Is Forex Trading Legal in Nepal? Find Out Here
Understanding the Legality of Forex Trading in Nepal Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, has gained popularity worldwide as traders …
Read Article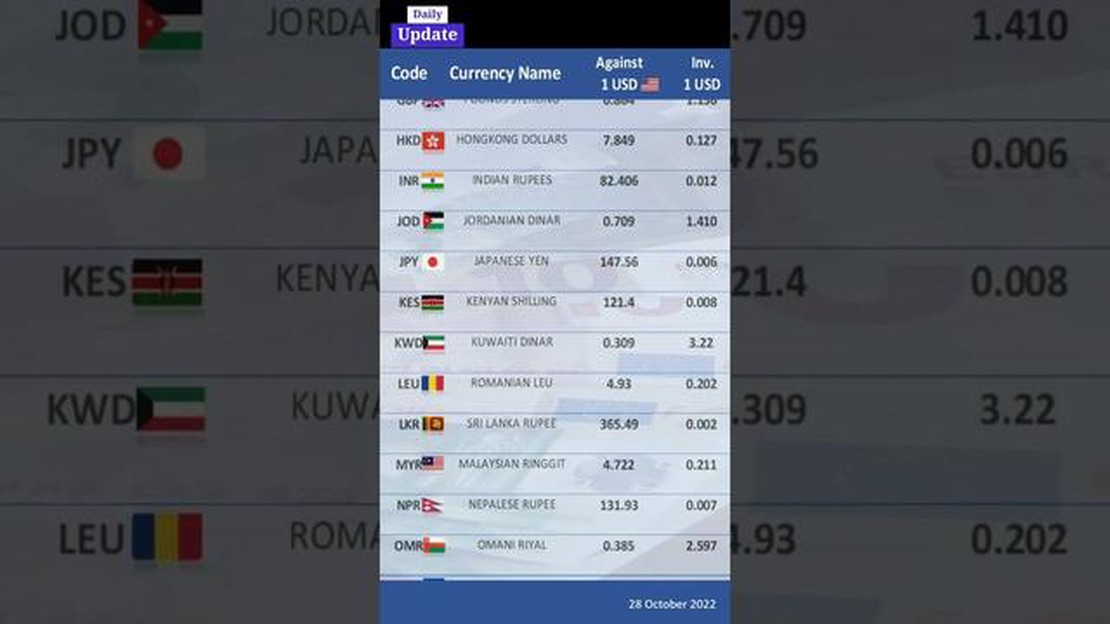
The USD INR exchange rate is the rate at which the United States Dollar (USD) can be converted into Indian Rupees (INR). It is an important indicator of the economic relationship between the two countries and is closely watched by investors, traders, and policymakers.
The exchange rate is influenced by a variety of factors, including interest rates, inflation, political stability, and market sentiment. Changes in these factors can lead to fluctuations in the exchange rate, which can have significant effects on trade and investment between the United States and India.
Currently, the USD INR exchange rate is at a level that is favorable for USD holders. This means that if you have USD, you can get more INR when you exchange it. However, if you have INR and you want to exchange it for USD, you will get fewer USD in return.
It is important to note that exchange rates are volatile and can change rapidly. Therefore, it is recommended to stay updated with the latest exchange rates and consult with a financial advisor or a currency exchange specialist before making any transactions.
Investing in foreign currencies carries a high level of risk and may not be suitable for all investors. It is important to carefully consider your investment objectives and consult with a financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
The current exchange rate between the United States dollar (USD) and the Indian rupee (INR) is an important factor for businesses and individuals who have transactions between the two countries. The exchange rate determines how much one currency is worth in terms of the other, and it can have a significant impact on the cost of imports, exports, and travel expenses.
As of the latest data available, 1 USD is equivalent to approximately X INR. This rate is constantly changing as the foreign exchange market is influenced by various economic factors, such as inflation, interest rates, and political stability. Therefore, it is important to check the current exchange rate before making any international transactions involving USD and INR.
The exchange rate can be found in financial newspapers, on financial websites, or through currency exchange rate apps. It is usually quoted with USD as the base currency and INR as the quote currency, indicating how much INR is needed to purchase 1 USD. For example, if the exchange rate is 70 INR/USD, it means that 70 Indian rupees are required to buy 1 US dollar.
It is important to note that exchange rates may vary slightly depending on the source and method of exchange. Banks and currency exchange services may add a small fee or commission, which can affect the overall exchange rate. Therefore, it is advisable to compare rates from different sources and choose the most favorable one for your specific needs.
Movements in the USD to INR exchange rate can also be influenced by global events and news, such as changes in government policies, economic indicators, and geopolitical tensions. Traders and investors closely monitor these factors to anticipate and react to fluctuations in currency values.
Read Also: Understanding ATR in Forex Trading: Definition, Calculation, and Application
In conclusion, the current exchange rate of USD to INR is an important factor for individuals and businesses engaged in transactions between the United States and India. It is a dynamic value that can fluctuate based on various economic and geopolitical factors. Keeping track of the exchange rate and understanding its implications can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions regarding international transactions.
Several factors play a significant role in influencing the exchange rate between the USD and INR. Understanding these factors can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions when dealing with currency exchange. Here are some key factors that influence the USD to INR exchange rate:
Economic factors: The economic conditions and performance of both the United States and India have a direct impact on the exchange rate between the USD and INR. Factors such as GDP growth rate, inflation, interest rates, employment levels, and trade balance can affect the demand and supply of currency, thus influencing its value.
Political factors: Political stability or instability in either country can affect the exchange rate. Governments’ policies, political events, and geopolitical tensions can create uncertainty in the markets, leading to fluctuations in the USD to INR exchange rate.
Monetary policies: Decisions made by the central banks of both countries regarding interest rates, money supply, and quantitative easing can impact the exchange rate. Higher interest rates can attract foreign investors, increasing the demand for the currency and strengthening its value, while lower interest rates can have the opposite effect.
International trade: The trade relationship between the United States and India can influence their respective currencies. Factors such as export and import volumes, tariffs, and trade agreements can affect the demand for USD or INR, thereby affecting the exchange rate.
Investor sentiment: Investor sentiment and market expectations can greatly influence the exchange rate. Positive economic news, strong corporate earnings, or political stability can increase investor confidence and attract foreign investments, strengthening the currency.
Speculation and market forces: Currency markets are often driven by speculative trading and market forces. Factors such as supply and demand dynamics, market speculation, and currency market interventions by central banks can create volatility in the USD to INR exchange rate.
Read Also: Understanding the 1% Rule in Options Trading for Beginner Investors
Global economic conditions: The performance of the global economy and financial markets can impact the USD to INR exchange rate. Factors such as global economic growth, commodity prices, and market sentiment towards emerging markets can influence the value of the currencies.
Government interventions: Central banks or governments may intervene in the currency market to stabilize or manipulate the exchange rate. These interventions, such as buying or selling currencies, can temporarily influence the USD to INR exchange rate.
It’s important to note that exchange rates are highly volatile and subject to change due to these and various other factors. Monitoring these factors and staying informed about the latest market developments can help individuals and businesses make more accurate predictions and decisions regarding currency exchange.
The current USD INR exchange rate is 75.73.
The USD INR exchange rate is important because it affects the cost of imports and exports between the United States and India. It also has an impact on the value of investments and can affect the purchasing power of individuals and businesses.
There are several factors that can affect the USD INR exchange rate. These include interest rates, inflation, economic growth, political stability, and market speculation. Changes in these factors can cause the exchange rate to fluctuate.
The USD INR exchange rate is currently higher than historical levels. In the past year, the exchange rate has been in the range of 70 to 76. This indicates that the Indian rupee has weakened against the US dollar.
A strengthening USD INR exchange rate means that the Indian rupee is getting stronger against the US dollar. This can have positive implications for Indian businesses and individuals who import goods or travel to the United States. However, it can also make Indian exports more expensive and reduce the purchasing power of Indian consumers.
Understanding the Legality of Forex Trading in Nepal Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, has gained popularity worldwide as traders …
Read ArticleUnderstanding Forex Trading: What You Need to Know Welcome to the world of forex trading! Whether you’re a seasoned investor or a beginner looking to …
Read ArticleBest Online Trading Sites: A Comprehensive Guide to Find the Perfect Platform Online trading has become increasingly popular in recent years, with …
Read ArticleWhat is the average GBP to euro exchange rate in 2023? As we enter a new year, it’s natural to wonder what the future holds for the GBP to Euro …
Read ArticleWhich forex indicator is the most accurate? When it comes to forex trading, having access to accurate information and reliable indicators can make all …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Moving Average in Management In the fast-paced world of business and management, companies are constantly seeking ways to stay ahead …
Read Article