What Time Does the USD Forex Market Open? | Forex Trading Hours
USD Forex Market Opening Time The USD Forex market is one of the largest and most active financial markets in the world, with trillions of dollars …
Read Article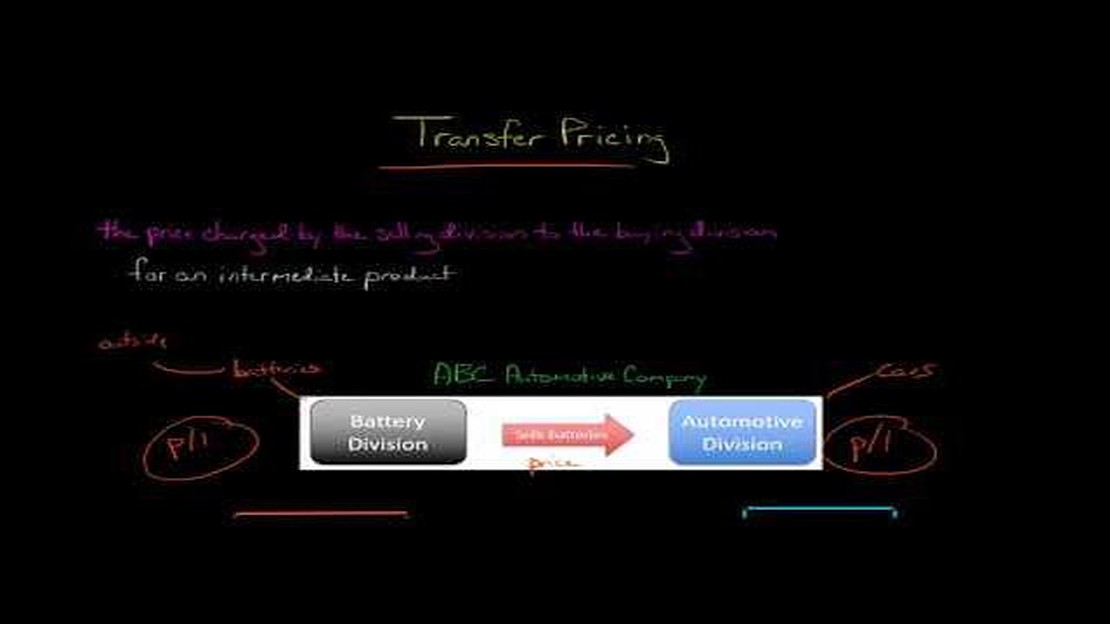
Transfer pricing is a crucial aspect of international business, as it involves the determination of prices for goods and services transferred between entities within the same multinational corporation. This complex process requires companies to carefully consider the most suitable method to determine such prices in order to comply with tax regulations and ensure fair allocation of profits.
There are several methods available for determining transfer prices, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. One commonly used method is the comparable uncontrolled price method, which compares the price of the product or service being transferred between related parties to the price of a similar product or service sold to unrelated parties. This method relies on the availability of reliable and comparable data, but it can be challenging to find suitable comparables in some cases.
Another method is the cost-plus method, which involves adding a predetermined profit margin to the cost of production. This method is more straightforward and can be easily implemented, but it may not accurately reflect market conditions or the value of the product or service. Additionally, this method may not be appropriate for companies operating in industries with rapidly changing costs or market conditions.
One alternative approach is the resale price method, which involves determining the price of the transferred product or service based on the price at which it is resold by the receiving entity to an unrelated party. This method can be useful when there is a reliable market price for the product or service, but it may not be appropriate for companies operating in markets with limited or volatile demand.
Ultimately, the choice of transfer pricing method will depend on the specific circumstances of the company and the nature of the products or services being transferred. It is crucial for businesses to carefully evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of each method and consider factors such as the availability of reliable data, market conditions, and industry-specific considerations in order to determine the best approach for their unique situation.
In the global marketplace, transfer pricing plays a crucial role in determining the allocation of profits and costs among related entities of a multinational corporation. However, there are various methods available for calculating transfer prices, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we will explore and evaluate different methods of transfer pricing to identify the optimal strategy for multinational companies.
The CUP method is widely regarded as the most reliable method for determining transfer prices. It involves comparing the price charged in a controlled transaction with the price charged in an uncontrolled transaction. By using this method, companies can rely on actual market prices to establish transfer prices, thereby minimizing the risk of transfer pricing disputes.
Read Also: Understanding the Power of Leverage: Exploring the Concept of 1:500 Leverage
The cost plus method involves adding a reasonable profit margin to the cost of producing a product or providing a service. This method is commonly used when the controlled transaction involves the provision of tangible goods. It ensures that the selling entity receives an appropriate return on its costs and efforts.
The resale price method focuses on the price at which a product is resold to an independent party. It involves applying an appropriate markup to the purchase price paid by the selling entity to determine the transfer price. This method is commonly used when the selling entity only performs limited functions, such as distribution or marketing.
Read Also: Understanding the Concepts of High of the Day and Low of the Day
By comparing these three methods, multinational companies can identify the most suitable approach for their transfer pricing needs. It is important to consider the nature of the controlled transaction, availability of comparable transactions, and the level of complexity involved. Ultimately, the optimal strategy should provide a fair allocation of profits and costs while minimizing transfer pricing risks.
Transfer pricing refers to the setting of prices for goods, services, or intellectual property that are transferred between related entities within a multinational corporation. The aim is to ensure that the prices are set in a manner that is fair and reflects the market value.
Transfer pricing is important because it can have significant tax implications for multinational corporations. By setting transfer prices at an appropriate level, companies can potentially minimize their overall tax liabilities. Additionally, transfer pricing plays a role in determining the profitability of each entity within a multinational corporation.
There are several methods of transfer pricing commonly used by multinational corporations. These include the comparable uncontrolled price method, the resale price method, the cost plus method, the profit split method, and the transactional net margin method. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages and the choice of method depends on various factors such as the nature of the transactions and the availability of data.
When determining the best approach to transfer pricing, there are several factors to consider. These include the nature of the transactions, the availability and reliability of data, the level of complexity involved, the tax policies and regulations in different jurisdictions, and the potential risks and benefits associated with each method. It is important for companies to carefully evaluate these factors and choose the approach that is most suitable for their specific circumstances.
USD Forex Market Opening Time The USD Forex market is one of the largest and most active financial markets in the world, with trillions of dollars …
Read ArticleAutocovariance function of the MA(1) process The autocorrelation function (ACF) is a powerful tool in time series analysis that allows us to …
Read ArticleIs it possible to exchange money at the airport? When traveling internationally, one of the most common questions that arises is whether or not it is …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Average Convergence Divergence Indicator The Average Convergence Divergence (ACD) indicator is a popular technical analysis tool …
Read ArticleWhen Do Options Automatically Get Exercised? Options trading is a complex financial instrument that allows investors to speculate on the price …
Read ArticleIs FBS available for use in USA? FBS is a popular online trading platform that offers a wide range of financial services to traders worldwide. With …
Read Article