TC2000's forex capabilities: everything you need to know
TC2000 Forex: Everything You Need to Know TC2000 is a popular trading platform known for its advanced features and powerful tools. While originally …
Read Article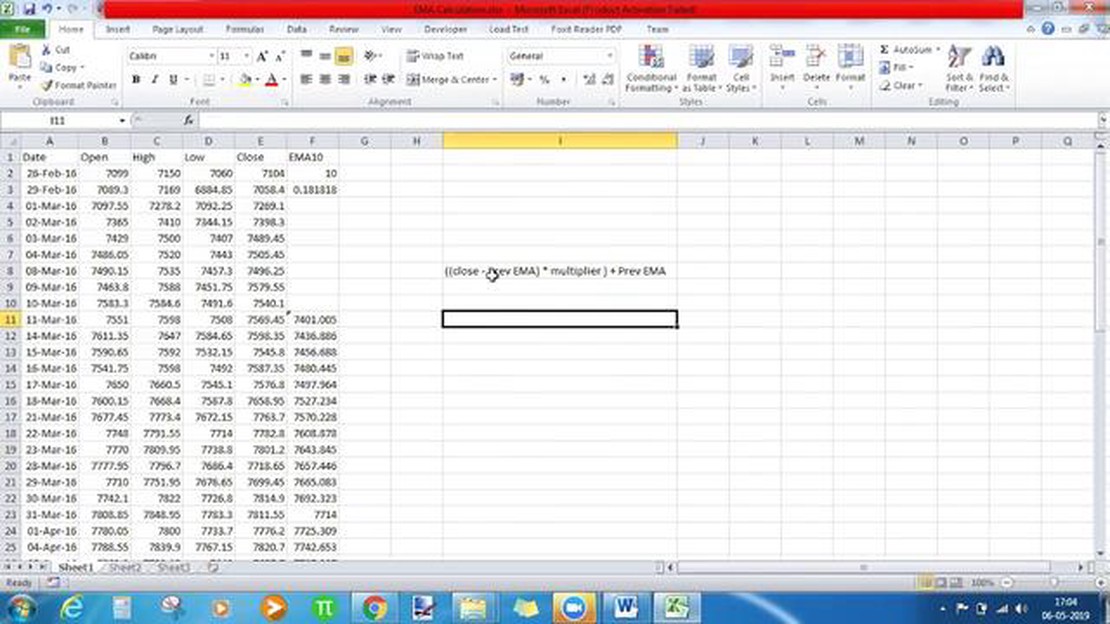
The exponential moving average (EMA) is a popular technical indicator used in financial analysis to identify trends and forecast future price movements. It is a type of moving average that emphasizes recent data points more heavily, making it more responsive to current market conditions.
To add an EMA to your charts, follow these step-by-step instructions:
It is important to note that the EMA is a lagging indicator, meaning it may not provide real-time signals. Traders often use it in conjunction with other technical analysis tools to confirm trends and signals.
By adding an EMA to your charts, you can gain valuable insights into the price movements of assets or securities, helping you make more informed trading decisions. Remember to adjust the EMA period and use it in combination with other indicators that suit your trading strategy.
An Exponential Moving Average (EMA) is a type of moving average that places more weight on recent data and exponentially decreases the weight of older data. It is commonly used in technical analysis to smooth out price data and identify trends. EMA is considered more responsive to changing market conditions compared to other types of moving averages, such as the Simple Moving Average (SMA).
The EMA calculation involves applying a weighting multiplier to each data point, with the multiplier typically decreasing over time. The formula for calculating the EMA is as follows:
EMA = (Current price - Previous EMA) * (2 / (Number of periods + 1)) + Previous EMA
Where:
The EMA gives more weight to recent prices, allowing it to respond quickly to price changes. This makes it a popular choice among traders and analysts who want to identify short-term trends and potential buy or sell signals. The EMA is often used in conjunction with other technical indicators to validate trading decisions.
It is important to note that the EMA is a lagging indicator, meaning it is based on past price data and may not accurately predict future price movements. As with any technical analysis tool, it should be used in combination with other methods and indicators to increase the accuracy of trading decisions.
Read Also: What Happens if My Call Option Reaches the Strike Price?
The Exponential Moving Average (EMA) is a commonly used technical indicator in financial analysis. It is a type of moving average that places more weight on recent data points, making it more responsive to price changes.
The EMA is calculated by taking a specified period of time and applying a smoothing factor that gives more weight to recent data points. This smoothing factor is usually calculated using the formula: EMA = (Closing Price - EMA(previous day)) * multiplier + EMA(previous day).
The EMA is more responsive to price changes because it places a greater emphasis on recent data points. This makes it useful for identifying trends and potential reversals in a stock’s price. When the EMA line is above the price, it indicates an uptrend, while when it is below the price, it suggests a downtrend.
Traders often use the EMA in conjunction with other technical indicators to make trading decisions. For example, they may use the EMA crossover strategy, where they look for the EMA line to cross above or below the price line as a signal to buy or sell a stock.
The EMA is also used to calculate other technical indicators, such as the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) and the Relative Strength Index (RSI). These indicators provide additional information about market trends and momentum.
In summary, the Exponential Moving Average is a versatile tool that can help traders identify trends and potential reversals in a stock’s price. By placing more weight on recent data points, it is more responsive to price changes and can provide valuable insights for making trading decisions.
An exponential moving average (EMA) is a type of moving average that places greater weight and importance on more recent data points. It provides a more accurate representation of the current trend compared to other moving averages.
To calculate an exponential moving average, follow these steps:
Read Also: Understanding Forex: What is Forex Trading and How Does it Work?
The resulting EMA values will provide a smoothed trendline that is responsive to recent changes in the data. Traders and analysts commonly use EMAs to identify bullish or bearish trends, generate buy or sell signals, and set stop-loss levels.
Remember, the shorter the time period used, the more sensitive the EMA will be to recent price changes. Conversely, longer time periods will result in a smoother and less reactive EMA.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial or investment advice. It is always recommended to consult with a professional financial advisor or broker before making any investment decisions.
An Exponential Moving Average (EMA) is a type of moving average that gives more weight to recent data points, making it more responsive to changes in price compared to a simple moving average.
Adding an EMA to a chart can help traders identify the overall trend of a security or an asset. It can also provide buy or sell signals when the price crosses above or below the EMA line.
The formula to calculate the EMA is: EMA = (Price - Previous EMA) * (2 / (1 + N)) + Previous EMA, where Price is the current price, Previous EMA is the EMA calculated for the previous day, and N is the number of periods.
Yes, the EMA can be used for short-term trading. Since it gives more weight to recent data points, it is more sensitive to short-term price movements. Traders can use shorter periods, such as 10 or 20, to generate more frequent buy/sell signals.
One drawback of using the EMA is that it may produce more false signals compared to other moving averages. Additionally, the EMA can be influenced heavily by sudden price spikes or gaps, which may distort its effectiveness.
An Exponential Moving Average (EMA) is a type of moving average that gives more weight to recent data points. It is calculated by applying a decreasing weight to each previous data point in the time series, with the most recent data point having the highest weight. This makes the EMA more responsive to changes in the underlying data and helps to identify trends more quickly.
TC2000 Forex: Everything You Need to Know TC2000 is a popular trading platform known for its advanced features and powerful tools. While originally …
Read ArticleHow to Start a Forex Funding Company Starting a forex funding company can be a lucrative venture for those who are knowledgeable about the foreign …
Read ArticleDisadvantages of an Option Agreement: What to Consider? An option agreement is a contract between a buyer and a seller that gives the buyer the right, …
Read ArticleIs it possible to withdraw money from QDRO without penalty? Qualified Domestic Relations Orders (QDROs) are legal orders used to divide retirement …
Read ArticleIs Tiger Trade Legal? Tigers are one of the most iconic and endangered species on our planet. Their majestic beauty and powerful presence have …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the process of Forex remittance Forex remittance, also known as foreign exchange remittance, is the process of transferring money from …
Read Article