Understanding the mechanics of stock options for pre-IPO companies
Understanding Stock Options for Pre-IPO Companies When it comes to working for a pre-IPO company, one of the key benefits that employees often receive …
Read Article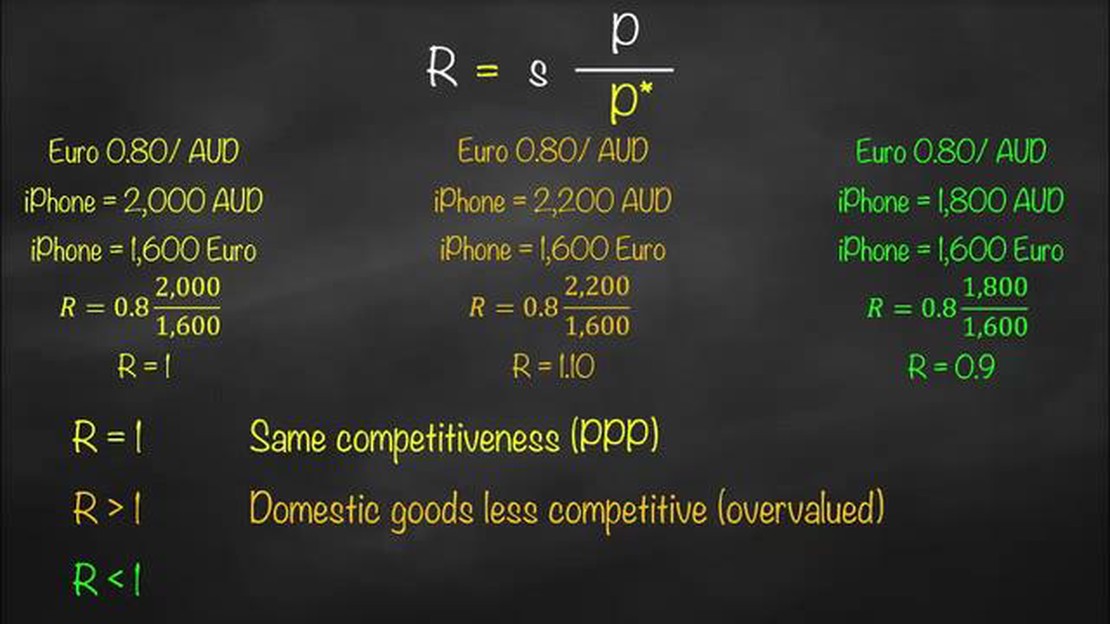
The real effective exchange rate (REER) is a crucial indicator that measures the competitiveness of a country’s currency in the international market. In the case of Ireland, understanding the factors that influence its REER is essential for policymakers and investors. This article aims to delve into the key factors that impact Ireland’s REER and explore their implications for the economy.
One of the primary factors influencing Ireland’s REER is its inflation rate. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of a currency, making it less attractive to foreign investors. A higher inflation rate in Ireland relative to its trading partners can lead to an appreciation of the REER, thereby reducing the country’s competitiveness in the global market. Therefore, monitoring and managing inflation is a key concern for Ireland’s policymakers.
Another factor that contributes to Ireland’s REER is its productivity levels. Ireland’s competitiveness heavily relies on its ability to produce goods and services efficiently. Higher productivity levels can lower production costs, making Irish exports more competitive in the international market. Therefore, policymakers often focus on improving productivity through investments in education, innovation, and infrastructure.
The monetary policy pursued by the Central Bank of Ireland also plays a vital role in determining the REER. By adjusting interest rates and managing the money supply, the central bank can influence the exchange rate. For example, a lower interest rate can make Ireland’s currency less attractive to foreign investors, leading to a depreciation of the REER. On the other hand, a higher interest rate can have the opposite effect.
In summary, understanding the key factors that influence Ireland’s real effective exchange rate is crucial for policymakers and investors. By monitoring and managing inflation, improving productivity, and implementing appropriate monetary policies, Ireland can enhance its competitiveness in the global market and ensure a stable exchange rate that supports economic growth.
The real effective exchange rate (REER) is an important indicator that reflects the competitiveness of a country’s goods and services in the international market. In the case of Ireland, several factors can influence its REER, thereby affecting the country’s overall economic performance. The following factors play a significant role in determining the REER in Ireland:
Read Also: Is Questrade only available in Canada?
In conclusion, the real effective exchange rate in Ireland is influenced by various factors, including economic growth, inflation, trade balance, interest rates, and government policies. Understanding these factors and their impact on the REER is crucial for policymakers and market participants to effectively manage the country’s exchange rate and maintain competitiveness in the global market.
Ireland plays a significant role in the global market, attracting both domestic and international investors due to its favorable business environment and skilled workforce. The country has emerged as an important player in sectors such as technology, pharmaceuticals, and finance.
One of the key factors contributing to Ireland’s success in the global market is its favorable corporate tax regime. The country’s low corporate tax rate of 12.5% has attracted numerous multinational companies, leading to the establishment of their European headquarters or regional offices in Ireland. This has resulted in an increase in foreign direct investment (FDI) and job creation.
Additionally, Ireland boasts a highly educated and productive workforce, which is a valuable asset in the global market. The country’s education system, with its emphasis on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) subjects, has fostered a highly skilled labor force that is in high demand globally. This has further strengthened Ireland’s position as a hub for technology and innovation.
Moreover, Ireland’s membership in the European Union (EU) provides businesses in the country with access to the wider EU market, facilitating trade and investment. This has contributed to Ireland’s status as an attractive location for international companies seeking to expand their operations within the EU.
Furthermore, Ireland’s strategic location, positioned between the United States and Europe, presents opportunities for companies to engage in transatlantic trade. The country’s well-developed infrastructure, including modern transportation and communication networks, facilitates efficient trade and connectivity with global markets.
In conclusion, Ireland’s favorable business environment, low corporate tax rate, skilled workforce, EU membership, and strategic location have positioned the country as an attractive destination for businesses looking to establish or expand their presence in the global market. These factors have contributed to Ireland’s economic growth and competitiveness on the international stage.
The real effective exchange rate (REER) is a measure of the value of a country’s currency relative to a weighted average of other currencies, adjusted for inflation. It is important to study in the context of Ireland because it provides insights into the competitiveness of the Irish economy and the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on trade and the overall economy.
Read Also: Understanding Psychology Trading: Key Concepts and Strategies
The key factors that influence the real effective exchange rate in Ireland include inflation differentials between Ireland and its trading partners, changes in relative productivity, fiscal policy, interest rate differentials, and capital flows. These factors impact the competitiveness of Ireland’s exports and imports, as well as its attractiveness for foreign investors.
The real effective exchange rate affects trade in Ireland by influencing the price competitiveness of Irish goods and services in international markets. If the real effective exchange rate is high, it means that Irish goods become more expensive relative to goods from other countries, which can lead to a decrease in exports and an increase in imports. Conversely, if the real effective exchange rate is low, it makes Irish goods more affordable and competitive, potentially leading to an increase in exports and a decrease in imports.
Fluctuations in the real effective exchange rate can have several implications for the Irish economy. A significant appreciation of the real effective exchange rate can make Irish exports less competitive, leading to a decrease in export revenues and potentially negative effects on employment and economic growth. On the other hand, a significant depreciation of the real effective exchange rate can boost export competitiveness, potentially increasing export revenues and promoting economic growth.
Policymakers in Ireland can manage the real effective exchange rate through various measures. They can use monetary policy tools, such as interest rate adjustments, to influence capital flows and the demand for the currency, which can in turn impact the exchange rate. They can also implement fiscal policies that support productivity and competitiveness, as well as measures to attract foreign investment. Additionally, policymakers can collaborate with other countries to coordinate exchange rate policies and reduce the volatility of the real effective exchange rate.
Understanding Stock Options for Pre-IPO Companies When it comes to working for a pre-IPO company, one of the key benefits that employees often receive …
Read ArticleWhat is JCP full form? Have you ever wondered what the meaning of JCP is? Well, you’re not alone. JCP is an acronym that stands for Java Community …
Read ArticleIs 200 enough for forex? Forex trading has become increasingly popular over the years, as more and more individuals are looking to capitalize on the …
Read ArticleDoes Montreal use euros? Montreal is a vibrant and multicultural city located in the province of Quebec, Canada. As a popular tourist destination, …
Read ArticleIs there MetaTrader for iPhone? If you are a trader or an investor, there is a high chance that you have heard about MetaTrader, one of the most …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Importance of the 34 EMA in Trading Strategies The 34 Exponential Moving Average (EMA) is an important technical indicator used by …
Read Article