Is Forex a Good Broker? | Expert Analysis and Reviews
Is Forex a Reliable Broker? A Comprehensive Review Choosing the right forex broker is crucial for every trader. With countless options available in …
Read Article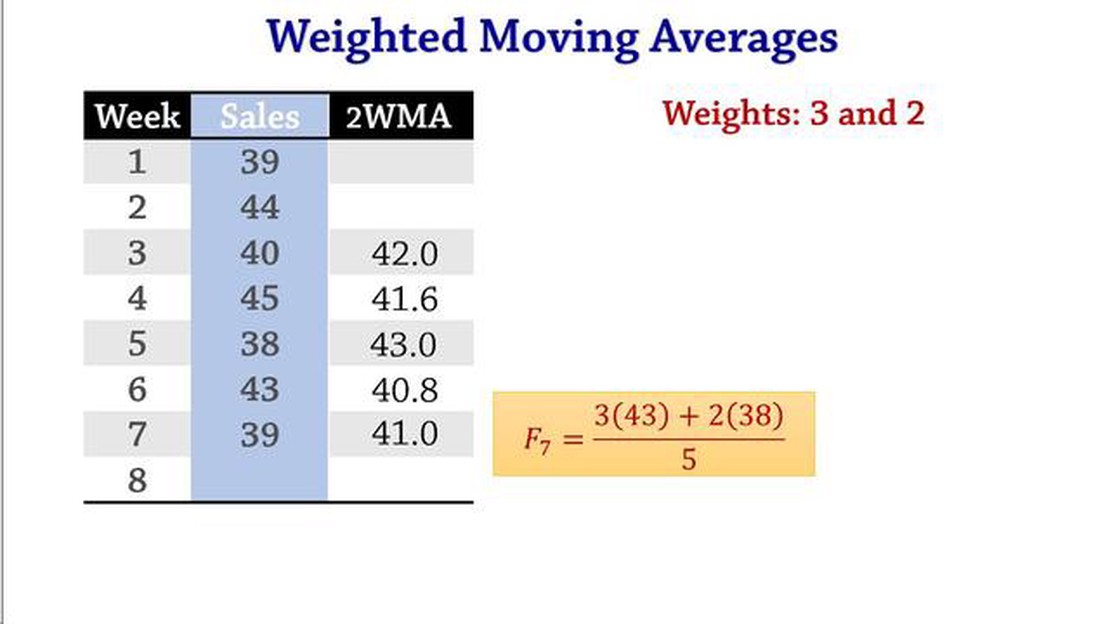
The weighted moving average is a popular method used to analyze time series data and forecast future values. However, like any other statistical technique, it has its limitations and drawbacks. In this article, we will explore the disadvantages of using weighted moving average and what you need to know before incorporating it into your analysis.
One of the main disadvantages of weighted moving average is that it is highly sensitive to extreme values or outliers. Since the weights assigned to each observation are based on their position in the time series, a single extreme value can dramatically impact the forecasted values. This can lead to inaccurate predictions and unreliable results.
Another drawback of weighted moving average is that it requires a predefined set of weights. These weights are usually determined based on expert judgment or historical patterns. However, if the underlying patterns in the data change, the predefined weights may no longer be appropriate, resulting in inaccurate forecasts. Moreover, determining the optimal set of weights can be a subjective and time-consuming process.
Furthermore, the weighted moving average technique assumes that the underlying data follows a linear trend. In reality, many time series data exhibit nonlinear patterns, such as exponential or seasonal trends. When using weighted moving average on such data, the forecasted values may deviate significantly from the actual values, leading to poor performance.
In conclusion, while weighted moving average offers a simple and intuitive way to analyze time series data, it is important to be aware of its limitations and drawbacks. It is advisable to carefully consider the characteristics of your data and explore alternative techniques before incorporating weighted moving average into your analysis.
While weighted moving average can be a useful tool for analyzing data and making forecasts, it does have some limitations that should be considered:
| Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
| Subjectivity | The weights assigned to the data points in a weighted moving average are subjective and can vary depending on the analyst’s judgment. This can result in different outcomes and may make it difficult to compare results across different analysts. |
| Limited historical data | In order to calculate a weighted moving average, you need historical data. If you have limited historical data, the results may not be accurate or reliable. |
| Noisy data | If the data you are analyzing contains a lot of noise or outliers, a weighted moving average may not be the most appropriate method. Since the weights are assigned based on historical data, outliers can have a significant impact on the results. |
| Weight selection | The selection of appropriate weights can be challenging. Different weightings can lead to different results, and it may be difficult to determine which set of weights is most appropriate for a given analysis. |
| Assumption of linearity | Weighted moving average assumes that the relationship between the data points is linear. If there is a non-linear relationship, the results may be skewed or misleading. |
| Lack of adaptability | A weighted moving average does not adapt to changes in the data over time. This can be a limitation if the underlying data has a changing trend or seasonality. |
It is important to be aware of these limitations and consider them when using a weighted moving average for data analysis and forecasting. Alternative methods, such as exponential smoothing or time series analysis, may be more appropriate in certain situations.
One of the major disadvantages of using a weighted moving average is that it may not provide an accurate representation of recent data. This is because the weightings assigned to older data points can overshadow the impact of more recent data points.
When calculating a weighted moving average, each data point is assigned a weight based on its position in the time series. Older data points are typically assigned lower weights, while more recent data points are assigned higher weights. The idea behind this is to give more importance to recent data, as it is assumed to be more relevant and reflective of current trends.
Read Also: Is Fixed Time Trading Halal or Haram? Explained.
However, the problem with this approach is that it assumes that older data points are less relevant, which may not always be the case. In certain situations, older data points can still have a significant impact on the overall trend or pattern being analyzed. By assigning them lower weights, the weighted moving average may not accurately capture these important trends or patterns.
Furthermore, if there are sudden or drastic changes in the data, the weighted moving average may take some time to adjust and reflect these changes. This can lead to delays in identifying and responding to emerging trends or shifts in the data.
Overall, while a weighted moving average can be an effective tool for analyzing time series data, it is important to recognize its limitations, particularly in terms of representing recent data accurately. It is always advisable to consider other forecasting methods and techniques that may provide a more well-rounded view of the data, especially when dealing with rapidly changing or volatile data.
One of the main disadvantages of using a weighted moving average is that it tends to overemphasize older data points. This is because the weights assigned to each data point in the calculation decrease as the data gets older.
While this can be beneficial in some cases, as it allows for slower changes in the average and can smooth out short-term fluctuations, it can also be a disadvantage. Overemphasis on older data can cause the weighted moving average to be slow to respond to recent trends or changes in the data.
This can be particularly problematic in situations where there are sudden shifts or outliers in the data. For example, if there is a sudden increase or decrease in sales, the weighted moving average may not reflect this change for several periods, leading to inaccurate forecasts or predictions.
Read Also: Reasons for hedging to be illegal in the US: Understanding the regulations and implications
To address this issue, it may be necessary to use a different type of moving average, such as an exponential moving average, which places more emphasis on recent data points. By giving more weight to recent data, an exponential moving average can provide a more accurate reflection of current trends and changes.
Overall, while the weighted moving average can be a useful tool in analyzing data trends, it is important to be aware of its limitations, including the overemphasis on older data. By understanding the drawbacks of this method, analysts can make more informed decisions and choose the appropriate moving average technique for their specific needs.
Weighted moving average is a financial indicator used to analyze trends in data over a specific period of time. It is calculated by multiplying each data point by a predetermined weight, summing the results, and then dividing by the sum of the weights.
Using a weighted moving average can provide a more accurate representation of the underlying trends in the data. It gives more weight to recent data points, allowing for better analysis of current market conditions. Additionally, it can help to smooth out fluctuations in the data, making it easier to identify long-term trends.
Yes, there are some disadvantages to using a weighted moving average. One drawback is that it can be more complicated to calculate compared to other moving average methods. Additionally, the choice of weights can have a significant impact on the results, and there is no one-size-fits-all approach to determining the optimal weights. It is also worth noting that weighted moving averages may be more sensitive to outliers or extreme values in the data.
The choice of weights in a weighted moving average can have a significant impact on the results. The weights determine the relative importance of each data point in the calculation of the average. Different weightings can emphasize different aspects of the data, such as giving more weight to recent data or placing more importance on certain time periods. It is important to choose weights that best reflect the desired analysis and align with the characteristics of the data being studied.
A weighted moving average may not be suitable for all types of data. It is generally more appropriate for data sets that exhibit a certain pattern or trend over time. If the data is highly volatile or erratic, a weighted moving average may not provide meaningful insight. It is important to consider the characteristics of the data and the specific analysis goals when determining whether a weighted moving average is appropriate.
Weighted moving average is a statistical method used to calculate a forecast by assigning different weights to different time periods. This means that recent data points are given more importance than older data points in determining the forecast.
Weighted moving average is used because it allows for more accurate predictions by giving more weight to recent data, which is generally more reflective of current market conditions. This helps businesses make informed decisions and anticipate trends.
Is Forex a Reliable Broker? A Comprehensive Review Choosing the right forex broker is crucial for every trader. With countless options available in …
Read ArticleThe Psychology of Trading Options: Understanding Your Mindset for Success Trading options can be a highly lucrative endeavor, but it also comes with …
Read ArticleWho acquired Optionetics? Optionetics, a prominent financial education company specializing in options trading, recently announced that it has been …
Read ArticleUnderstanding Weighted Moving Average: A Beginner’s Guide The weighted moving average is a commonly used tool in technical analysis that helps traders …
Read ArticleIs the trading floor worth it? Trading on a physical exchange, also known as a trading floor, has been a staple of the financial industry for decades. …
Read ArticleWhere to Get Level 2 Market Data Forex Forex trading is a highly competitive market that requires access to accurate and timely data. Level 2 market …
Read Article