Option Trading in Australia: Everything You Need to Know
Option Trading in Australia: Everything You Need to Know Option trading has become increasingly popular in Australia, offering investors a unique way …
Read Article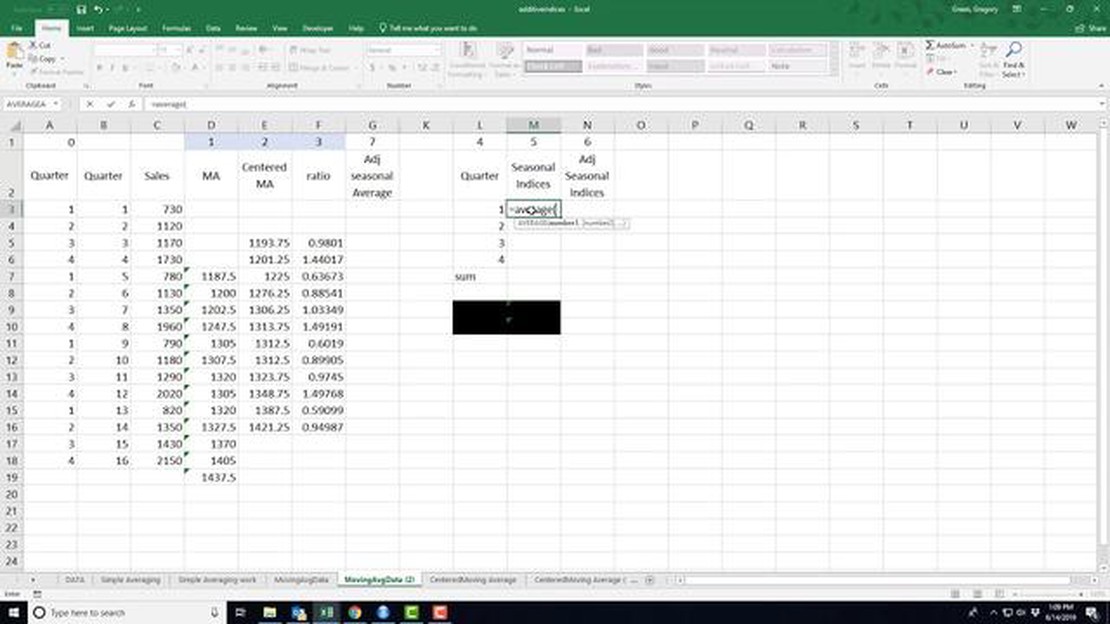
In the field of statistics and finance, moving averages are commonly used to analyze and interpret data over time. One popular type of moving average is the centered moving average of order 5, which provides a smooth representation of the underlying data. This article aims to explain the concept of the centered moving average of order 5, how it is calculated, and its practical applications.
The centered moving average of order 5 is a technique that calculates the average value of a series of data points by taking the average of the neighboring values. It is called “centered” because the calculation is centered at each data point, taking into account the values before and after it. This helps to eliminate the lag that can occur with other types of moving averages, resulting in a more accurate representation of the data.
To calculate the centered moving average of order 5, we take the average of the two values before the selected data point, the selected data point itself, and the two values after it. This ensures that the calculation is evenly weighted and reflects the overall trend of the data. This moving average is often used to smooth out sudden fluctuations or noise in the data, making it easier to identify and analyze long-term trends.
Practically, the centered moving average of order 5 can be used in various fields, such as finance, economics, and stock market analysis. It is often applied to stock prices, exchange rates, and economic indicators to identify trends, support decision-making, and forecast future values. By removing short-term fluctuations, this moving average provides a clearer picture of the underlying patterns and helps analysts and traders make informed predictions.
In conclusion, the centered moving average of order 5 is a powerful statistical tool used to analyze and interpret time-series data. It helps to smooth out noise and fluctuations, providing a clearer view of underlying trends. Understanding how to calculate and utilize the centered moving average can greatly enhance your ability to analyze data and make informed decisions in various fields.
The Centered Moving Average of Order 5, also known as the 5-period moving average, is a statistical calculation used to analyze a set of data points over a specific time period. It is widely used in finance, economics, and other fields to smooth out fluctuations in data and identify trends or patterns.
The Centered Moving Average of Order 5 is calculated by adding up the values of the five data points in the center of the time period and then dividing the sum by 5. This creates a new data point that represents the average value of the five points. As time progresses, the Centered Moving Average of Order 5 is recalculated by shifting the time period forward one data point.
The Centered Moving Average of Order 5 is particularly useful in filtering out short-term fluctuations in the data and highlighting the underlying long-term trend. By providing a smoothed average value, it helps to reduce noise and identify significant changes or patterns in the data. It is commonly used in technical analysis to generate trading signals and identify support and resistance levels.
For example, let’s say we have a set of closing prices for a stock over a 10-day period:
[10, 12, 11, 13, 15, 14, 16, 18, 17, 19]
To calculate the Centered Moving Average of Order 5, we would select the five data points in the center of the time period, which are [11, 13, 15, 14, 16]. We then add up these values (11 + 13 + 15 + 14 + 16 = 69) and divide the sum by 5 to get the moving average of 13.8. As time progresses, we would shift the time period forward one data point and recalculate the moving average.
The Centered Moving Average of Order 5 is just one of many moving average calculations that can be used to analyze data. Depending on the specific requirements and characteristics of the data, different orders or types of moving averages may be more appropriate. It is important to consider the intended use of the moving average and the time period being analyzed in order to select the most suitable calculation method.
Read Also: Step-by-Step Guide: How to Change Currency on OCBC
The centered moving average of order 5 is a statistical calculation that is used to smooth out fluctuations and highlight trends in a dataset. It is calculated by taking the average of a set of values surrounding a particular data point.
To calculate the centered moving average of order 5, you take the average of the middle three values in a set of five consecutive data points. This average is then assigned to the central data point. This process is repeated for each data point in the dataset, resulting in a new dataset that is smoothed and centered around the original data points.
The centered moving average is often used in time series analysis to identify underlying patterns or trends in data. By smoothing out the data, it can help to remove random noise or short-term fluctuations, making it easier to see long-term trends or patterns.
This technique is particularly useful when dealing with data that has a seasonal or cyclical component. It can help to highlight the underlying trend by removing the seasonal fluctuations or variations that may be present.
The centered moving average of order 5 is calculated using the formula:
Centered Moving Average5(n) = (X(n-2) + X(n-1) + Xn + X(n+1) + X(n+2)) / 5
Where:
By calculating and analyzing the centered moving average of order 5, you can gain insights into the underlying trends and patterns in your data, helping to inform decision-making and forecasting.
Read Also: How much can FX traders earn in New York City? - A comprehensive guide
To calculate the Centered Moving Average (CMA) of order 5, follow these steps:
For example, let’s say we have the following list of numbers:
To calculate the centered moving average of order 5 for this list, we start with the 3rd data point, which is 7. We add the previous 2 data points (5 and 3), the current data point (7), and the following 2 data points (9 and 11), which gives us a sum of 35. We then divide this sum by 5, which gives us a centered moving average of 7.
We repeat this process for all the data points within the range, resulting in the following centered moving averages:
These values represent the centered moving averages for each data point within the given range.
The centered moving average of order 5 is a useful statistical tool that helps smooth out fluctuations in data. It is commonly used in finance, economics, and other fields to analyze trends and patterns in time series data.
The centered moving average of order 5 is a statistical calculation used to smooth out a time series by averaging a sequence of data points. It calculates the average of the current data point and the two data points before and after it.
The centered moving average of order 5 is calculated by taking the average of the current data point and the two data points before and after it. This is done by adding the five data points together and dividing the sum by 5.
The centered moving average of order 5 is useful because it helps to remove noise and fluctuations from a time series, making it easier to identify underlying trends or patterns. It can also be used to forecast future values based on past data.
Sure! Let’s say we have the following time series data: 10, 12, 15, 14, 13, 12, 11, 10. To calculate the centered moving average of order 5, we would start with the third data point (15) and average it with the two data points before and after it (12 and 14). This gives us an average of 13.67. We would then repeat this process for the remaining data points, resulting in a centered moving average of 13.67, 13.33, 13.33, 12.67, 11.67, and 10.67.
Option Trading in Australia: Everything You Need to Know Option trading has become increasingly popular in Australia, offering investors a unique way …
Read ArticleCalculating a 2 Year Moving Average: Step-by-Step Guide Understanding and analyzing trends in data is essential for making informed decisions and …
Read ArticleGuide on Writing a Forex Book Writing a forex book can be a rewarding and informative experience, allowing you to share your knowledge and insights …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Commodity System: Definition and Key Principles When it comes to the global economy, understanding the commodity system is crucial. …
Read ArticleSwahili as a Trade Language: Unraveling its Historical Significance The Swahili language, also known as Kiswahili, is one of the most widely spoken …
Read ArticleWhat is a Disqualifying Disposition of Incentive Stock Options on W2? Incentive Stock Options (ISOs) are a type of employee stock option that can …
Read Article