7 Crucial Tips to Understand Before Starting Affiliate Marketing
7 Things to Know Before Starting Affiliate Marketing Affiliate marketing has become one of the most popular ways to earn passive income online. It …
Read Article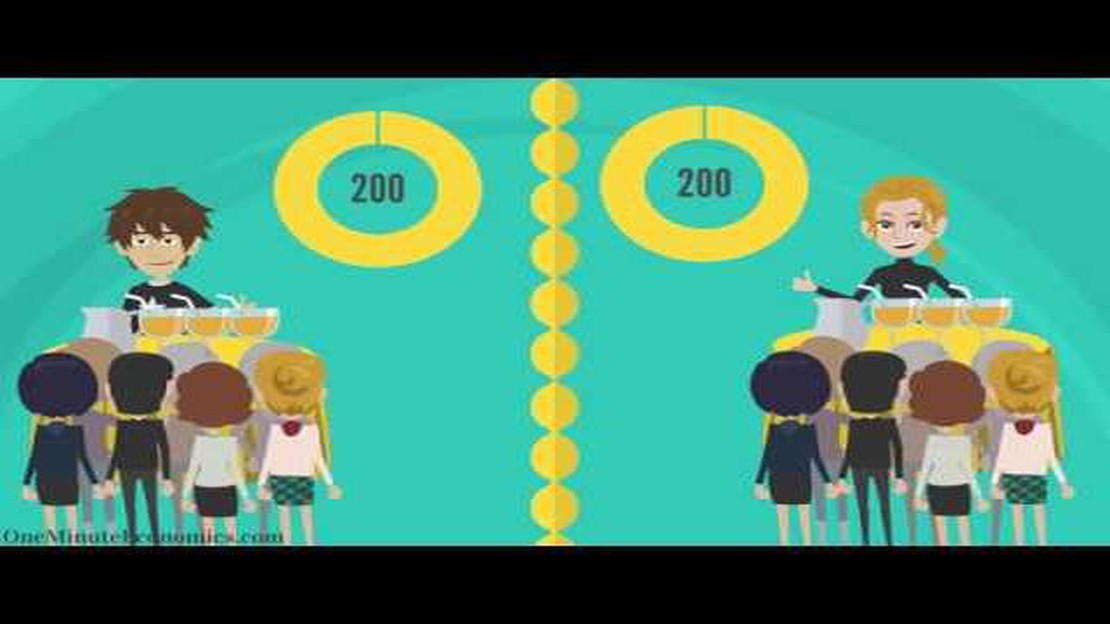
Market dynamics are complex and ever-changing, influenced by a multitude of factors such as competition, consumer demand, and government regulations. In order to understand and predict market behavior, economists and researchers often turn to game theory and the concept of Nash equilibrium.
Nash equilibrium is a fundamental concept in game theory that describes a situation where each participant in a game, given the strategies of the other participants, has no incentive to change their own strategy. It represents a stable state where no individual can gain by deviating from their chosen strategy unilaterally. In the context of market dynamics, Nash equilibrium helps us analyze how firms make decisions in response to their competitors’ actions.
When applying Nash equilibrium to market dynamics, we essentially view each firm as a player in a game, with the goal of maximizing their own profits. Each firm chooses a strategy, such as pricing their products, and takes into account the expected reactions of their competitors. The interaction between firms creates a dynamic environment where each player’s actions affect the outcomes of others, leading to a complex web of strategic decision-making.
For example, let’s consider a scenario where two firms are competing in a market. Both firms have the option to either lower or maintain their prices. If both firms choose to lower their prices, they may attract more customers and potentially increase their market share. However, this would also lead to a decrease in profit margins. On the other hand, if one firm lowers its prices while the other maintains higher prices, the firm with lower prices may benefit from increased sales while the other risks losing customers.
At Nash equilibrium, both firms would reach a point where neither has an incentive to change their pricing strategy. If one firm were to deviate and lower its prices further, it could potentially attract more customers, but at the risk of starting a price war with the other firm. Similarly, if one firm were to increase its prices, it may lose customers to the other firm and suffer a decrease in market share.
Understanding Nash equilibrium in market dynamics is essential for businesses seeking to gain a competitive advantage. By analyzing strategic interactions and predicting the outcomes of different scenarios, firms can make informed decisions to maximize their profits and maintain a stable market equilibrium. Game theory provides a powerful tool for analyzing and navigating the complex dynamics of the marketplace, enabling businesses to stay ahead in an ever-evolving competitive landscape.
Nash equilibrium is a concept in game theory that describes a stable state in which no player has an incentive to change their strategy, given the strategies of the other players. It is named after the mathematician John Nash, who first introduced the concept in his seminal paper “Non-cooperative Games” in 1950.
In a game, each player has a set of strategies they can choose from. The outcome of the game depends on the strategies chosen by all players. A Nash equilibrium occurs when no player can unilaterally deviate from their chosen strategy and improve their outcome.
To understand Nash equilibrium, let’s consider a simple example: the prisoner’s dilemma. In this game, two individuals are arrested and held in separate cells. They are given the option to either cooperate with each other or betray each other. The outcome of their decision affects their prison sentence.
| Player A Strategy | Player B Strategy | Player A Outcome | Player B Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cooperate | Cooperate | -2 years | -2 years |
| Cooperate | Betray | -10 years | 0 years |
| Betray | Cooperate | 0 years | -10 years |
| Betray | Betray | -5 years | -5 years |
In this game, both players have two strategies: cooperate or betray. The outcome of the game depends on the strategies chosen by both players. If both players choose to cooperate, they each receive a prison sentence of -2 years. If one player chooses to betray while the other cooperates, the betrayer receives a prison sentence of 0 years while the cooperator receives a prison sentence of -10 years. If both players choose to betray, they each receive a prison sentence of -5 years.
Read Also: Understanding Spot Option Trades: A Comprehensive Guide
In this example, the Nash equilibrium occurs when both players choose to betray. In this state, neither player has an incentive to unilaterally change their strategy. If one player were to cooperate while the other betrays, the cooperating player would receive a prison sentence of -10 years instead of -5 years. Likewise, if the betraying player were to cooperate while the other betrays, they would receive a prison sentence of 0 years instead of -5 years.
Nash equilibrium is a powerful concept in understanding strategic interactions in various fields, including economics, politics, and evolutionary biology. It helps to analyze and predict the behavior of individuals or groups in situations where multiple players are involved and their decisions affect each other’s outcomes.
Read Also: How to Find the Best Binary Option Broker: Top Tips and Recommendations
Nash equilibrium is a concept in game theory that involves predicting the behavior of rational players in a strategic setting. It is a state where no player has an incentive to unilaterally change their strategy, given the strategies of all other players. Understanding the key concepts related to Nash equilibrium is crucial for comprehending market dynamics.
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Strategy | A strategy is a set of actions or choices that a player can make. In a game, each player has their own set of strategies to choose from. |
| Payoff | Payoff is the reward or utility that a player receives based on the outcome of a game. It can be in the form of money, points, satisfaction, etc. |
| Simultaneous Games | Simultaneous games are those where players make their decisions without knowledge of each other’s actions. They choose their strategies simultaneously. |
| Sequential Games | Sequential games are those where players make their decisions in a sequence or order. The actions of one player may depend on the action of previous players. |
| Best Response | A best response is a strategy that maximizes a player’s expected payoff, given the strategies played by other players. It is the optimal choice for a player. |
| Nash Equilibrium | Nash equilibrium is a state in a game where each player’s strategy is a best response to the strategies of all other players. No player has an incentive to deviate from their strategy. |
These key concepts form the foundation of understanding Nash equilibrium in market dynamics. By analyzing the strategies, payoffs, and decision-making processes of rational players, economists and researchers can gain insights into the behavior and outcomes of markets.
Nash equilibrium is a concept in game theory that describes a situation where all players in a game or market have chosen their strategies, and no player has an incentive to change their strategy, given the strategies chosen by others.
In market dynamics, Nash equilibrium is used to understand the behavior of firms and consumers. It helps to analyze how different market participants make decisions based on their perceived payoffs, and how these decisions affect market outcomes.
In theory, Nash equilibrium can be achieved in real-life markets, but in practice, achieving perfect Nash equilibrium is often unlikely due to various factors such as imperfect information, changing market conditions, and competition. However, market participants often strive to reach a state of equilibrium where they are satisfied with their strategies, even if it is not the perfect Nash equilibrium.
One limitation is that Nash equilibrium assumes that all players act rationally and have perfect knowledge about the game or market. In reality, not all players may act rationally, and there may be asymmetry of information, which can lead to different outcomes than predicted by Nash equilibrium. Additionally, Nash equilibrium does not account for factors such as external shocks, government regulations, or strategic behavior that deviates from the assumptions of the game.
Yes, there are alternative equilibrium concepts such as evolutionary game theory, which takes into account the dynamics of how strategies evolve over time, and behavioral game theory, which incorporates psychological factors and deviations from rational behavior. These alternative concepts aim to provide a more realistic understanding of market dynamics by considering the complexities of human decision-making.
Nash equilibrium is a concept in game theory that describes a state in which each player in a game has chosen a strategy that no player can benefit by changing their strategy, assuming that all other players keep their strategies unchanged.
Nash equilibrium is relevant to market dynamics as it helps to analyze and understand the behavior and interaction of different market participants. It provides insights into how individuals or firms make decisions in a market to maximize their own gains while taking into account the actions of others.
7 Things to Know Before Starting Affiliate Marketing Affiliate marketing has become one of the most popular ways to earn passive income online. It …
Read ArticleCurrency Pair with the Highest Liquidity Are you looking to improve your forex trading strategy and optimize your trading profits? One key factor to …
Read ArticleIs options trading safer than forex? In the world of financial markets, there are various investment opportunities that offer different levels of risk …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Sideways Market Indicator in MT4 Many traders in the forex market experience frustration when they encounter a sideways market, also …
Read ArticleIs Forex Trading Risky: Understanding the Risks and Rewards Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is the process of buying and …
Read ArticleCan You Get a 7% Interest Savings Account? When it comes to saving money, finding the right savings account can make a big difference. But with so …
Read Article