7 Proven Strategies to Make $200 a Day in Forex Trading
Learn How to Make $200 a Day in Forex Trading In the fast-paced world of forex trading, finding a consistent and profitable strategy is key to …
Read Article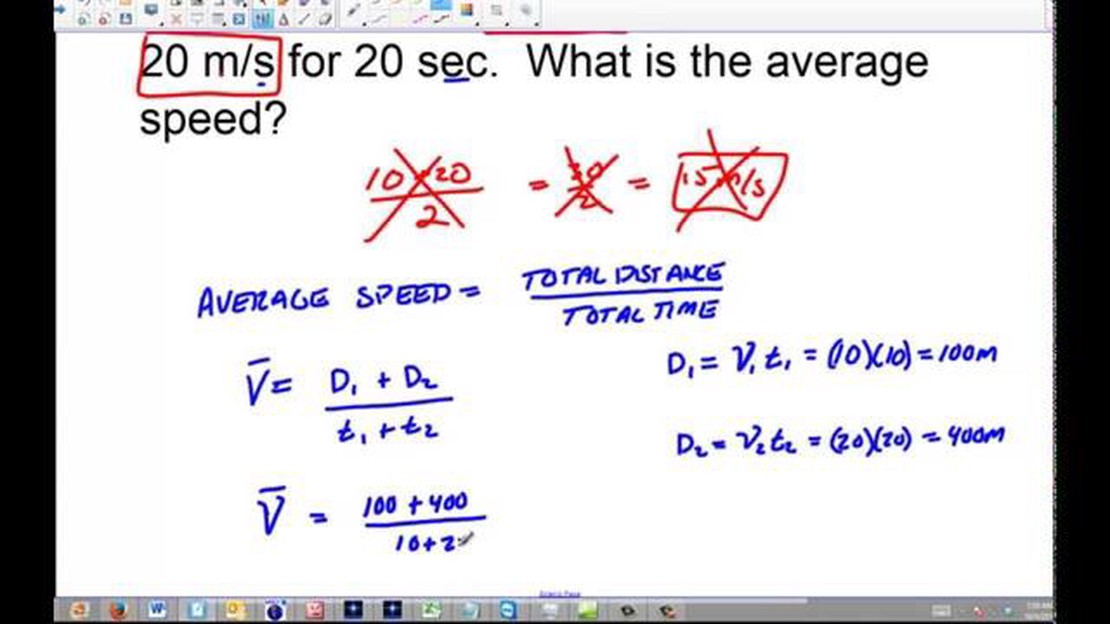
If you’re studying physics or simply curious about the principles of motion, you’ll likely come across the concept of average speed. Average speed is a fundamental concept that helps us understand how quickly an object is moving over a given distance. Whether you’re calculating the speed of a moving car or the velocity of a falling object, the formula for average speed will be your go-to tool.
To calculate average speed, you’ll need to know two key pieces of information: the total distance traveled and the total time taken. Remember that speed is a scalar quantity, which means it only has magnitude and no direction. So, even if an object moves in different directions, the average speed will always be positive. This is because the distance traveled is always a positive value.
Once you have the distance and time values, you can use the simple formula: Average Speed is equal to Total Distance divided by Total Time. It’s important to remember that the units of distance and time must be consistent in order to obtain accurate results. If, for example, your distance is in kilometers and your time is in seconds, you’ll need to convert one of the values to match the other. This ensures that your final answer is in the correct unit.
In conclusion, calculating average speed in physics is a straightforward process. By knowing the distance traveled and the time taken, and ensuring that the units are consistent, you can easily determine the average speed of an object. This fundamental concept is essential in understanding the principles of motion and is a vital tool in various scientific calculations.
Average speed is a concept in physics that measures the overall rate at which an object moves. It is calculated by dividing the total distance traveled by the object by the total time taken to cover that distance. Average speed is a scalar quantity, meaning it only has magnitude and no direction.
In physics, speed refers to how fast an object is moving, while velocity takes into account both the object’s speed and its direction. Average speed is used to evaluate the overall efficiency or effectiveness of motion. It is commonly represented by the letter “v” or the symbol “v̅”.
The formula to calculate average speed is:
| Average speed (v̅) = | Total distance traveled | / | Total time taken |
For example, if a car travels a total distance of 300 kilometers in a time of 5 hours, the average speed can be calculated as:
Average speed (v̅) = 300 km / 5 hours = 60 km/h
It is important to note that average speed does not provide information about the specific details of an object’s motion throughout its journey, such as changes in speed or direction. It simply gives an overall measure of how quickly an object is moving on average.
Understanding average speed is fundamental in various areas of physics, such as analyzing motion, calculating momentum, and determining forces acting on objects. It allows scientists and researchers to make predictions and analyze the efficiency of various systems and processes.
Average speed is a measure of how fast an object is moving over a given distance. It is calculated by dividing the total distance an object travels by the time it takes to cover that distance.
In physics, average speed is represented by the symbol “v-bar”. It is a scalar quantity, meaning it only has magnitude, not direction. This means that average speed does not take into account the direction of motion, only the overall distance traveled and the total time taken.
To calculate average speed, you need to know the total distance traveled and the total time taken. The formula for average speed is:
| Average Speed (v-bar) | = | Total Distance | / | Total Time |
|---|
Read Also: Ways to Minimize Tax Liability While Trading: Tips and Strategies
For example, if an object travels a total distance of 100 meters in a time of 20 seconds, the average speed can be calculated as:
| Average Speed (v-bar) | = | 100 meters | / | 20 seconds |
| = | 5 meters per second |
So, the average speed of the object in this example is 5 meters per second.
The average speed is a measure of how fast an object moves over a certain distance during a given time interval. It is a scalar quantity and is calculated by dividing the total distance traveled by the total time taken.
Read Also: Is Auto Trading Profitable?: Examining the Potential Gains and Risks
The formula for calculating average speed is:
Average Speed = Total Distance Traveled / Total Time Taken
In this formula, the total distance traveled is the length of the path taken by the object, while the total time taken is the duration of the journey. The units of distance and time should be consistent in order to obtain the correct average speed value. For example, if the distance is measured in kilometers and the time is measured in hours, the average speed will be in kilometers per hour (km/h).
It is important to note that average speed does not give any information about the object’s instantaneous speed at any given moment during the journey. It is simply a measure of the overall speed of the object throughout the entire journey.
By using this formula, you can easily calculate the average speed of an object and analyze its motion. Whether you are studying physics, engineering, or any other field that involves motion, understanding how to calculate average speed will be crucial in analyzing and interpreting various scenarios.
Example:
Let’s say a car travels a distance of 100 kilometers in 2 hours. To calculate the average speed, we will divide the total distance traveled (100 kilometers) by the total time taken (2 hours).
Average Speed = 100 kilometers / 2 hours = 50 kilometers per hour (km/h)
Therefore, the car’s average speed during this journey is 50 kilometers per hour.
Average speed is the total distance traveled by an object divided by the total time taken to travel that distance.
To calculate average speed, you need to divide the total distance traveled by the total time taken. The formula for average speed is: average speed = total distance / total time.
No, average speed cannot be negative. If an object changes direction and moves in the opposite direction, the speed can be negative, but the average speed will always be positive or zero.
Common units used to measure average speed include meters per second (m/s), kilometers per hour (km/h), miles per hour (mph), and feet per second (ft/s).
Average speed is important in physics because it allows us to understand how quickly or slowly an object is moving over a given distance. It helps us analyze motion and make predictions about future movements.
Learn How to Make $200 a Day in Forex Trading In the fast-paced world of forex trading, finding a consistent and profitable strategy is key to …
Read ArticleReasons behind the decline of MSN usage MSN, which was once one of the leading messaging platforms, has seen a significant decline in its user base …
Read ArticleFind forex pair volatility: strategies and methods The foreign exchange market, or Forex, is a highly volatile market where currencies are traded. The …
Read ArticleAre Stock Options Considered Income? Stock options are a popular form of compensation for employees, especially in the tech industry. They provide …
Read ArticleWill Marlin rifles be made again? For the avid hunters and experienced shooters out there, Marlin rifles have always been a trusted and reliable …
Read ArticleDo I have to pay tax on foreign money transfer to Philippines? When sending money to the Philippines, it is important to understand the tax …
Read Article