What is the full form of EOD in share market? - Explanation and Definition
What is the full form of EOD in share market? EOD stands for End of Day in the share market. It is a term used to denote the closing time of trading …
Read Article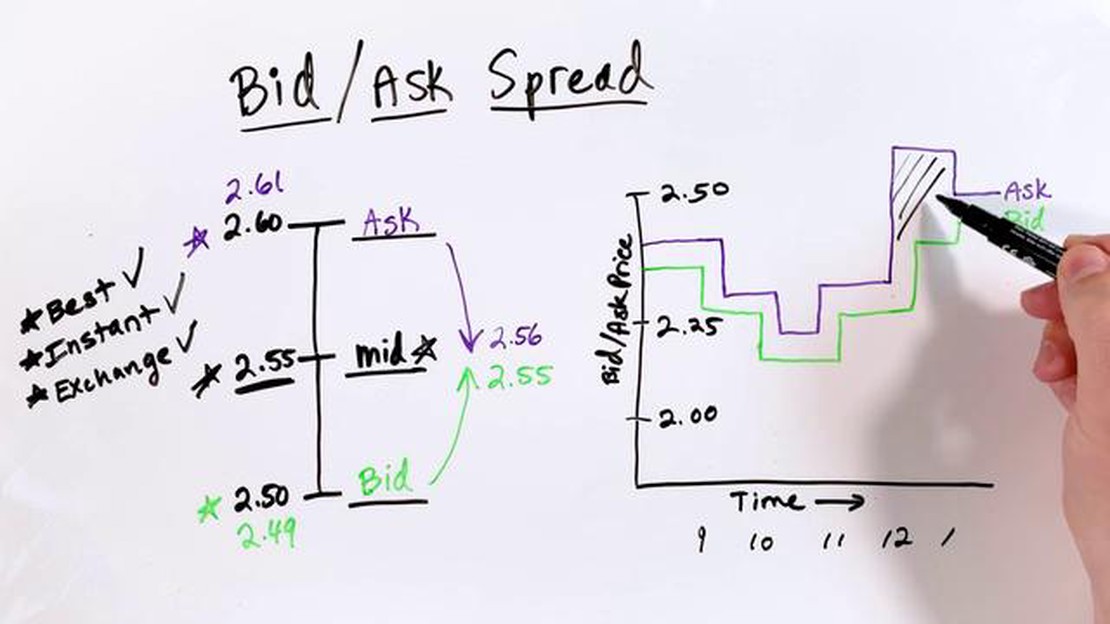
Option trading is a complex and dynamic market where investors can speculate on the future movement of an underlying asset. When trading options, it’s essential to understand key concepts like the bid-ask spread.
The bid-ask spread is the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay (bid) and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept (ask). This spread represents the market’s liquidity and the cost of executing a trade. Understanding the bid-ask spread is crucial for option traders as it affects their potential profits and risks.
Option traders need to consider both the bid and the ask prices when entering or exiting a trade. The bid is the price at which a trader can sell an option, while the ask is the price at which a trader can buy an option. The bid-ask spread reflects the market’s supply and demand dynamics, with tighter spreads indicating a more liquid market.
It’s important to note that the bid-ask spread can vary significantly based on various factors such as market conditions, option liquidity, and the underlying asset’s volatility. Traders should always be aware of the bid-ask spread and aim to minimize the impact of this cost when executing their option strategies.
The bid-ask spread refers to the difference between the highest price that a market maker is willing to pay to buy a security and the lowest price at which they are willing to sell it. In the context of option trading, the bid-ask spread represents the difference between the highest price that a buyer is willing to pay for an option contract and the lowest price at which a seller is willing to sell it.
The bid price is the maximum amount that a buyer is willing to pay for an option, while the ask price is the minimum amount that a seller is willing to accept for the same option. The bid-ask spread is influenced by factors such as the market demand for the option, the liquidity of the underlying security, and the overall level of market volatility.
When placing a trade, it is important to consider the bid-ask spread as it directly affects the cost of entering or exiting a position. A wider bid-ask spread indicates lower liquidity and may result in higher transaction costs. Traders should aim to minimize the impact of the bid-ask spread on their trades to maximize potential profits.
It is worth noting that bid and ask prices can change rapidly, especially in highly volatile markets, as market conditions and investor sentiment can impact the supply and demand for options. As a result, bid-ask spreads may fluctuate throughout the trading day.
Read Also: Understanding GM Employee Stock Options: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding bid-ask spreads is crucial for option traders as it enables them to make informed decisions when entering or exiting positions. By monitoring bid and ask prices, traders can assess the liquidity and competitiveness of the market, ensuring that they receive fair prices for their trades.
In conclusion, the bid-ask spread represents the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept for an option contract. Traders should be aware of bid-ask spreads and consider them when placing trades to minimize transaction costs and maximize potential profits.
The bid-ask spread is a key concept in option trading that plays a crucial role in determining the cost of executing trades and the profitability of options strategies. It refers to the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay (bid price) and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept (ask price) for an option contract.
The bid-ask spread is significant because it represents the transaction cost of buying or selling options. The wider the spread, the higher the cost of executing trades. This can reduce potential profits for traders and investors. On the other hand, a narrower spread allows for more efficient trading and potentially higher returns.
The bid-ask spread is influenced by various factors, including the liquidity of the options market, market volatility, and the supply and demand dynamics for specific option contracts. When options are highly liquid and actively traded, the bid-ask spread tends to be tighter, as there is more competition between buyers and sellers. Conversely, illiquid options tend to have wider spreads, making it more expensive to trade them.
Traders need to be aware of the bid-ask spread and consider it when making trading decisions. For example, if a trader wants to buy an option, they will typically have to pay the ask price, which is higher than the bid price. Conversely, if they want to sell an option, they will likely receive the bid price, which is lower than the ask price. This difference in prices can result in immediate losses or gains when entering or exiting positions.
Furthermore, the bid-ask spread can impact the profitability of certain options strategies, such as spread trades or straddles. These strategies involve simultaneously buying and selling different options contracts to profit from price movements or changes in volatility. A wider bid-ask spread can reduce the potential profitability of these strategies, as the cost of entering and exiting positions is higher.
In conclusion, understanding the bid-ask spread is essential for option traders, as it directly affects trading costs, potential profits, and the efficiency of options strategies. By carefully considering the bid-ask spread, traders can make more informed decisions and optimize their trading outcomes.
Read Also: Discover the Benefits of MTN Investment: All You Need to Know
The bid-ask spread in option trading refers to the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay for an option (the bid price) and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept for the option (the ask price). It represents the cost of executing a trade and is influenced by factors such as supply and demand, market liquidity, and the option’s strike price and expiration date.
The bid-ask spread is important for option traders because it directly affects the cost of executing trades. A wider spread means higher transaction costs and may make it more difficult for traders to buy or sell options at favorable prices. Understanding the spread is crucial for determining the profitability of a trade and effectively managing risk.
Several factors can cause the bid-ask spread to widen. These include low trading volume in the options market, decreased market liquidity, higher volatility in the underlying asset, larger trade sizes, and wider price fluctuations. Additionally, options with higher strike prices and those with longer expiration dates tend to have wider spreads.
Option traders can minimize the impact of bid-ask spreads by using limit orders instead of market orders. By setting a limit on the price they are willing to pay or accept for an option, traders can potentially get better prices and reduce transaction costs. Additionally, traders can opt for options with narrower spreads, trade during periods of higher liquidity, and consider executing spreads or strategies that involve multiple options.
No, the bid-ask spread cannot be completely eliminated in option trading. The spread is inherent to the market and reflects the difference between buyers’ and sellers’ price expectations. However, traders can work to minimize the impact of the spread by employing trading strategies that aim to capture favorable price movements, using limit orders, and staying informed about market conditions that can influence the spread.
The bid-ask spread is the difference between the highest price that a buyer is willing to pay for an option (the bid price) and the lowest price that a seller is willing to accept for the option (the ask price).
What is the full form of EOD in share market? EOD stands for End of Day in the share market. It is a term used to denote the closing time of trading …
Read ArticleWhy is MDT stock so low? Medtronic PLC (MDT) is a global healthcare solutions company that manufactures and markets medical devices and technologies …
Read ArticleReasons for Low Day Trading Buying Power Day trading can be an exciting and potentially profitable venture, but it also comes with its fair share of …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Moving Average Standard Deviation The moving average standard deviation is a statistical measure that is commonly used in financial …
Read ArticleHow to Create a Machine Learning Model for Trading Machine learning has revolutionized the way we approach trading in financial markets. By harnessing …
Read ArticleAre Pivot Points accurate for trading? When it comes to trading, there are many indicators and tools that traders use to forecast market movements and …
Read Article