Is CCI a Trustworthy Indicator? Discover Its Impact on Trading
Should You Use the CCI Indicator in Your Trading Strategy? When it comes to trading, having reliable technical indicators is crucial for making …
Read Article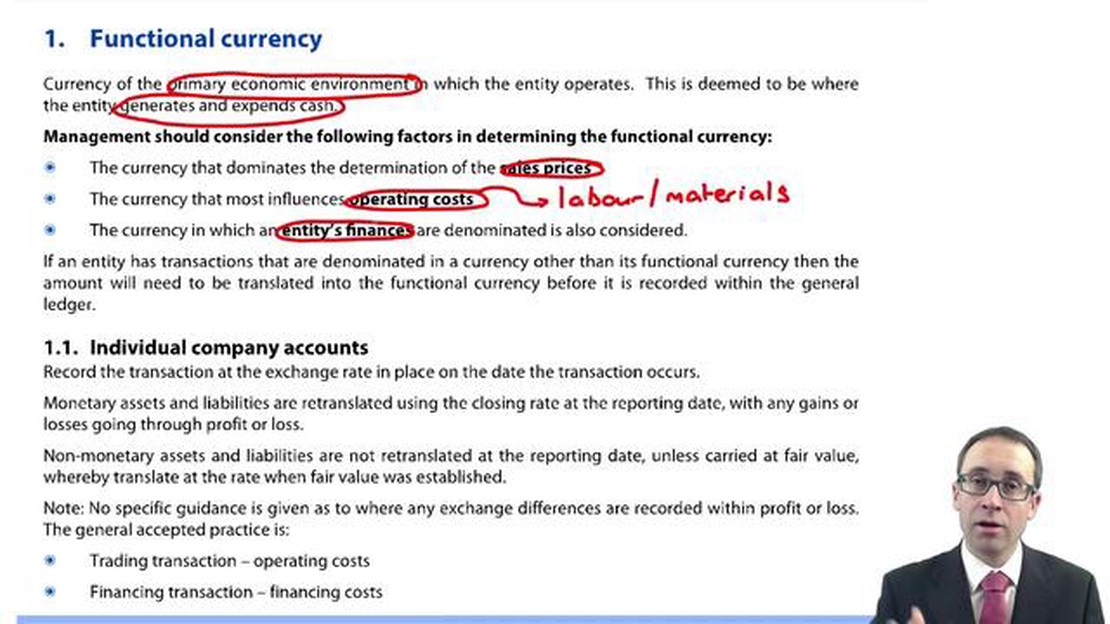
When operating in a global business environment, it is crucial to understand the distinction between functional currency and foreign currency. These terms refer to the different ways in which companies measure and report their financial transactions and results.
The functional currency is the currency of the primary economic environment in which the company operates and generates cash flows. It is the currency that best represents the economic substance of the company’s operations. On the other hand, foreign currency refers to any currency other than the functional currency and is commonly used in international transactions.
The distinction between functional currency and foreign currency is important for several reasons. First, it determines how transactions denominated in foreign currency are recorded and reported in the company’s financial statements. The choice of the functional currency also impacts the translation of foreign currency financial statements into the functional currency for consolidation purposes.
Additionally, understanding the distinction between functional currency and foreign currency is crucial for assessing the risk associated with foreign currency fluctuations. Companies with high exposure to foreign currency fluctuations may use various hedging strategies to manage this risk effectively. Without a clear understanding of the functional currency and foreign currency, companies may fail to accurately assess and mitigate their currency risk exposures.
In conclusion, understanding the distinction between functional currency and foreign currency is essential for multinational companies operating in a global business environment. It affects how transactions are reported, financial statements are consolidated, and currency risks are managed. By accurately identifying the functional currency and effectively managing foreign currency exposures, companies can enhance their financial reporting and mitigate potential risks.
The distinction between functional currency and foreign currency is of utmost importance in financial accounting and reporting. It plays a vital role in determining how transactions should be recorded and reported, as well as the impact of foreign exchange fluctuations on financial statements.
Functional currency is the primary currency used by an entity for its day-to-day operations and financial reporting. It reflects the economic environment in which the entity operates and generates cash flows. The functional currency is determined based on a combination of factors, including the currency of the country in which the entity is located, the currency in which the entity primarily generates revenue and incurs costs, and the currency in which the entity typically settles its liabilities.
On the other hand, foreign currency refers to any currency other than the functional currency. It includes currencies in which financial transactions are denominated, such as sales in foreign currencies, purchases from foreign suppliers, or borrowing and lending in foreign currencies. Foreign exchange differences arise when translating these foreign currency transactions into the functional currency at the exchange rate prevailing at the transaction date or reporting date.
It is crucial to differentiate between the two currencies because the accounting treatment for transactions and foreign exchange differences varies depending on whether they are in the functional currency or a foreign currency. Revenue, expenses, assets, and liabilities denominated in the functional currency are usually recognized at the exchange rate prevailing at the transaction date or reporting date.
On the other hand, transactions denominated in a foreign currency are usually remeasured into the functional currency using the exchange rate prevailing at the transaction date, and any subsequent changes in the exchange rate are recognized as foreign exchange gains or losses in the income statement. These gains or losses can have a significant impact on the financial performance and position of the entity.
Read Also: Current Gold and Silver Trading Prices Today
The distinction between functional currency and foreign currency is particularly relevant for entities operating in multiple countries or engaging in international transactions. It ensures that financial statements accurately reflect the underlying economic substance of the transactions and the financial position of the entity, despite the impact of foreign exchange fluctuations.
In conclusion, understanding the distinction between functional currency and foreign currency is essential for proper financial accounting and reporting. It enables businesses to accurately record transactions, properly report their financial performance, and assess the impact of foreign exchange fluctuations on their financial position.
Read Also: Automating Trading with Zerodha: Everything You Need to Know
When determining the functional currency of an entity, there are several factors that need to be considered. These factors include:
It is important to carefully evaluate each of these factors in order to determine the most appropriate functional currency for an entity. The choice of functional currency can have significant impacts on an entity’s financial statements, performance analysis, and management decisions.
Functional currency refers to the primary currency in which a company conducts its business and keeps its financial records. Foreign currency, on the other hand, refers to any other currency used by the company in its transactions outside of its functional currency.
The determination of functional currency is based on the primary economic environment in which the company operates. Factors considered include the currency of the country in which the company operates, the currency used for sales and purchases, and the currency in which financing and cash flows are generated.
Having multiple functional currencies can complicate a company’s financial reporting and accounting processes. It would require the company to convert financial statements from one currency to another, which can involve exchange rate fluctuations and potential foreign exchange gains or losses.
Transactions in foreign currency are generally recorded using the exchange rate at the date of the transaction. Any resulting gains or losses from exchange rate fluctuations are recognized in the company’s financial statements.
Yes, a company can change its functional currency if there has been a significant change in the primary economic environment in which it operates. However, such a change would require a thorough analysis and approval by relevant accounting authorities.
In accounting, functional currency refers to the primary currency in which a company operates and makes transactions. It is the currency that reflects the economic substance of the company’s operations. On the other hand, foreign currency is any currency other than the functional currency. It is the currency in which a transaction is denominated when it is not in the functional currency.
The determination of functional currency depends on various factors such as the primary economic environment in which the company operates, the currency of the country whose economic environment it primarily operates within, the currency in which the company generates and expends cash, and the currency that influences sales prices. It requires judgment and analysis of the specific circumstances of the entity.
Should You Use the CCI Indicator in Your Trading Strategy? When it comes to trading, having reliable technical indicators is crucial for making …
Read ArticleShort Selling Options: An Example Short selling is a strategy used by investors to profit from a decline in the price of an asset. It involves …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Difference Between ATS and Dark Pools Alternative Trading Systems (ATS) and Dark Pools are two popular options for traders looking …
Read ArticleIs DIRECTV Traded on the Stock Exchange? If you’re interested in investing in DIRECTV, you might be wondering if it’s traded on the stock exchange. …
Read ArticleTips to Avoid Slippage in Forex Trading Forex trading can be a highly profitable venture, but it also comes with its challenges. One of the biggest …
Read ArticleWhat is forex economic analysis? Forex economic analysis plays a crucial role in the financial markets as it provides traders and investors with …
Read Article