Steps to Open a Professional Forex Account: A Comprehensive Guide
How to Open a Professional Forex Account Are you interested in expanding your investment portfolio and exploring new financial opportunities? Opening …
Read Article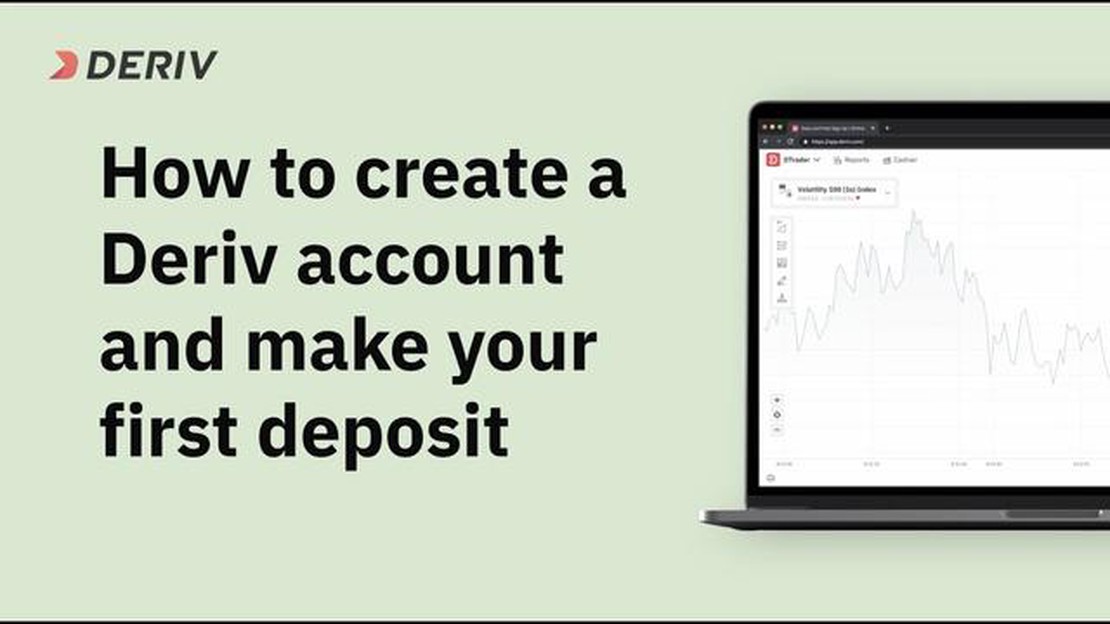
Sending and receiving emails is an essential part of our daily lives, both professionally and personally. However, understanding the various email formats can be confusing. One such format is the Deriv email format, which has gained popularity in recent years. In this article, we will delve into the Deriv email format, its purpose, and how it differs from other formats.
The Deriv email format is a standardized way of structuring and presenting email content. It is designed to improve the readability and organization of emails, making it easier for recipients to understand the message. The format includes specific guidelines for the layout, headings, paragraphs, and quoting of text within an email.
One of the key features of the Deriv email format is the use of tags to highlight important content. The strong tag is used to emphasize text, while the em tag is used for emphasis with additional importance. These tags help to draw attention to specific points and ensure that the recipient does not miss crucial information.
Another notable aspect of the Deriv email format is the use of the
blockquote
tag for quoting previous messages. This tag allows for clear differentiation between the quoted text and the sender’s response, making it easier to follow the conversation and maintain context. Additionally, the format recommends the use of paragraphs and headings to organize the content and make it more scannable.
The Deriv email format is designed to provide a clear and concise structure for email communication. By understanding the different components of the format, you can better comprehend the information conveyed in Deriv emails.
Here is a breakdown of the Deriv email format:
By understanding the different components of the Deriv email format, you can effectively communicate and interpret information in Deriv emails. Following this format can help ensure that your emails are well-structured and properly convey your message.
The Deriv email format is a standardized structure that defines how emails from Deriv are organized and presented. It ensures consistency in the layout and content of all email communications sent by Deriv to its clients.
Emails from Deriv follow a specific format to effectively convey important information and instructions to recipients. This format includes various elements, such as the email header, subject line, body content, and signature.
Email Header:
The email header contains details about the sender and recipient, such as the email addresses, date and time of the email, and the subject line. It provides basic information about the email and helps the recipient identify the sender and subject matter at a glance.
Subject Line:
The subject line of a Deriv email is brief yet informative. It summarizes the purpose or topic of the email in a concise manner, allowing recipients to quickly understand the content and prioritize their inbox management.
Body Content:
Read Also: Understanding the Three Drug Delivery Systems: A Comprehensive Guide
The body of a Deriv email contains the main message or information being conveyed. It is structured with paragraphs and often includes headings, bullet points, or numbered lists for better readability. The content may include important updates, account information, announcements, promotional offers, or any other relevant information for the recipient.
Signature:
Read Also: Exploring the Bearish and Bullish Signals of the Dark Cloud Cover Candlestick Pattern
Deriv emails typically conclude with a signature that includes the sender’s name, position, company information, and contact details. This allows recipients to easily identify the sender and establish communication if necessary.
Adhering to the Deriv email format ensures that important emails are easily recognizable, highly readable, and convey the necessary information effectively. It enhances communication between Deriv and its clients by providing a consistent and professional email experience.
The Deriv email format follows a specific structure that consists of several key components. These components are crucial in ensuring that the email is correctly interpreted and displayed by various email clients and devices.
 4. Call to Action (CTA): The call to action is a specific instruction or request made by the sender to the recipient. It can be in the form of a clickable button, hyperlink, or a simple text-based link. The CTA serves as a direct prompt for the recipient to take a desired action, such as making a purchase, subscribing to a service, or providing feedback.
5. Signature: The email signature provides the sender’s contact information, including their name, job title, company, phone number, and website. It serves as a professional sign-off and helps the recipient identify the sender’s identity and affiliation. Including a signature is a common practice for formal or business-related emails.
6. Images and Attachments: Emails often include images and attachments to supplement the text content. Images can be in the form of logos, banners, or product images, while attachments can include documents, spreadsheets, or PDF files. It is important to optimize images for email display and ensure that attachments are relevant and appropriately sized.
7. Email Footer: The email footer usually contains legal disclaimers, unsubscribe links, and other regulatory information, if applicable. It is placed at the bottom of the email and helps ensure compliance with email marketing regulations and provide recipients with options to manage their email preferences.
4. Call to Action (CTA): The call to action is a specific instruction or request made by the sender to the recipient. It can be in the form of a clickable button, hyperlink, or a simple text-based link. The CTA serves as a direct prompt for the recipient to take a desired action, such as making a purchase, subscribing to a service, or providing feedback.
5. Signature: The email signature provides the sender’s contact information, including their name, job title, company, phone number, and website. It serves as a professional sign-off and helps the recipient identify the sender’s identity and affiliation. Including a signature is a common practice for formal or business-related emails.
6. Images and Attachments: Emails often include images and attachments to supplement the text content. Images can be in the form of logos, banners, or product images, while attachments can include documents, spreadsheets, or PDF files. It is important to optimize images for email display and ensure that attachments are relevant and appropriately sized.
7. Email Footer: The email footer usually contains legal disclaimers, unsubscribe links, and other regulatory information, if applicable. It is placed at the bottom of the email and helps ensure compliance with email marketing regulations and provide recipients with options to manage their email preferences.
By understanding and incorporating these key components into the Deriv email format, senders can create effective and visually appealing emails that engage recipients and achieve their desired objectives.
To understand the Deriv Email format, you need to familiarize yourself with the different elements and sections of the email. It typically includes a subject line, sender information, recipient information, body content, and attachments. By understanding the structure and purpose of each section, you can effectively interpret and respond to Deriv Emails.
If you receive a Deriv Email with attachments, you should carefully review the content of the email and the purpose of the attachments. If the attachments are relevant to your responsibilities or tasks, you can open and download them. However, if you are unsure about the legitimacy or safety of the attachments, it is advisable to consult with your IT department or supervisor before taking any action.
The subject line of a Deriv Email is crucial as it provides a concise summary of the email’s content and purpose. It helps the recipient prioritize and understand the email’s significance without having to open and read the entire message. A clear and descriptive subject line facilitates effective email management and ensures that important emails receive proper attention.
The sender information in a Deriv Email consists of the name, email address, and any additional contact details of the sender. It is important to verify the authenticity of the sender before taking any action or responding to the email. If you are unfamiliar with the sender or suspicious of the email’s content, it is recommended to exercise caution and consult with your IT department or supervisor.
How to Open a Professional Forex Account Are you interested in expanding your investment portfolio and exploring new financial opportunities? Opening …
Read ArticleWhy is Forex haram in Islam? In Islam, the concept of halal (permissible) and haram (prohibited) plays a significant role in guiding the daily lives …
Read ArticleRSUs at Twitter: A Comprehensive Guide to How They Work RSUs, or Restricted Stock Units, are a popular form of equity compensation used by many tech …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the W Pattern Strategy: A Comprehensive Guide When it comes to trading and investing, having a well-defined strategy is crucial for …
Read ArticleThe Role of Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market, is the largest financial market …
Read ArticleGuide on Using Bollinger Bands for Trading When it comes to technical analysis in the world of trading, Bollinger Bands are a popular tool used by …
Read Article