Understanding Schedule D UK: A Guide to Tax Reporting for British Businesses
Understanding Schedule D UK: A Comprehensive Guide When it comes to running a business in the United Kingdom, understanding the tax reporting …
Read Article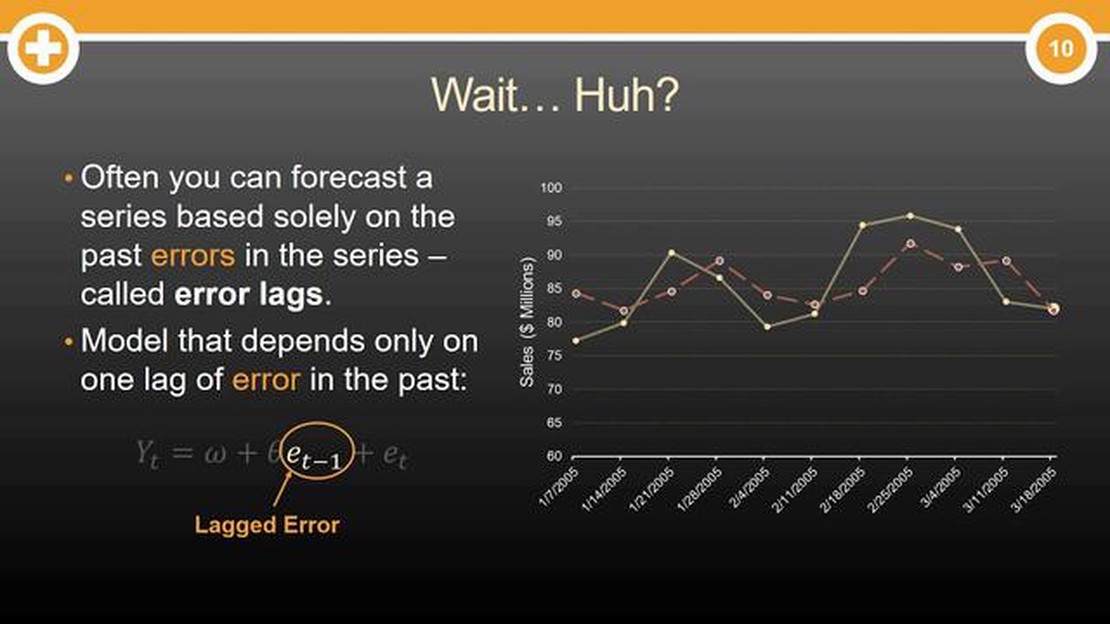
In the world of finance and statistics, the moving average (MA) is a commonly used indicator to analyze and understand trends in data. It helps traders and analysts to smooth out erratic movements and identify the underlying trend in a series of numbers. The moving average is calculated by taking the average of a certain number of data points over a specified period of time.
The equation for calculating the moving average MA is relatively straightforward. In its simplest form, the formula involves summing up a specific number of data points and dividing the sum by the total number of data points. For example, if you are calculating a 5-day moving average, you would sum up the values of the past five days and divide the sum by 5.
MA = (Sum of Values / Number of Values)
Once you have calculated the moving average, you can plot it on a graph to visualize the trend. When the moving average is increasing, it suggests an uptrend, and when it is decreasing, it indicates a downtrend. Traders often use the moving average to determine entry and exit points for buying and selling securities.
There are different types of moving averages, such as the simple moving average (SMA) and the exponential moving average (EMA), which use different weighting methods to give more weight to recent data points. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on the specific requirements of the analysis.
Understanding the equation for the moving average MA is crucial for anyone involved in financial analysis and trading. It provides a simple yet effective tool for identifying trends and making informed decisions based on historical data. By mastering this equation, traders and analysts can gain valuable insights into the market and increase their chances of success.
The Moving Average (MA) is a widely used technical analysis tool that helps traders identify trends and potential buy or sell signals in financial markets. It is a calculation that takes the average price over a specified period of time and updates as new data becomes available. The MA is plotted as a line on a price chart, providing traders with a visual representation of price movement.
The MA is calculated by adding together a predetermined number of closing prices and dividing by the number of periods. For example, a 5-day MA would sum up the closing prices of the past 5 days and divide by 5. The result is a single value that represents the average price over the specified time frame.
The MA can be used in different ways depending on the trader’s strategy. One common approach is to use multiple MAs with different time periods to identify trend changes. For example, when a shorter-term MA crosses above a longer-term MA, it may signal a bullish trend. Conversely, when a shorter-term MA crosses below a longer-term MA, it may indicate a bearish trend.
The MA can also be used to determine support and resistance levels. When the price is trading above the MA, it may act as a support level, preventing the price from falling further. Conversely, when the price is trading below the MA, it may act as a resistance level, preventing the price from rising further.
Traders can customize the MA by adjusting the time period and type of average used in the calculation. The most common types of MAs are simple moving averages (SMA) and exponential moving averages (EMA). The SMA gives equal weight to each period, while the EMA places more weight on recent prices, making it more responsive to price changes.
In conclusion, the Moving Average (MA) is a versatile tool that can help traders identify trends, anticipate market reversals, and determine support and resistance levels. By understanding how to interpret and use MAs, traders can make more informed trading decisions and improve their overall profitability.
The Moving Average (MA) is a commonly used statistical calculation that helps smooth out fluctuations in data by averaging out the values over a specific period of time. It is widely used in technical analysis to identify trends and potential buy/sell signals in stock prices, commodity prices, and other financial instruments.
To calculate the Moving Average, you need to follow these steps:
Read Also: Understanding the Difference Between SL and TL in Trading
Here is an example to illustrate the calculation:
| Day | Closing Price | Moving Average |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25.50 | |
| 2 | 26.20 | |
| 3 | 26.80 | |
| 4 | 27.50 | |
| 5 | 26.90 |
Read Also: Are Stock Options Given to Google Employees Annually?
Let’s calculate the 3-day moving average for the closing prices:
The first entry in the Moving Average column will be 27.07. To calculate the moving average for subsequent days, you will repeat the steps above by shifting the period forward and including the next data point.
By calculating the moving average, you can reduce the impact of random fluctuations and obtain a trend line that reflects the overall direction of the data. This can be useful in identifying potential support and resistance levels, as well as momentum indicators in financial markets.
There are several benefits to using the Moving Average (MA) as a technical analysis tool. Here are some key advantages:
Overall, the Moving Average MA is a versatile tool that can assist traders and analysts in understanding and navigating the price action of various financial instruments. Its ability to smooth out data, identify trends, and generate entry/exit signals makes it a valuable component of any technical analysis toolbox.
A moving average is a commonly used statistical calculation that helps smooth out fluctuations in data over a certain time period. It is calculated by averaging a set of values over that time period, and as new data becomes available, the oldest value is dropped and the newest value is added to the calculation.
The moving average equation is calculated by summing up a set of values over a specific time period and then dividing that sum by the number of values in that set. This gives the average value for that time period. As new values are added, the oldest value is subtracted from the sum and the newest value is added, resulting in the updated moving average value.
The purpose of using a moving average is to smooth out data and identify trends or patterns. It helps to filter out short-term fluctuations or noise in the data, making it easier to see the overall direction or behavior of the data over time.
Sure! Let’s say we have a set of data for the average daily temperature over a 7-day period: 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14. To calculate the moving average for this period, we add up these values (8 + 9 + 10 + 11 + 12 + 13 + 14 = 77) and divide by the number of days (7). So the moving average for this period would be 77/7 = 11.
The main difference between a simple moving average (SMA) and an exponential moving average (EMA) is how the weights of the data are assigned. In SMA, each data point has equal weight, while in EMA, more weight is given to recent data points. This means that EMA responds more quickly to changes in the data, but it can also be more sensitive to short-term fluctuations.
The moving average MA is a commonly used technical analysis indicator that helps identify trends in financial markets. It is calculated by taking the average value of a set of data points over a specified period of time.
The moving average MA is calculated by summing up a set of data points over a specified period of time and then dividing the sum by the number of data points. This provides an average value that represents the trend over that period of time.
Understanding Schedule D UK: A Comprehensive Guide When it comes to running a business in the United Kingdom, understanding the tax reporting …
Read ArticleIs options trading real or fake? Options trading is a financial strategy that has been gaining popularity in recent years, but it has also become the …
Read ArticleCan You Trade Binary Options on Forex? Forex trading and binary options are both popular methods for individuals to profit from the financial markets. …
Read ArticleUnderstanding VaR: Value at Risk Explained When it comes to managing risk, one concept stands out as a crucial tool for financial institutions and …
Read ArticleForeign Currency Exchange Options at Cape Town Airport If you’re traveling to Cape Town in 2022, one of the things you’ll need to consider is how to …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Most Effective Stock Price Action Strategies Understanding and analyzing the price action of stocks is crucial for successful …
Read Article