Unraveling the Symbolism of the Black Crow: Insights and Meanings
Meaning and Symbolism of Black Crows Throughout history, the black crow has been an enigmatic symbol that has captivated the human imagination. …
Read Article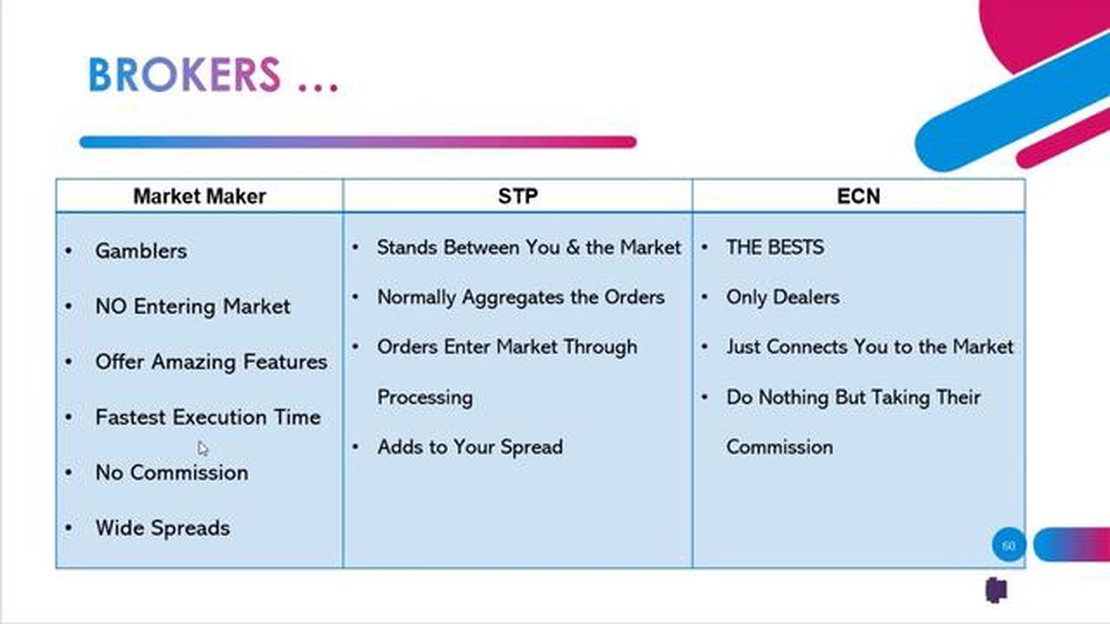
ECN/STP and Market Maker are two different types of forex brokers that operate in the financial market. While both facilitate the buying and selling of currencies, there are key differences between the two that traders should be aware of.
ECN/STP brokers (Electronic Communication Network/Straight Through Processing) are known for providing direct access to the interbank market. They do not make money from spreads but charge a commission on each trade instead. These brokers pass the clients’ orders directly to liquidity providers, such as banks and other financial institutions, which ensures that traders receive the best available bid and ask prices. ECN/STP brokers also allow for anonymous trading, as the client’s information is not visible to the liquidity providers.
Market Makers, on the other hand, create a market for their clients by taking the other side of the trade. They do not pass the clients’ orders to the interbank market but instead act as counterparties to their clients’ trades. Market Makers make money from the spreads they offer, which means they profit from the difference between the bid and ask prices. They often provide fixed spreads, which can be an advantage for traders who prefer a more predictable trading environment. However, Market Makers may have a conflict of interest as they can manipulate prices to their advantage.
In conclusion, the main difference between ECN/STP and Market Maker brokers lies in their business models. ECN/STP brokers provide direct access to the interbank market, charging a commission on each trade and offering competitive bid and ask prices. Market Makers, on the other hand, act as counterparties to their clients’ trades and profit from the spreads they offer. Traders should consider their trading style and preferences when choosing between the two types of brokers.
ECN/STP brokers offer several advantages for traders:
Despite these advantages, there are also some disadvantages of trading with ECN/STP brokers:
Overall, choosing an ECN/STP broker requires careful consideration of these advantages and disadvantages, as well as an assessment of individual trading needs and preferences.
Read Also: Binary Option vs. Forex: What's the Difference?
Market maker brokers, also known as dealing desk brokers, play a significant role in the forex market. They provide liquidity and create a market for traders to buy and sell currencies. However, there are advantages and disadvantages associated with trading with market maker brokers.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| * Tight Spreads: Market maker brokers often offer fixed spreads, which can be advantageous for traders who prefer stable trading costs. |
Read Also: Is a moving average a convolution?
It is important for traders to carefully consider these advantages and disadvantages before choosing to trade with a market maker broker. Factors such as trading strategy, capital size, and risk tolerance should be taken into account when making a decision.
The main difference between ECN/STP and Market Maker is how they execute trades. ECN/STP brokers provide a direct link between traders and liquidity providers, allowing for faster trade execution and potentially lower spreads. Market Maker brokers, on the other hand, act as the counterparty to the trades, creating a market for traders and often providing fixed spreads.
ECN/STP brokers are generally more suitable for scalping traders. This is because they offer faster trade execution, lower spreads, and no restrictions on trading styles. Market Maker brokers sometimes have restrictions on scalping, as they act as the counterparty to trades and may have concerns about potential losses from rapid scalping strategies.
Yes, ECN/STP brokers typically charge commissions on trades. This is because they provide a direct link to liquidity providers and charge a fee for this service. The commissions can vary depending on the broker and the size of the trade, but they are usually a fixed amount per lot traded.
Market Maker brokers have the potential to manipulate prices, as they act as the counterparty to trades. They have the ability to widen spreads, delay trade execution, or fill orders at a different price than requested. However, reputable Market Maker brokers are regulated and follow strict guidelines to ensure fair trading practices.
ECN/STP brokers offer better liquidity compared to Market Maker brokers. This is because they provide a direct link to a network of liquidity providers, allowing for faster trade execution and access to deeper order books. Market Maker brokers may have limited liquidity as they create their own market for traders.
Meaning and Symbolism of Black Crows Throughout history, the black crow has been an enigmatic symbol that has captivated the human imagination. …
Read ArticleIs Citi Velocity free? If you are considering using Citi Velocity, a popular trading platform offered by Citigroup, you may be wondering about the …
Read ArticleWhen does the EUR USD market close? If you are interested in the Forex market, specifically in the EUR USD currency pair, it is important to be aware …
Read ArticleBeginner’s Guide to Nifty Option Trading Welcome to the beginner’s guide on how to start Nifty option trading! If you’re new to the world of options …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Leverage of Vantage Markets When it comes to financial markets, understanding leverage is crucial for investors and traders. …
Read ArticleDoes Nadex have demo account? If you are new to trading or just want to test out your strategies in a risk-free environment, you may be wondering if …
Read Article