Best ESPP Strategy: Maximizing Your Employee Stock Purchase Plan
Best Strategy for ESPP: Maximizing Your Employee Stock Purchase Plan Employee Stock Purchase Plans (ESPPs) are a popular way for employees to invest …
Read Article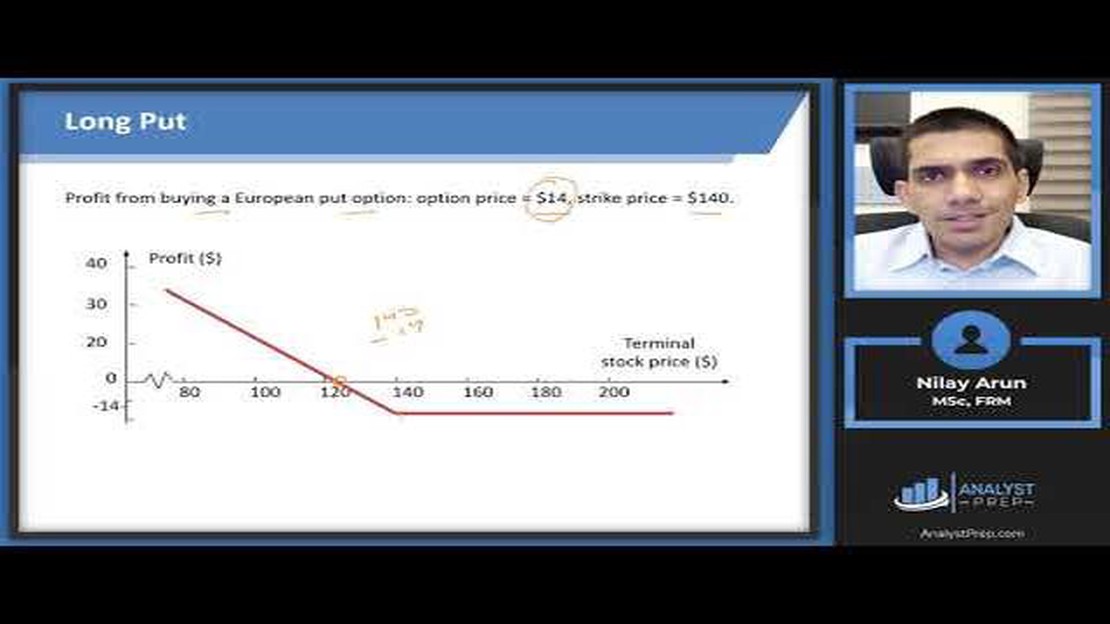
Options are financial instruments that allow traders to profit from price movements of underlying assets without actually owning those assets. However, understanding how options work and calculating their potential payoff can be quite complex. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the process of calculating the payoff of options, empowering you with the knowledge to make informed investment decisions.
Firstly, we will explore the basic components of options, namely the strike price, expiration date, and option type (call or put). These factors greatly influence the potential payoff of an option. By understanding how they interact, you will be able to accurately assess the profitability of different options strategies.
Secondly, we will delve into the mathematics behind option pricing models such as the Black-Scholes model and the Binomial model. These mathematical frameworks take into account various factors, including market volatility and interest rates, to estimate the fair value of an option. By understanding these models, you will be able to calculate the potential payoff of an option with greater accuracy.
Moreover, we will discuss the concept of option strategies and how they can affect the potential payoff. Whether you’re interested in covered calls, spreads, or straddles, understanding how these strategies can alter the payoff profile is crucial in maximizing your investment returns.
In conclusion, calculating the payoff of options requires a deep understanding of various factors such as strike price, expiration date, option type, market volatility, and option pricing models. By mastering these concepts, you will be able to assess the potential profitability of different options strategies and make informed investment decisions. Whether you’re a novice trader or an experienced investor, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to navigate the complex world of options trading.
Options are financial instruments that give traders the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price, known as the strike price, within a specific time period. The payoff of an option refers to the profit or loss that a trader will realize from exercising the option at expiration.
To understand the basics of options payoff, it’s essential to know the two types of options: call options and put options.
A call option gives the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price before the expiration date. If the market price of the asset is above the strike price at expiration, the call option is in the money and will have a positive payoff. On the other hand, if the market price is below the strike price, the call option is out of the money and will have a negative payoff.
A put option gives the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price before the expiration date. If the market price of the asset is below the strike price at expiration, the put option is in the money and will have a positive payoff. Conversely, if the market price is above the strike price, the put option is out of the money and will have a negative payoff.
The payoff of an option can be calculated using the formula:
Read Also: Is Forex Ban in India? Exploring the Current Regulations and Their Impact
Payoff = Market Price - Strike Price
However, it’s important to note that the payoff only represents the profit or loss at expiration. Throughout the life of the option, the payoff will change as the market price of the underlying asset fluctuates.
Understanding the basics of options payoff is crucial for traders to make informed decisions when trading options. By analyzing the potential payoffs, traders can evaluate the risk and reward of different option strategies and implement appropriate strategies to hedge or speculate in the market.
There are several factors that can affect the payoff of options, including:
1. Underlying Asset Price: The price of the underlying asset is a key determinant of options payoff. For call options, the payoff increases as the price of the underlying asset rises above the strike price. Conversely, for put options, the payoff increases as the price of the underlying asset falls below the strike price.
2. Time to Expiration: The time remaining until the options contract expires also affects the payoff. As the expiration date approaches, the options may lose value, especially if the underlying asset price is not favorable to the option holder.
3. Volatility: Options payoff is also influenced by the volatility of the underlying asset. Higher volatility can increase the likelihood of significant price movements, which can be favorable for options holders, particularly for those with call options.
4. Interest Rates: Changes in interest rates can affect the cost of carrying the underlying asset and the options contract. Higher interest rates can increase the cost of holding options, thereby reducing their potential payoff.
Read Also: Understanding the Role and Function of Exchange Bureaus: Your Ultimate Guide
5. Dividends: If the underlying asset pays dividends, it can affect the options payoff. The announcement or payment of dividends can impact the price of the underlying asset, which subsequently affects the options contract.
6. Market Conditions: General market conditions, such as economic indicators, geopolitical events, and investor sentiment, can also influence options payoff. These factors may impact the underlying asset’s price and volatility.
7. Option Pricing Model: The specific option pricing model used can affect the calculated payoff. Popular models include the Black-Scholes model and the binomial options pricing model.
It is important for options traders and investors to consider these factors when evaluating potential payoffs and making informed decisions about options trading strategies.
Options payoff refers to the amount of profit or loss that is generated from trading options. It is calculated by taking into consideration the difference between the strike price and the market price of the underlying asset at the expiry of the option.
The payoff of an option can be calculated by subtracting the strike price from the market price of the underlying asset at the expiration date. If the result is positive, it indicates a profit, while a negative result indicates a loss.
Sure! Let’s say you purchase a call option with a strike price of $50 and the market price of the underlying asset at the expiration date is $60. In this case, the payoff of the option would be $60 - $50 = $10. So, you would make a profit of $10.
When calculating the payoff of an option, you should consider the strike price, the market price of the underlying asset at the expiration date, the premium paid for the option, and any transaction costs. These factors can all impact the overall payoff of the option.
Best Strategy for ESPP: Maximizing Your Employee Stock Purchase Plan Employee Stock Purchase Plans (ESPPs) are a popular way for employees to invest …
Read ArticleUnderstanding MCX Analysis Software: Features and Benefits If you’re a trader looking to take your skills to the next level, you need to check out MCX …
Read ArticleUnderstanding Non-Standard Calls: An In-Depth Guide Communication has come a long way since the invention of the telephone. Along with the …
Read ArticleUnderstanding Stock Options in the US: A Comprehensive Guide Stock options are a popular investment instrument in the United States. They give …
Read ArticleIs Merrill Lynch a broker-dealer? Merrill Lynch is a well-known name in the financial industry, but many people may not be aware of its specific role …
Read ArticleIs there a fee for currency conversion at Citibank? When it comes to banking and international transactions, one of the questions that often arises is …
Read Article