The future of WDC stock: expert analysis and predictions
The Future of WDC Stock: Expert Predictions and Analysis In recent years, Western Digital Corporation (WDC) has become one of the leading players in …
Read Article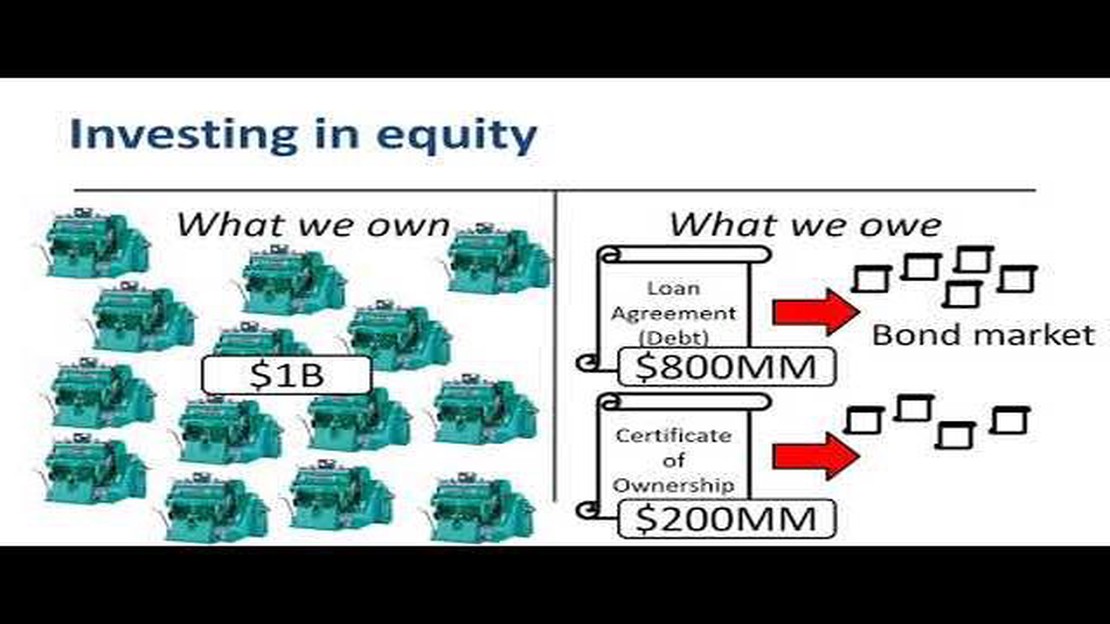
In the world of finance, two terms that often get used interchangeably are “equity” and “F&”. However, these two concepts have distinct meanings and play different roles in the financial industry. It is important for investors and individuals to understand the difference between equity and F& in order to make informed financial decisions.
Equity, also known as “stock” or “shares”, represents ownership in a company. When an individual purchases equity in a company, they become a shareholder and have a stake in the company’s assets and profits. The value of equity can fluctuate based on various factors such as market conditions, company performance, and investor sentiment.
F&, on the other hand, stands for “fixed income and derivatives”. F& is a broader category that includes a range of financial instruments such as bonds, options, and futures contracts. Unlike equity, F& instruments provide investors with fixed returns or payments over a specific period of time. These instruments are often considered less risky than equity as they have a predetermined payout.
In summary, equity represents ownership in a company and its value is dependent on market conditions and company performance. F&, on the other hand, includes fixed income and derivative instruments that provide investors with fixed returns or payments. Each has its own risk and return profile, and understanding the distinction between equity and F& is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
“Equity and F& are two important concepts in finance that are often misunderstood. By understanding the difference between the two, investors can better diversify their portfolios and manage their risk.”
Equity and futures/options are two different types of financial instruments that are commonly used in investing and trading. While both can be used to generate profits, they have several key differences that make them unique.
Definition: Equity refers to ownership in a company, represented by shares of stock. When you own equity, you have a claim on the assets and earnings of the company.
Futures: Futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell a specific asset or commodity at a predetermined price on a specified future date. These contracts are standardized and traded on exchanges. Futures trading allows investors to speculate on the price movement of the underlying asset without actually owning it.
Options: Options contracts give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an asset at a predetermined price within a specified timeframe. Unlike futures contracts, options trading gives investors the choice to exercise or not exercise the contract.
Leverage: One of the key differences between equity and futures/options is the use of leverage. In futures/options trading, investors can control a larger position with a smaller initial investment, thanks to leverage. This can amplify both profits and losses. Equity trading, on the other hand, typically does not involve leverage.
Risk and Returns: Equity investments have the potential for both capital gains (increase in stock price) and dividends (share of company earnings). However, the value of equity can fluctuate significantly in the short term, potentially resulting in losses. Futures and options also involve risk, but the potential returns can be much higher, especially when leverage is used.
Read Also: Examples of Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) Systems
Liquidity: Equity markets tend to have higher liquidity compared to futures and options markets. This means that it is generally easier to buy and sell shares of stock compared to trading futures or options contracts.
Timeframe: Equity investments are typically considered long-term investments, as investors buy shares of stock with the expectation of holding them for a sustained period of time. Futures and options trading, on the other hand, can be short-term or even day trading strategies since these contracts have expiration dates.
Regulation: Equity markets are regulated by government authorities, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States. Futures and options markets are also regulated, primarily by exchanges and self-regulatory organizations, such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC).
Conclusion: While equity and futures/options are both important tools for investors and traders, they have distinct differences. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed investment decisions and managing the associated risks.
Read Also: How Much Can I Make Per Day in Forex? Find Out Now!
Equity trading is the buying and selling of shares or stocks in publicly traded companies. Equity refers to an ownership interest in a company, and equity trading allows individuals and institutions to buy and sell these ownership stakes on various stock exchanges. This type of trading represents a key component of the financial markets and plays a crucial role in the global economy.
Equity trading involves the purchase and sale of shares through exchanges or over-the-counter markets. Shares, also known as stocks, represent a fraction of ownership in a company. When individuals or institutions buy shares, they become shareholders and have certain rights, such as voting rights and a share in the company’s profits. Equity trading gives investors the opportunity to speculate on the future performance of a company and potentially earn returns on their investments.
Equity trading can take different forms, such as day trading, swing trading, and long-term investing. Day trading involves buying and selling shares within a single trading day to take advantage of short-term price movements. Swing trading involves holding shares for a few days or weeks to capture larger price swings. Long-term investing, on the other hand, involves holding shares for an extended period, often years, with the goal of capital appreciation and dividend income.
Equity traders use various strategies to make informed investment decisions. They may rely on fundamental analysis, which involves evaluating a company’s financial health, profitability, and growth potential. Technical analysis, on the other hand, involves studying historical price and volume data to predict future price movements. Traders also consider market trends, news, and other factors that can impact the value of a company’s shares.
Equity trading carries risks, as the value of shares can fluctuate due to factors such as market conditions, economic events, and company-specific news. Traders need to carefully manage their risk through strategies like stop-loss orders and diversification. It is also important for equity traders to stay updated with relevant information and continuously monitor their investments to make informed decisions.
In conclusion, understanding equity trading is essential for investors looking to participate in the financial markets and potentially generate returns. This form of trading involves buying and selling shares of publicly traded companies, and traders use various strategies to make informed investment decisions. With careful risk management and continuous monitoring, equity trading can provide opportunities for individuals and institutions to grow their wealth over time.
Equity trading involves buying and selling shares of individual companies, while F&O trading involves trading in derivatives such as futures and options contracts.
Equity trading involves buying and selling shares of individual companies on stock exchanges. Investors can make profits by buying low and selling high or by receiving dividends from the companies they own shares in.
Futures and options contracts are financial instruments that derive their value from an underlying asset. In the case of futures contracts, the buyer agrees to purchase an asset at a predetermined price and date in the future. Options contracts give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price within a specified period of time.
F&O trading is generally considered to be riskier than equity trading. This is because derivatives such as futures and options contracts can magnify both potential profits and losses. The leverage involved in F&O trading can lead to significant gains or losses in a short period of time.
The Future of WDC Stock: Expert Predictions and Analysis In recent years, Western Digital Corporation (WDC) has become one of the leading players in …
Read ArticleCommBank Foreign Exchange Fees: What You Need to Know Foreign exchange fees can be a significant cost when travelling abroad or making international …
Read ArticleBest Time Frames for Scalpers Scalping is a popular trading strategy used by many traders in the Forex and stock markets. It involves taking advantage …
Read ArticleWhat is futures and options trading? Welcome to our beginner’s guide to futures and options trading! Whether you’re new to the world of investing or …
Read ArticleCall of Duty Black Advanced Warfare System Requirements Call of Duty: Black Advanced Warfare is the latest installment in the hugely popular Call of …
Read ArticleForex Chart Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide Forex chart analysis is an essential skill for anyone interested in trading currencies. In today’s …
Read Article