Forex Market Open Hours Today in India: Find the Exact Time to Trade
Forex Market Open Hours in India Today When it comes to trading in the foreign exchange market, it is crucial to know the exact hours when the market …
Read Article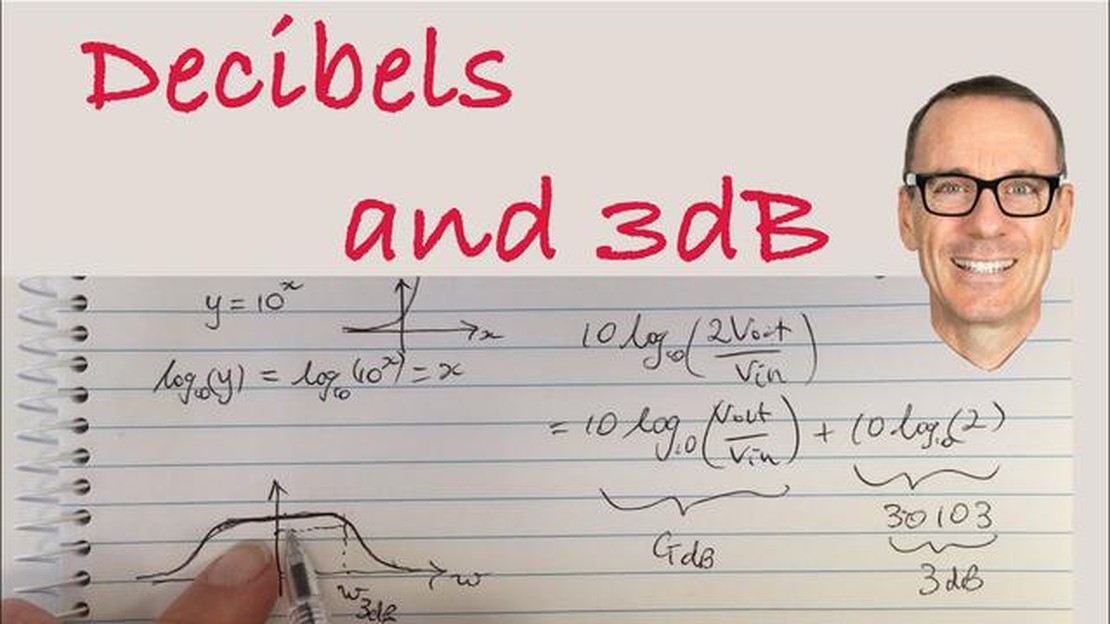
Filters are essential components in electronic circuits that allow certain frequencies to pass through while attenuating or blocking others. To fully understand the behavior of a filter, it is important to grasp the concept of the 3dB frequency.
The 3dB frequency, also known as the cutoff frequency, is a crucial parameter that indicates the point at which the output power of a filter is reduced by half (-3dB) compared to the input power. In other words, it represents the frequency at which the filter starts to significantly attenuate the signal it is designed to process.
Understanding the 3dB frequency of a filter is of utmost importance, as it determines the bandwidth and performance of the filter. Filters with low 3dB frequencies allow a wide range of frequencies to pass through, providing a larger bandwidth. On the other hand, filters with high 3dB frequencies have narrower bandwidths, allowing only a select few frequencies to pass through.
Furthermore, the 3dB frequency is used to classify filters into different types, such as low-pass, high-pass, band-pass, and band-stop filters. It serves as a reference point to distinguish between the frequencies that a filter allows to pass through and those that it attenuates or blocks.
For engineers and designers working with filters, understanding the 3dB frequency is essential for selecting the right filter for a specific application. By knowing the cutoff frequency, they can determine the filter’s suitability for a particular range of frequencies and ensure optimal performance in their designs.
In conclusion, the 3dB frequency plays a critical role in the functionality and design of filters. It determines the point at which a filter begins to attenuate or block certain frequencies, affecting its bandwidth and classification. Adequate knowledge of the 3dB frequency allows engineers to make informed decisions about filter selection, leading to improved performance and efficiency in electronic circuits.
The 3dB frequency, also known as the cutoff frequency or the half-power frequency, is a crucial parameter in the field of signal processing and filter design. It refers to the frequency at which a filter’s response drops to half (-3dB) of its maximum or peak value.
In other words, the 3dB frequency determines the range of frequencies that a filter allows to pass through with minimal attenuation or loss. It is an indicator of the filter’s performance and its ability to pass or block certain frequencies.
This frequency is important because it serves as a reference point for understanding the behavior and characteristics of a filter. It helps engineers and researchers analyze and design filters for various applications such as audio signal processing, image processing, and communication systems.
Read Also: Is Repaint Indicator Good? Learn the Pros and Cons
The 3dB frequency is often used to define the bandwidth of a filter, which is the range of frequencies where the filter’s response is within a certain tolerance level. For example, a low-pass filter with a 3dB frequency of 10kHz may have a bandwidth from 0Hz to 10kHz, indicating that it allows frequencies below 10kHz to pass through with minimal attenuation.
Furthermore, the 3dB frequency is also significant in terms of system stability and distortion. It helps to determine the stability of a control system by examining the gain margin and phase margin at this frequency. It also affects the distortion characteristics of audio signals, as certain frequencies near the 3dB frequency may experience phase shifts and alterations in their amplitude due to the filter’s response.
Overall, understanding the 3dB frequency and its importance in filter design and signal processing allows engineers and researchers to optimize system performance, improve signal integrity, and achieve desired filtering characteristics.
The 3dB frequency is an important parameter in filter design and analysis. It is the frequency at which the filter’s output power is reduced by half (or the voltage gain is reduced by 3 decibels) compared to its maximum value. Here are a few reasons why the 3dB frequency is important:
Read Also: Understanding the Distinction between XOF and CFA: Key Differences Explained
In summary, the 3dB frequency is a key parameter for understanding the performance and characteristics of a filter. It defines the usable bandwidth, affects signal distortion, influences filter stability, and may correspond to the cutoff frequency. Engineers and designers rely on the 3dB frequency to optimize filter performance and ensure the desired response for their applications.
The 3dB frequency is an important parameter that is used in various applications in the field of electronics and signal processing. Here are some common applications where the 3dB frequency plays a crucial role:
These are just a few examples of the many applications where the 3dB frequency is utilized. Understanding the 3dB frequency is crucial for engineers and researchers working in the fields of electronics, telecommunications, and signal processing, as it allows for the efficient design and optimization of various systems and devices.
The 3dB frequency of a filter is the point at which the filter’s output power has been reduced by 3dB (half) compared to its maximum or reference power level.
The 3dB frequency is important in filter design because it specifies the frequency at which the filter starts to attenuate the signal. It gives an indication of the filter’s bandwidth and determines the range of frequencies that the filter can effectively pass or reject.
The 3dB frequency is calculated by finding the frequency at which the filter’s gain or amplitude response is -3dB compared to its maximum or reference level. This can be determined from the filter’s transfer function or frequency response plot.
A higher 3dB frequency indicates that the filter has a wider bandwidth and can pass a larger range of frequencies. Conversely, a lower 3dB frequency means that the filter has a narrower bandwidth and can only pass a smaller range of frequencies. The choice of the 3dB frequency depends on the specific application and desired filter characteristics.
Yes, the 3dB frequency can be adjusted for a filter by modifying the filter’s design parameters, such as the values of the resistors, capacitors, or inductors. Changing these values will alter the filter’s frequency response, including the 3dB frequency.
Forex Market Open Hours in India Today When it comes to trading in the foreign exchange market, it is crucial to know the exact hours when the market …
Read ArticleCan Speculative Trading Be Profitable? Speculative trading, also known as speculative investing or trading, refers to the practice of buying and …
Read ArticleWhen does the forex market close? If you’re new to forex trading, one of the important things to understand is the trading hours of the forex market. …
Read ArticleForex Card Transaction Charges: How Much Do They Cost? If you are planning to travel abroad, you may be considering using a forex card to manage your …
Read ArticleUnderstanding relative value strategies in CFA Relative value strategies are an important tool for investors looking to capitalize on pricing …
Read ArticleIs Forex Trading Real or Fake? Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, has gained immense popularity in recent years. It is a …
Read Article