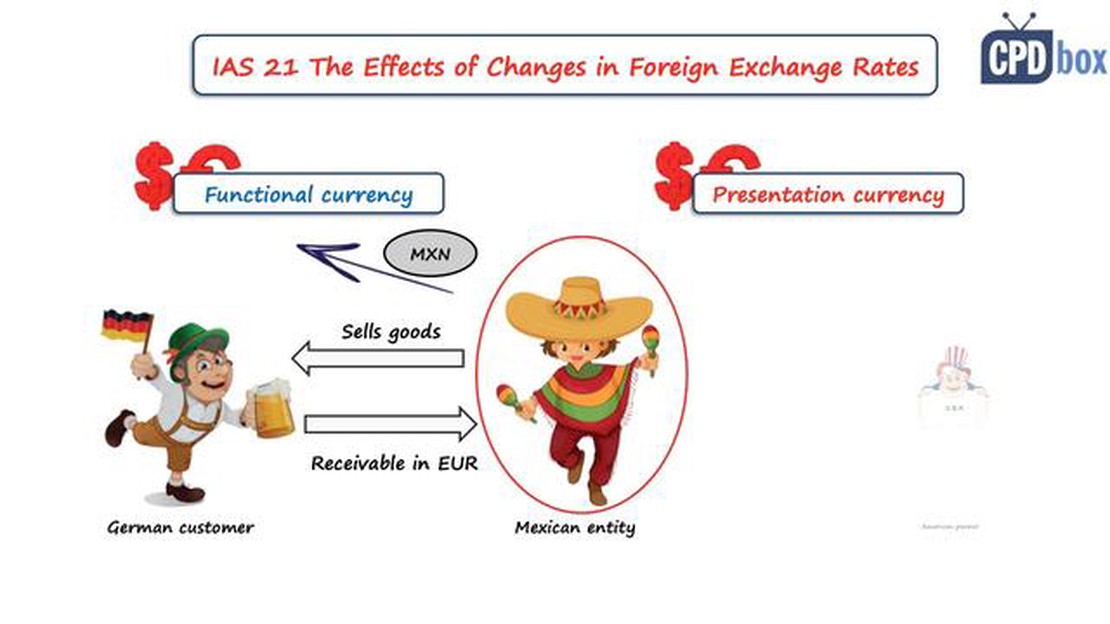
The International Accounting Standard (IAS) 21 is a standard formulated by the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Foundation. It provides guidelines for accounting and reporting when transactions are conducted in foreign currencies. This standard is crucial for global companies operating in multiple countries or conducting business in foreign currencies.
IAS 21 aims to ensure that financial statements prepared in different currencies can be compared accurately. It sets out rules for translating foreign currency transactions, balances, and foreign operations into the functional currency of the reporting entity. By following the guidelines of IAS 21, companies can provide users of financial statements with transparent and reliable information regarding the impact of foreign currency transactions on their financial performance and position.
The standard requires a multi-step approach for translating foreign currency transactions. First, the functional currency needs to be determined. The functional currency is the currency of the primary economic environment in which the entity operates. Once the functional currency is determined, foreign currency transactions are translated using the exchange rate at the date of the transaction.
IAS 21 also addresses the translation of foreign currency monetary items and non-monetary items. Monetary items, such as cash and liabilities, are translated using the closing exchange rate at the balance sheet date, while non-monetary items, such as inventory and property, are translated at historical exchange rates. The resulting exchange differences are recognized in the financial statements as income or expenses.
It is important for companies to understand and comply with IAS 21 to ensure accurate and consistent reporting of their foreign currency transactions. By following the standard, companies can provide stakeholders with reliable and transparent financial information, allowing for better decision-making and analysis of their global operations.
The International Accounting Standard 21 (IAS 21) sets out guidelines for accounting for foreign currency transactions and translating financial statements into a reporting currency. It provides guidance on how to record foreign currency transactions, how to translate financial statements into a reporting currency, and how to account for changes in exchange rates.
IAS 21 is applicable to all entities that prepare financial statements in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). The standard outlines the principles that entities should follow when dealing with foreign currency transactions and the effects of changes in exchange rates on their financial statements.
The objective of IAS 21 is to prescribe how to include foreign currency transactions and foreign operations in the financial statements of an entity and how to translate financial statements into a presentation currency. It also provides guidance on determining the functional currency of an entity and how to account for exchange differences arising from translating financial statements into a different presentation currency.
| Key areas covered by IAS 21 |
|---|
| Accounting for foreign currency transactions |
| Translation of financial statements into a reporting currency |
| Determining the functional currency |
| Accounting for changes in exchange rates |
When it comes to accounting for foreign currency transactions, IAS 21 requires entities to recognize foreign currency transactions using the exchange rate at the date of the transaction. Any difference between the initial recognition and the subsequent revaluation of the transaction will be recognized in the income statement.
For translating financial statements into a reporting currency, the standard provides guidance on the methods that can be used, such as the spot rate method and the closing rate method. The translation method used depends on the functional currency of the entity and whether it operates in a highly inflationary economy.
The standard also addresses how to determine the functional currency of an entity. The functional currency is the currency of the primary economic environment in which the entity operates. It is determined based on several factors, including the currency that influences sales prices, the currency that influences financing and borrowing costs, and the currency of the country in which the entity operates.
Finally, IAS 21 provides guidance on accounting for changes in exchange rates. It requires entities to recognize exchange differences in the financial statements as they arise and to include them in the determination of profit or loss for the period.
Read Also: What Happens to Options with Dividends? - Explained and Answered
In conclusion, IAS 21 sets out guidelines for accounting for foreign currency transactions and translating financial statements into a reporting currency. It is applicable to entities that prepare financial statements in accordance with IFRS and covers areas such as the accounting for foreign currency transactions, translation of financial statements, determining the functional currency, and accounting for changes in exchange rates.
The IAS 21 standard, also known as International Accounting Standard 21, provides guidelines for accounting for foreign currency transactions and translating the financial statements of foreign operations. It is an essential standard for multinational organizations that conduct business in different currencies.
There are several key concepts that are important to understand in the IAS 21 standard:
1. Functional Currency:
The functional currency is the currency of the primary economic environment in which the entity operates. It is the currency of the country where the entity primarily earns and spends its cash. The functional currency is important because it determines how foreign currency transactions are initially recognized and subsequently translated into the reporting currency.
2. Reporting Currency:
The reporting currency is the currency in which the financial statements are presented. It is typically the currency of the country where the entity is domiciled or has its headquarters. The reporting currency is used to consolidate the financial statements of the entity’s foreign operations.
3. Foreign Currency Transactions:
Read Also: How Many Children Died in 9/11? | Child Fatalities in the September 11 Attacks
A foreign currency transaction is a transaction that is denominated in a currency other than the functional currency. The IAS 21 standard provides guidance on how to initially record foreign currency transactions and subsequently translate them into the reporting currency. The standard also addresses the recognition of exchange differences arising from those transactions.
4. Exchange Rate:
The exchange rate is the rate at which one currency can be exchanged for another. The IAS 21 standard provides guidelines for determining the exchange rate to be used for translating foreign currency amounts into the functional currency and the reporting currency. It specifies the use of spot exchange rates, historical exchange rates, and other appropriate rates depending on the circumstances.
5. Foreign Operations:
A foreign operation is an entity that is a subsidiary, associate, joint venture, or branch of the reporting entity and operates in a country different from the reporting entity. The IAS 21 standard provides guidance on how to translate the financial statements of foreign operations into the reporting currency and how to account for exchange differences arising from that translation.
By understanding these key concepts in the IAS 21 standard, multinational organizations can properly account for foreign currency transactions and present accurate financial statements that reflect the economic reality of their operations.
The IAS 21 standard of accounting is a set of guidelines and rules set by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) that governs the accounting for foreign currency transactions and foreign operations. It provides guidance on how to translate foreign currency transactions and foreign operations into a reporting currency.
The IAS 21 standard is important because it ensures consistency and comparability in the financial reporting of entities that operate in different countries or have foreign currency transactions. It promotes transparency and helps investors and stakeholders understand the financial position and performance of an entity in a global context.
The main requirements of the IAS 21 standard include determining the functional currency of an entity, translating foreign currency transactions into the functional currency at the exchange rate on the transaction date, and translating foreign operations’ financial statements into the entity’s presentation currency using appropriate exchange rates.
The IAS 21 standard impacts financial statements by requiring entities to translate their foreign currency transactions and foreign operations into a reporting currency. This can affect the amounts reported in the financial statements, such as revenues, expenses, assets, and liabilities, as they are converted using different exchange rates.
Yes, there are certain exceptions and exemptions under the IAS 21 standard. For example, companies are allowed to use different methods for translating foreign currency transactions and foreign operations if certain criteria are met. Additionally, certain transactions, such as those between entities within the same economic environment, are exempt from the requirements of the standard.
Guide to Tax Implications for Forex Traders in Singapore Forex trading has gained popularity in Singapore over the years, with many individuals trying …
Read ArticleIs FX swap an OTC derivative? Introduction: Table Of Contents Is FX Swap an OTC Derivative? Exploring the Characteristics FAQ: What is an FX swap and …
Read ArticleIs Thomas Cook Forex Card Free? When planning a trip abroad, one of the most important things to consider is how to carry money. Carrying cash can be …
Read ArticleHow to Contact HDFC Customer Care: Step-by-Step Guide Having trouble with your HDFC account? Need assistance with your banking transactions or have …
Read ArticleIs binary trading allowed in UAE? Binary trading is a popular form of investment and has gained significant attention in recent years. However, if you …
Read ArticleIs Hedging Allowed in USA? When it comes to managing financial risk, one strategy that is often employed is hedging. Hedging involves taking a …
Read Article