Understanding Basket Trading in Zerodha: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Basket Trading in Zerodha Are you interested in exploring advanced trading strategies? Look no further! This comprehensive guide will …
Read Article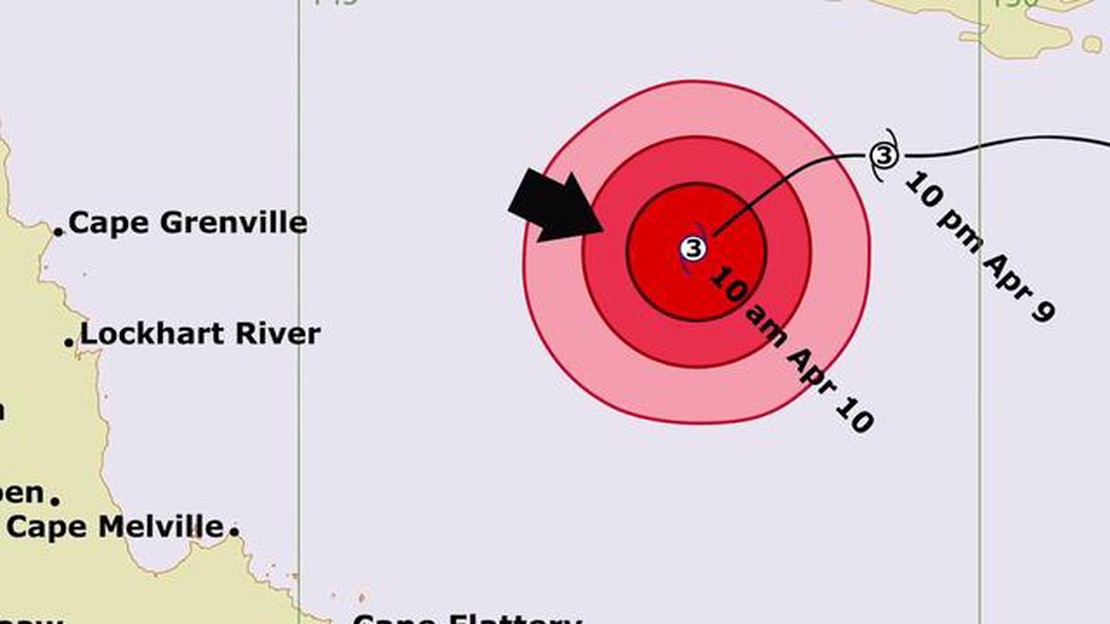
Cyclones are one of the most powerful and destructive natural disasters on our planet. These violent storms, also known as hurricanes or typhoons, can cause widespread devastation and loss of life. As such, accurately predicting cyclones is of paramount importance in order to minimize their impact and protect vulnerable communities.
Over the years, scientists and meteorologists have made significant advancements in cyclone prediction. Through the use of advanced technology, such as weather satellites and computer models, forecasters can track the formation and movement of cyclones with increasing accuracy.
However, predicting cyclones remains a complex and challenging task. Cyclone formation and behavior are influenced by a multitude of factors, including sea surface temperatures, atmospheric conditions, and geographic features. These variables interact in intricate ways, making it difficult to make precise predictions.
Despite these challenges, the accuracy of cyclone prediction has greatly improved in recent years. Forecasters can now provide accurate forecasts of a cyclone’s path and intensity several days in advance, giving communities valuable time to prepare and evacuate if necessary.
It is important to note that while accurate cyclone prediction is possible, there are still limitations to our understanding of these storms. Forecasting the exact track and intensity of a cyclone can be challenging, especially when it comes to rapid intensification or sudden changes in direction. As our knowledge and technology continue to advance, however, we can expect further improvements in cyclone prediction, ultimately helping us better protect those in harm’s way.
Cyclones are complex weather phenomena that can cause vast destruction and loss of life. Predicting their path, intensity, and timing has always been a challenge for meteorologists. However, with advancements in technology and the availability of vast amounts of data, the accuracy of cyclone predictions has significantly improved over the years.
One of the key factors in accurately predicting cyclones is the collection of reliable and timely data. Satellites equipped with advanced sensors provide continuous monitoring of weather patterns, allowing meteorologists to detect the early signs of cyclone formation. This data is then combined with information from buoys, weather stations, and aircraft to create a comprehensive picture of the cyclone’s development.
In recent years, computer models have played a crucial role in cyclone prediction. These models use complex algorithms to simulate the behavior of the atmosphere and oceans, taking into account various factors such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and pressure. By running multiple simulations with different initial conditions, meteorologists can assess the most likely path and intensity of a cyclone.
While cyclone prediction has become more accurate, it’s important to note that there are still limitations. The interaction between multiple atmospheric factors makes cyclones inherently unpredictable. Small changes in initial conditions or errors in data collection can lead to significant deviations in predicted paths. Additionally, factors such as rapid intensification or weakening of a cyclone pose additional challenges for accurate prediction.
Despite these limitations, the accuracy of cyclone prediction continues to improve. Forecasters can now provide timely warnings to populations at risk, allowing them to take necessary precautions and evacuate if required. Continuous research and technological advancements are further enhancing our understanding of cyclone formation and behavior, helping to refine prediction models and reduce uncertainties.
In conclusion, while predicting cyclones with absolute accuracy remains a challenge, significant progress has been made in recent years. With the combination of advanced data collection, sophisticated computer models, and ongoing research, meteorologists are better equipped than ever to predict the path and intensity of cyclones. This improved accuracy has undoubtedly saved countless lives and mitigated the impact of cyclones on affected regions.
Predicting cyclones accurately is a challenging task due to their inherent complexity. Cyclones are large-scale weather systems characterized by low atmospheric pressure and strong winds that rotate around a central core. These powerful storms can cause severe damage to both land and sea, making reliable forecasting crucial for the safety and preparedness of affected areas.
The complexity of cyclone forecasting is rooted in the intricate interactions between various atmospheric and oceanic factors. These include sea surface temperatures, wind patterns, atmospheric instability, and the overall atmospheric circulation. Additionally, factors such as topography, geographical location, and climate patterns can further complicate the forecasting process.
Forecasting cyclones relies on computer models that simulate the behavior of the atmosphere and oceans. These models incorporate vast amounts of data and employ complex equations to predict the future track, intensity, and impact of a cyclone. However, due to the numerous interacting factors involved, uncertainties always exist, and accuracy levels can vary.
Read Also: How to Use Option Chain to Predict Market Trends
Advancements in technology and the availability of satellite data have improved cyclone forecasting over the years. Satellite imagery provides valuable information on cyclone formation, movement, and structure, enhancing the accuracy of predictions. Additionally, specialized instruments, such as weather buoys and aircraft, collect vital data to improve forecasting models and understanding.
Despite these advancements, accurately predicting the behavior of cyclones remains a formidable challenge. Their complex nature makes it difficult to forecast their exact path, intensity, and associated hazards. However, ongoing research and improvements in modeling techniques continue to enhance our understanding of cyclones and their forecasting, thereby improving the accuracy of predictions and better informing emergency response efforts.
Read Also: Is there a foolproof strategy for winning 100% of the time in forex trading?
Cyclones are highly unpredictable weather events that can cause significant damage and loss of life. However, with advancements in technology, scientists and meteorologists are now able to more accurately predict and track cyclones, giving people in their path valuable time to prepare and evacuate if necessary.
One of the key tools used in cyclone prediction is satellite imagery. Satellites provide real-time data on the formation and movement of cyclones, allowing scientists to observe their development and track their path. This information is crucial in determining when and where a cyclone is likely to make landfall, enabling authorities to issue timely warnings to at-risk communities.
In addition to satellites, weather radars play a vital role in cyclone prediction. Radars provide detailed information on the intensity and structure of cyclones, helping scientists understand their behavior and make more accurate forecasts. By analyzing radar data, meteorologists can identify key indicators of cyclone strength, such as wind speed and rainfall intensity, and make predictions about potential impacts on coastal areas.
Advanced computer models and simulations also contribute to cyclone prediction. These models use complex algorithms to process vast amounts of data and generate forecasts of cyclone paths and intensities. By inputting current weather conditions and historical data, these models can simulate the behavior of cyclones and provide valuable insights into their future trajectory.
Furthermore, drones have emerged as a valuable tool in cyclone prediction. Drones equipped with advanced sensors and cameras can gather data from within a cyclone, providing scientists with a detailed understanding of its internal structure and dynamics. This information allows for more accurate predictions of cyclone intensities and potential impacts, further enhancing the ability to forecast and prepare for these devastating storms.
In conclusion, advanced technology plays a crucial role in cyclone prediction, enabling scientists and meteorologists to better understand the behavior of these powerful storms and make more accurate forecasts. Satellites, weather radars, computer models, and drones all contribute to our ability to predict cyclones and mitigate their potential impacts, ultimately saving lives and reducing the damage caused by these natural disasters.
Cyclones can be predicted to some extent, but their accuracy can vary depending on various factors.
The accuracy of cyclone prediction can be affected by factors such as the strength and size of the cyclone, the availability of data, and the forecasting models used.
Cyclones can usually be predicted a few days in advance, but the accuracy of the prediction decreases as the forecast timeframe increases.
It is difficult to accurately predict cyclones because they are complex weather systems influenced by a variety of factors, including atmospheric conditions and ocean temperatures, which can change rapidly.
Advancements in technology and meteorological understanding have improved cyclone prediction models, allowing for more accurate forecasts and earlier warnings.
Cyclone predictions have become more accurate over the years, thanks to advancements in technology and improved forecasting models. However, there are still uncertainties associated with predicting the exact path and intensity of a cyclone.
Understanding Basket Trading in Zerodha Are you interested in exploring advanced trading strategies? Look no further! This comprehensive guide will …
Read ArticleHow are publicly traded common stocks valued in a decedent’s gross estate and how are they valued if the decedent dies over the weekend? When a person …
Read ArticleWhat Does TFG Stand for? Have you ever come across the acronym TFG and wondered what it stands for? TFG is a widely used abbreviation that can have …
Read ArticleBest Broker for Scalping Options Scalping options is a popular trading strategy that involves making quick trades to take advantage of small price …
Read ArticleAverage Cost and GAAP: Exploring Acceptance and Application Accounting is a field that follows a set of rules and standards to ensure clarity and …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Dynamics of the Bid-Ask Spread When it comes to financial markets, one important concept that traders need to understand is the …
Read Article