What moves the E-mini S&
Key factors driving the E-mini S&P market The E-mini S&P 500 is a futures contract that tracks the performance of the S&P 500 index. It is one of the …
Read Article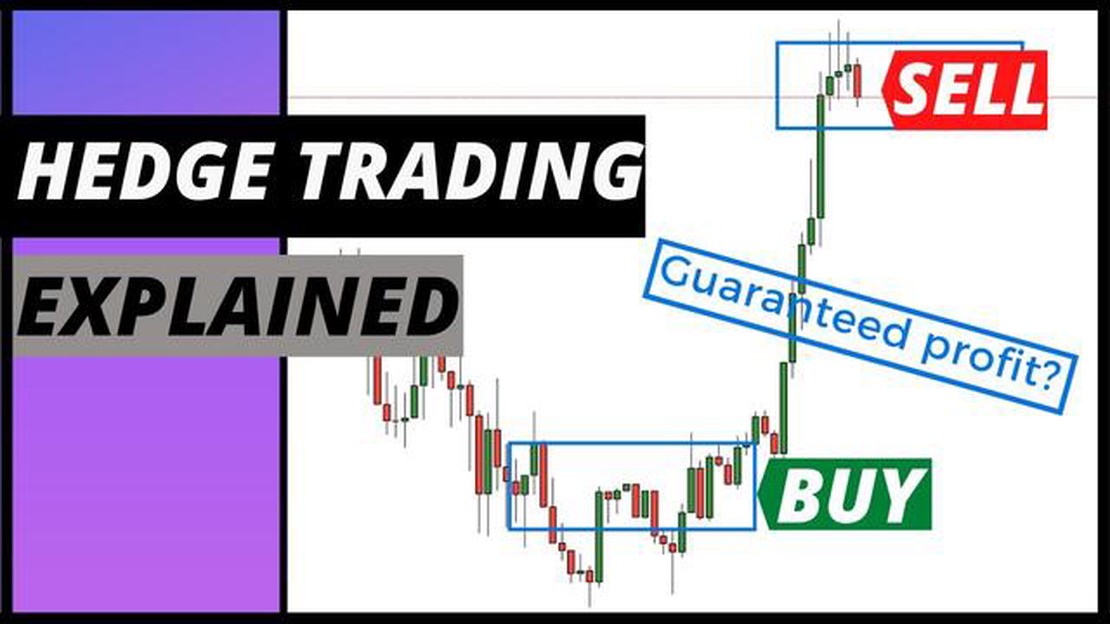
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world. Traders participate in this market to buy and sell currencies with the aim of earning profits from fluctuations in exchange rates. One of the strategies used in forex trading is hedging, which involves taking positions to mitigate potential losses and reduce risk.
Hedging is a risk management technique that allows traders to protect their investments by taking offsetting positions in the forex market. It involves opening two opposite positions in the same currency pair, with the goal of reducing potential losses if the market moves against the trader’s initial position. Hedging can be achieved through various techniques, such as using different currency pairs, derivatives, or options.
One example of hedging in the forex market is using multiple currency pairs. Traders can open positions in correlated currency pairs, such as EUR/USD and GBP/USD, to hedge their exposure to the USD. If the USD strengthens, the trader’s position in the EUR/USD currency pair may incur losses, but their position in the GBP/USD currency pair may offset these losses. This strategy allows traders to protect their investments from adverse changes in the exchange rate of a specific currency.
Another example of hedging in forex trading is using derivatives, such as futures contracts, to offset potential losses. Traders can enter into a futures contract that mirrors the value of their initial position, effectively locking in the exchange rate at which they entered the market. If the exchange rate moves against the trader, the losses on their initial position will be offset by the gains on the futures contract.
Hedging in the forex market is a valuable tool for managing risk and protecting investments. It allows traders to minimize potential losses and reduce their exposure to market volatility. By understanding different hedging strategies and their application in forex trading, traders can enhance their ability to navigate the dynamic and unpredictable forex market.
Forex trading, or foreign exchange trading, is the buying and selling of currencies on the foreign exchange market. This decentralized market operates globally and is open 24 hours a day, five days a week. Unlike traditional stock markets, forex trading involves the simultaneous buying of one currency and selling of another currency.
The forex market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion. It offers opportunities for individuals, institutions, and corporations to profit from fluctuations in currency prices. Traders can trade a wide range of currency pairs, including major pairs like the EUR/USD and GBP/USD, as well as minor and exotic pairs.
Forex trading can be conducted through various platforms, including online trading platforms provided by brokers. These platforms allow traders to access real-time market prices, execute trades, and monitor their positions. Traders can speculate on the direction of currency prices by either buying or selling a currency pair.
When trading forex, traders can make profits through capital appreciation or depreciation. If a trader expects a currency to appreciate in value, they can buy the currency pair, hold it for a certain period of time, and sell it at a higher price. Conversely, if a trader expects a currency to depreciate in value, they can sell the currency pair, buy it back at a lower price, and make a profit.
Read Also: Understanding the Distinction: Rus Options vs. Stock Options
Forex trading also involves risks, as currency prices can be affected by various factors such as economic indicators, geopolitical events, and market sentiment. Traders need to employ risk management strategies and stay informed about market trends and developments.
In conclusion, forex trading is a dynamic and potentially lucrative market where traders can profit from fluctuations in currency prices. It offers opportunities for both short-term and long-term trading strategies, and requires knowledge, skill, and risk management to succeed.
The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market, is a global decentralized market where currencies are traded. It is the largest and most liquid market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of around $6.6 trillion.
The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, allowing participants to trade currencies at any time. It is a market where currencies are bought and sold in pairs, with each currency having a specific value relative to another currency.
The value of a currency can fluctuate due to various factors, including economic and political events, interest rates, and market sentiment. These fluctuations create opportunities for traders to profit by buying a currency at a lower price and selling it at a higher price, or vice versa.
Forex trading can be done by individuals, institutions, banks, and corporations. It is accessible to anyone with an internet connection and a trading account. Traders can access the forex market through a forex broker, who acts as an intermediary between buyers and sellers.
Read Also: Can Implied Volatility Exceed 100%? Understanding the Limits of Volatility Measures
There are different types of participants in the forex market, including retail traders, who trade for themselves, and institutional traders, such as banks and hedge funds, who trade on behalf of clients. Central banks also play a significant role in the forex market, as they can influence currency values through monetary policy decisions.
One of the key features of the forex market is its high liquidity, which means that traders can enter and exit positions quickly without significant price differences. This liquidity is driven by the large number of participants and the continuous trading activity.
Another important concept in forex trading is leverage, which allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. This can amplify both profits and losses, making it important for traders to use risk management strategies.
In conclusion, the foreign exchange market is a dynamic and fast-paced market where currencies are traded. It offers opportunities for individuals and institutions to profit from fluctuations in currency values. Understanding the basics of the forex market is essential for anyone looking to participate in forex trading.
Hedging in forex trading is a strategy where traders take positions in order to reduce or eliminate the risk of potential losses. It involves opening multiple positions in opposite directions to minimize the impact of market fluctuations.
Sure! Let’s say a forex trader has a long position on EUR/USD and wants to hedge against potential losses. They can open a short position on USD/CHF, which is negatively correlated with EUR/USD. This way, if EUR/USD starts to decline, the losses on the long position can be offset by gains on the short position.
Yes, hedging is a common strategy in forex trading. It is used by both individual traders and institutional investors to manage their risk exposure. By hedging their positions, traders can protect themselves against unexpected market movements and minimize potential losses.
While hedging can be an effective risk management strategy, it is not without drawbacks. One drawback is that hedging can limit potential profits. When traders open opposite positions to hedge, any gains on one position may be offset by losses on the other position. Additionally, hedging can increase trading costs, as traders need to open and maintain multiple positions.
Key factors driving the E-mini S&P market The E-mini S&P 500 is a futures contract that tracks the performance of the S&P 500 index. It is one of the …
Read ArticleUnderstanding D3 in Trading: A Comprehensive Guide When it comes to trading in today’s fast-paced financial markets, having access to accurate and …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Forex Trading Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide Forex trading is a complex and dynamic world where currency pairs are exchanged, and …
Read ArticleWhat is IRC service? Internet Relay Chat (IRC) is a communication protocol that has been used for decades to enable real-time text-based conversations …
Read ArticleWhy Forex Trading Is So Addictive Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, has captivated the attention of millions of individuals …
Read ArticleDoes Pfizer Pay Monthly Dividends? If you are a shareholder or are considering investing in Pfizer, you may be wondering whether the company pays …
Read Article