Understanding MACD 5 35 5: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding MACD 5 35 5: A Comprehensive Guide The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is a popular technical indicator used by traders and …
Read Article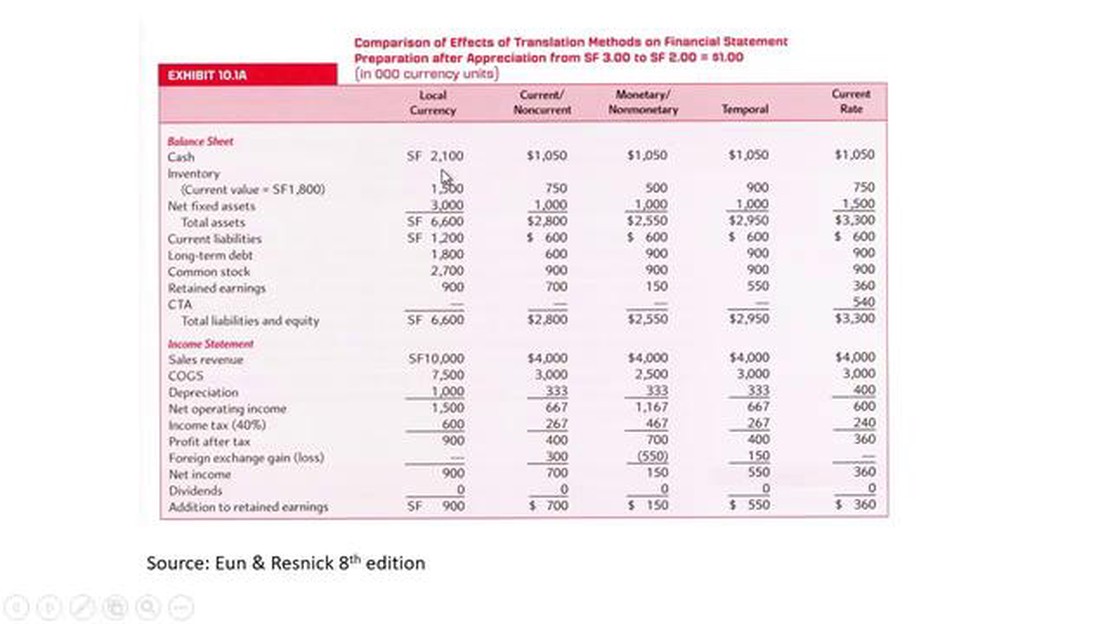
Translation exposure refers to the financial risk that arises from changes in exchange rates affecting the value of a company’s assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies. Understanding and managing translation exposure is crucial for multinational companies operating in a globalized economy.
There are four main methods of measuring and managing translation exposure:
1. Current rate method:
The current rate method is the simplest and most straightforward approach to translation exposure. It involves translating all assets and liabilities at the current exchange rate at the reporting date. This method provides a snapshot view of the company’s financial position.
2. Temporal method:
The temporal method takes into account the specific exchange rates at which assets and liabilities were acquired or incurred. It translates monetary items at the current exchange rate and non-monetary items at historical rates. This method provides more accurate information about the company’s exposure to exchange rate fluctuations.
3. Monetary/non-monetary method:
The monetary/non-monetary method distinguishes between monetary and non-monetary items for translation purposes. Monetary items, such as cash, accounts receivable, and accounts payable, are translated at the current exchange rate. Non-monetary items, such as inventory and fixed assets, are translated at the historical exchange rate. This method helps to isolate the impact of exchange rate changes on the company’s cash flows.
4. Net investment method:
The net investment method focuses on the translation exposure of a company’s foreign subsidiaries. It translates the subsidiary’s net assets at the current exchange rate and recognizes the resulting gain or loss in the consolidated financial statements. This method provides insights into the overall impact of exchange rate fluctuations on the company’s net investment abroad.
Each method has its advantages and limitations, and companies often use a combination of them to manage their translation exposure effectively. By understanding these methods and their implications, companies can make informed decisions to minimize the financial risks associated with exchange rate fluctuations.
Read Also: Is Pocket Option Legal in USA? Everything You Need to Know
Translation exposure refers to the risk businesses face when their financial statements, assets, liabilities, and equity are presented in different currencies. It occurs due to fluctuations in exchange rates, which can significantly impact a company’s financial position and performance.
In international business, companies often deal with multiple currencies, especially if they have subsidiaries or conduct cross-border trade. As exchange rates fluctuate, the value of these currencies changes, affecting the financial statements of the companies involved.
Translation exposure can lead to both gains and losses for businesses. If the functional currency of a subsidiary weakens relative to the reporting currency, the translated financial statements of the subsidiary will show lower values, resulting in foreign exchange losses. Conversely, if the functional currency strengthens, the subsidiary’s financial statements will reflect higher values, leading to foreign exchange gains.
There are four main methods used to manage translation exposure:
Read Also: Advantages of Low Spread in Forex Trading: Explained
Overall, understanding translation exposure is crucial for businesses operating in the global marketplace. By implementing appropriate strategies to manage this risk, companies can navigate the complexities of international business and protect their financial positions.
Translation exposure is an important concept in international finance that refers to the risk that a company faces due to fluctuations in exchange rates. When a company has transactions denominated in foreign currencies, it is exposed to translation exposure. This exposure can have a significant impact on the company’s financial performance.
There are several methods that companies can use to manage translation exposure. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on a variety of factors, including the company’s risk tolerance and the nature of its business. In this article, we will explore four of the most common methods of translation exposure.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Transaction exposure | This method focuses on managing the risk associated with individual transactions. It involves hedging the foreign exchange risk by using derivatives such as forward contracts or options. By entering into these contracts, companies can lock in a specific exchange rate for a future transaction, thereby reducing the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on the transaction’s value. |
| Economic exposure | This method takes a broader view of translation exposure and focuses on the overall impact of exchange rate fluctuations on a company’s cash flows and profitability. It involves analyzing the sensitivity of the company’s cash flows to changes in exchange rates and developing strategies to mitigate the effects of these changes. This can include adjusting pricing strategies, entering into long-term contracts, or diversifying the company’s operations. |
| Translation exposure | This method focuses on managing the risk associated with the translation of financial statements from a foreign currency to the company’s reporting currency. It involves using financial instruments such as forward contracts or currency swaps to hedge the translation risk. Companies can also use accounting techniques such as selecting an appropriate functional currency or using the temporal or current rate method to reduce the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on their financial statements. |
| Netting exposure | This method involves offsetting foreign currency assets and liabilities to reduce the company’s overall exposure to exchange rate fluctuations. By netting off these positions, companies can reduce the impact of exchange rate movements on their financial performance. This method is commonly used by multinational corporations with operations in multiple currencies. |
In conclusion, translation exposure is a significant risk that companies face in international finance. By understanding and utilizing the different methods of managing translation exposure, companies can minimize the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on their financial performance and enhance their risk management strategies.
Translation exposure refers to the risk that a company faces due to the fluctuations in exchange rates when translating its financial statements from one currency to another. It is the potential impact of exchange rate movements on the financial results and positions of a company.
The four methods of translation exposure are the current rate method, the temporal method, the monetary/non-monetary method, and the functional currency method.
The current rate method is a method of translation exposure that uses the current exchange rate to translate all balance sheet and income statement items. Under this method, all assets and liabilities are translated at the current exchange rate, while the income statement items are translated at the average exchange rate for the period.
The temporal method is a method of translation exposure that uses the historical exchange rate to translate monetary assets and liabilities, and the current exchange rate to translate non-monetary assets and liabilities. The income statement items are translated at the average exchange rate for the period.
Understanding MACD 5 35 5: A Comprehensive Guide The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is a popular technical indicator used by traders and …
Read ArticleWhat is the Role of a Forex Trader? Forex trading is a profession that requires a deep understanding of the financial markets and the ability to make …
Read ArticleExamples of Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) An Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) system is a telephony technology that routes incoming calls to the …
Read ArticleCAD to Euro: Will the Currency Exchange Rate Go Up? The Canadian dollar (CAD) to Euro (EUR) exchange rate is a topic of interest for investors and …
Read ArticleInvesting Tips: How to Invest Money Wisely Investing money can seem like a daunting task, especially for beginners who have little to no knowledge …
Read ArticleInforming St George Bank about your overseas travel plans Informing St George about your overseas travel plans is an important step to ensure the …
Read Article