When Will the Dollar Rise? Predictions and Projections
When will the dollar rise? The strength of the US dollar is a topic that impacts global economics and financial markets. As one of the world’s most …
Read Article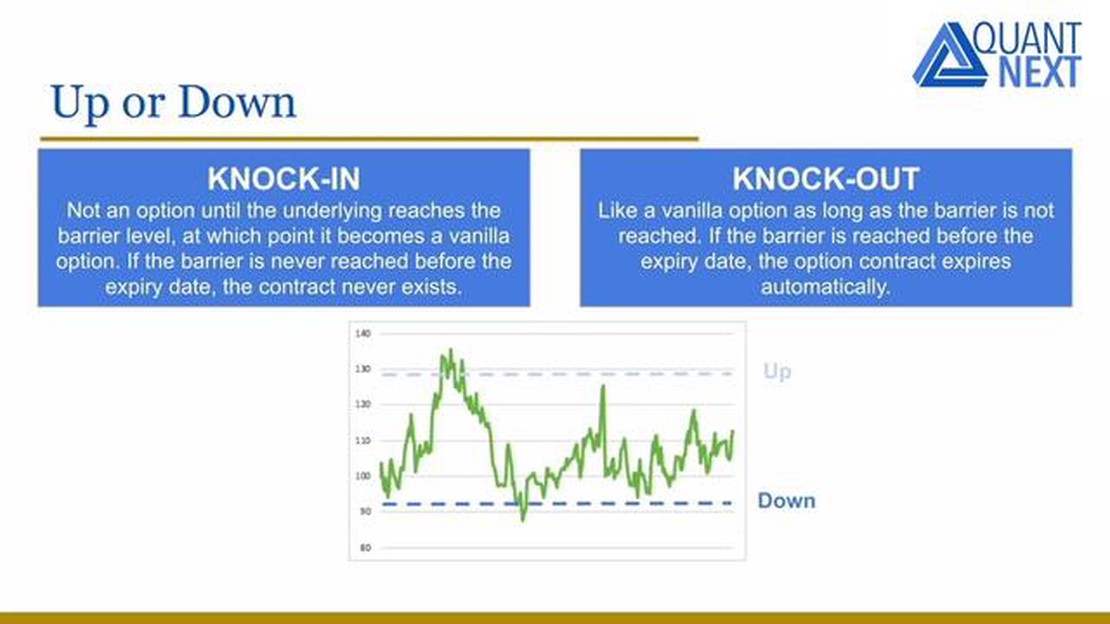
A barrier option is a type of derivative that derives its value from the underlying asset’s price reaching or breaching a certain level, known as the barrier. This unique feature sets barrier options apart from traditional options, as their payoff depends on whether the barrier is hit during the option’s lifetime.
Barrier options can be categorized into two main types: knock-in options and knock-out options. Knock-in options activate or “knock in” when the underlying asset’s price reaches the barrier level before the option’s expiration. On the other hand, knock-out options “knock out” or become void if the barrier is hit during the option’s lifetime.
To fully understand barrier options, it is important to grasp their characteristics and how they can be used in various investment strategies. This comprehensive guide will explore the different types of barrier options, their pricing models, and the factors that affect their valuation. Additionally, we will delve into the advantages and disadvantages of trading barrier options, providing a comprehensive overview for both novice and experienced investors.
Throughout this guide, we will explain key terms and concepts related to barrier options, such as the barrier level, option expiration, and intrinsic value. We will also discuss popular barrier option strategies, including trend following and volatility trading. By the end of this guide, readers will have a solid understanding of barrier options and be able to incorporate them into their investment portfolios with confidence.
Barrier options are a class of derivative securities that have an embedded condition or “barrier” that must be met for the option to be exercised. These types of options are popular among investors and traders because they offer unique risk and return profiles.
There are several different types of barrier options, each with its own specific characteristics:
1. Up-and-Out Option: This type of barrier option has a barrier set above the current price of the underlying asset. If the price of the underlying asset reaches or exceeds the barrier level, the option is knocked out and becomes worthless.
2. Up-and-In Option: In contrast to an up-and-out option, an up-and-in option starts out as worthless and only becomes active or “knocked in” if the price of the underlying asset reaches or exceeds the barrier level. Once the barrier is hit, the option behaves like a regular vanilla option.
3. Down-and-Out Option: Similar to an up-and-out option, a down-and-out option has a barrier set below the current price of the underlying asset. If the price of the underlying asset falls to or below the barrier level, the option is knocked out and becomes worthless.
Read Also: Can I Use MT4 with Forex.com? Your Guide to Trading with MetaTrader 4 on Forex.com
4. Down-and-In Option: In contrast to a down-and-out option, a down-and-in option starts out as worthless and only becomes active or “knocked in” if the price of the underlying asset falls to or below the barrier level. Once the barrier is hit, the option behaves like a regular vanilla option.
5. Double Barrier Option: A double barrier option has two barrier levels, one above the current price of the underlying asset and one below. The option may be knocked out if either barrier is hit, and it becomes active or “knocked in” if both barriers are hit.
6. Knock-in vs Knock-out: In addition to the different types of barrier options based on the direction of the barrier, options can also be classified as either knock-in or knock-out. Knock-in options become active if the barrier is hit, while knock-out options are rendered worthless if the barrier is hit.
7. Partial Barrier Observation: Some barrier options allow for partial barrier observations, where the option remains active or knocked out only if the barrier is crossed by a certain percentage or for a certain duration.
Overall, barrier options offer investors and traders a range of potential strategies and risk management tools. Understanding the different types of barrier options is essential for effectively incorporating them into investment portfolios or trading strategies.
A barrier option is a type of derivative that has a pre-specified barrier level. This barrier level can be either above (up barrier) or below (down barrier) the current asset price. The option only comes into effect if the asset price reaches or crosses this barrier level during the option’s lifetime.
There are two main types of barrier options: knock-in and knock-out options. A knock-in option becomes activated if the barrier level is breached, while a knock-out option ceases to exist if the barrier level is hit.
Barrier options provide investors with various ways to structure their investment strategies. Some common types of barrier options include:
Read Also: What Happens to My Shares If I Leave the Company: Key Considerations
The payoff of a barrier option depends on whether it is a call or put option, as well as whether it is a knock-in or knock-out option. For example, an up-and-out call option would have a payoff equal to the difference between the asset price at expiration and the strike price, as long as the asset price did not breach the barrier level. If the asset price did breach the barrier level, the option would cease to exist.
The pricing of barrier options can be more complex than that of plain vanilla options, due to the additional feature of the barrier level. This can be accounted for using various pricing models and methodologies, such as the Black-Scholes model or Monte Carlo simulations.
In summary, barrier options provide investors with the ability to structure their investment strategies based on certain barrier levels. These options can be either knock-in or knock-out options and come in various forms, such as up-and-in or down-and-out. The pricing of barrier options can be more complex than plain vanilla options, but there are established models and methodologies available to account for the barrier feature.
Barrier options are a type of derivative contract that have an additional condition or “barrier” that must be met for the option to either become active or to cease to exist.
Barrier options can help investors manage risk by allowing them to set specific price levels at which the option will either become active or expire.
Barrier options work by setting a specific price level, known as the barrier, that must be reached for the option to become active or to cease to exist.
There are several types of barriers in barrier options, including up-and-in, down-and-in, up-and-out, and down-and-out barriers.
Barrier options can be more complex than traditional options due to the additional condition of the barrier that must be met for the option to become active or expire.
When will the dollar rise? The strength of the US dollar is a topic that impacts global economics and financial markets. As one of the world’s most …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Value of 1 Volume in the Forex Market When it comes to understanding the intricacies of forex trading, one of the key concepts that …
Read ArticleWhat are the Best Days to Trade Binary Options? When it comes to trading binary options, timing is everything. The days of the week can greatly …
Read ArticleIs Forex Trading Allowed in Singapore? Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, has become increasingly popular in Singapore. Traders …
Read ArticleWhat is the value of 1 lot in trading? Trading in financial markets involves various terms and concepts that a trader needs to understand. One such …
Read ArticleIs eToro MT4 or MT5? If you’re interested in online trading, you may have come across eToro - a popular social trading platform. One of the first …
Read Article