How to Change Your Name and Gender in CT: A Comprehensive Guide
Steps to Change Name and Gender in CT If you are considering changing your name or gender in the state of Connecticut, this comprehensive guide will …
Read Article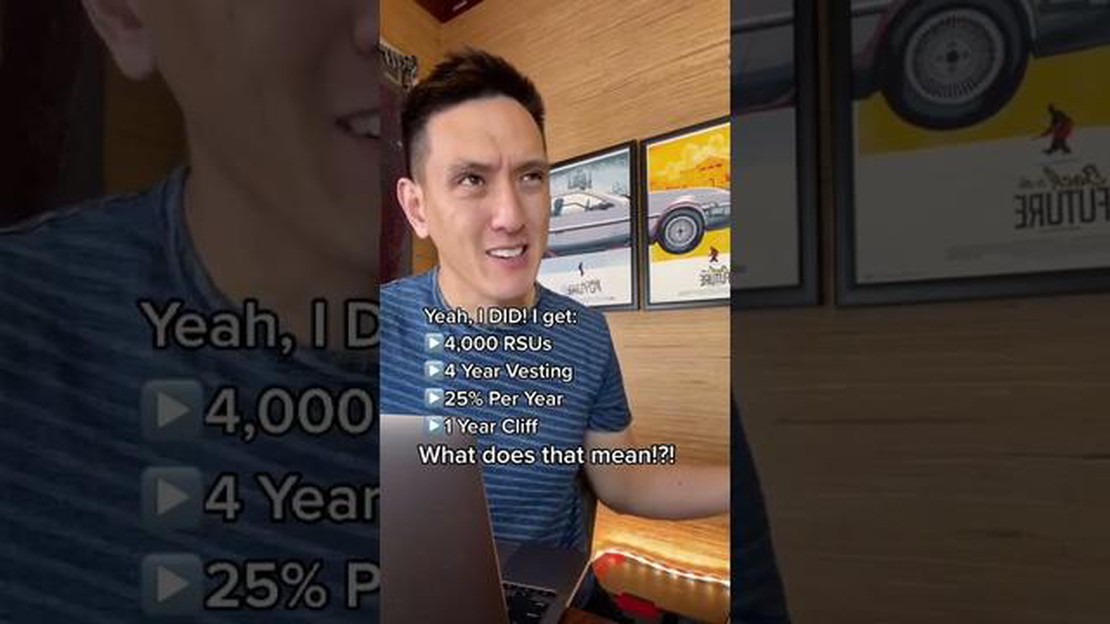
RSUs, or Restricted Stock Units, are a popular form of equity compensation used by many tech companies, including Twitter. RSUs are granted to employees as part of their compensation package, and they represent a promise to distribute company stock in the future. At Twitter, RSUs are an important part of the overall compensation strategy and are used to attract and retain top talent.
When an employee receives RSUs, they are given a specific number of units that will vest over a predetermined period of time. The vesting schedule typically ranges from three to five years, with a portion of the RSUs vesting each year. Once the RSUs have vested, the employee becomes the owner of the underlying company stock.
Tweeting news and insights about RSUs has become an integral part of Twitter’s culture, as many employees look forward to the potential financial gain associated with the vesting of their RSUs. Moreover, RSUs are often seen as an incentive for employees to stay with the company and align their interests with the long-term success of Twitter.
In conclusion, RSUs are a valuable form of compensation used at Twitter and other tech companies. By offering RSUs, Twitter can attract and retain talented employees who are motivated to contribute to the company’s growth and success. The vesting of RSUs not only provides financial incentives for employees but also promotes a sense of ownership and loyalty to the company.
In the context of employee compensation, Restricted Stock Units (RSUs) are a type of equity-based compensation that companies like Twitter use to reward and retain their employees. RSUs represent a promise to provide a certain number of company shares to employees at a future date.
RSUs are typically granted to employees as a part of their overall compensation package, alongside salary, bonuses, and other benefits. However, unlike traditional stock options, RSUs do not require the employee to purchase the shares at a certain price. Instead, RSUs are granted as a form of compensation and are typically subject to a vesting schedule.
A vesting schedule is a timeline that determines when an employee’s RSUs become fully owned and transferable. At Twitter, the typical vesting period for RSUs is four years, with a one-year cliff. This means that employees must remain with the company for one year before any of their RSUs vest. After the cliff, RSUs vest on a quarterly basis over the remaining three years.
Once RSUs are vested, employees have the option to either sell the shares at the current market price or hold on to them. If employees choose to hold on to the RSUs, they can potentially benefit from any future increase in the company’s stock price. However, it’s important to note that RSUs are subject to taxes upon vesting, and employees may be required to pay taxes based on the value of the vested RSUs at the time of vesting.
Overall, RSUs are a valuable tool for companies like Twitter to attract and retain talent. By granting employees RSUs, companies provide an opportunity for employees to have a stake in the company’s success and align their interests with those of the shareholders. Additionally, RSUs can serve as a long-term incentive for employees to stay with the company and contribute to its growth and profitability.
Read Also: Margin on NSE Options: Understanding the Basics and Calculating Margins
In conclusion, RSUs are an important part of employee compensation at Twitter and other companies in the tech industry. They provide employees with the potential to earn ownership in the company and benefit from its success. Understanding how RSUs work can help employees make informed decisions about their compensation and long-term financial goals.
RSUs, or Restricted Stock Units, are a form of equity compensation commonly used by companies to reward and incentivize employees. When employees are granted RSUs, they receive a promise of future shares of company stock, typically at no cost. However, these shares are subject to certain vesting requirements and restrictions.
The vesting period is the length of time an employee must wait before the RSUs fully “vest.” During this period, the employee does not have full ownership of the shares and cannot sell or transfer them. Typically, RSUs vest over a period of several years, with a certain percentage of shares becoming vested each year.
Once the RSUs have vested, employees can choose to sell or hold onto the shares. If they choose to sell, they will receive the market value of the shares at the time of sale. If they choose to hold onto the shares, they can potentially benefit from any future increase in the company’s stock price.
One important thing to note is that RSUs are different from stock options. With stock options, employees have the option to buy company stock at a specified price, whereas with RSUs, employees receive the stock directly. This means that employees do not have to come up with any money to exercise RSUs, unlike stock options.
RSUs can be a valuable employee benefit, as they provide a direct stake in the company’s success. The value of RSUs can fluctuate based on the performance of the company’s stock, which creates an incentive for employees to work hard and contribute to the company’s growth.
Read Also: What happens to options if a stock goes private? - Explained
Overall, understanding how RSUs work is essential for employees who receive this form of equity compensation. By understanding the vesting schedule and the potential benefits of holding onto RSUs, employees can make informed decisions about their financial future.
RSUs, or Restricted Stock Units, are a type of compensation offered by companies to their employees as a form of equity ownership. They represent a promise to deliver company stock at a future date, subject to certain conditions.
At Twitter, RSUs are granted to employees as part of their overall compensation package. These RSUs generally vest over a period of time, typically four years, and are subject to specific vesting conditions. Once the RSUs vest, employees receive shares of Twitter stock.
The vesting conditions for RSUs at Twitter may vary depending on the employee’s position and length of service. Generally, RSUs at Twitter vest over a four-year period, with 25% of the RSUs vesting after one year and the remaining RSUs vesting monthly over the next three years.
No, RSUs cannot be sold before they vest. The whole purpose of RSUs is to incentivize employees to stay with the company for a certain period of time. Once the RSUs vest, employees have the option to sell the shares or hold onto them.
RSUs are taxed as ordinary income at the time of vesting. This means that the value of the RSUs at the time they vest is added to the employee’s income for that year and subject to regular income tax rates. When the employee eventually sells the shares, any gains or losses will be taxed as capital gains.
RSUs, or Restricted Stock Units, are a form of compensation that companies use to reward their employees. RSUs represent a certain number of shares in the company’s stock, and are typically granted to employees as part of their overall compensation package. They work by vesting over a set period of time, usually several years. Once the RSUs vest, the employee can choose to sell the shares or continue holding them.
RSUs and stock options are both forms of equity compensation, but they differ in how they are structured. With RSUs, employees receive a certain number of shares outright, while stock options give employees the right to purchase a certain number of shares at a set price. RSUs have value even if the stock price does not increase, while stock options only have value if the stock price goes up.
Steps to Change Name and Gender in CT If you are considering changing your name or gender in the state of Connecticut, this comprehensive guide will …
Read ArticleIs Forex Automation a Possibility? Forex, the foreign exchange market, is known for its high volatility and potential for substantial profits. Traders …
Read ArticleAlternatives to eToro: Exploring Better Investment Platforms eToro is a popular online trading platform that allows users to trade various financial …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Meaning of a Tweezer Bottom in Technical Analysis Tweezer Bottom is a technical analysis pattern that can provide valuable insights …
Read ArticleCan Forex Really Make You Money? When it comes to making money, the forex market is often mentioned as one of the most lucrative. With trillions of …
Read ArticleA Guide to Trading NIFTY Options Trading in NIFTY options can be an exciting and potentially lucrative endeavor for beginners looking to enter the …
Read Article